Recombinant Mouse Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 (Map2k1)
-
货号:CSB-YP013409MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP013409MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP013409MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP013409MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP013409MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Map2k1; Mek1; Prkmk1; Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1; MAP kinase kinase 1; MAPKK 1; EC 2.7.12.2; ERK activator kinase 1; MAPK/ERK kinase 1; MEK 1
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length of Mature Protein
-
表达区域:2-393
-
氨基酸序列PKKKPTPIQ LNPAPDGSAV NGTSSAETNL EALQKKLEEL ELDEQQRKRL EAFLTQKQKV GELKDDDFEK ISELGAGNGG VVFKVSHKPS GLVMARKLIH LEIKPAIRNQ IIRELQVLHE CNSPYIVGFY GAFYSDGEIS ICMEHMDGGS LDQVLKKAGR IPEQILGKVS IAVIKGLTYL REKHKIMHRD VKPSNILVNS RGEIKLCDFG VSGQLIDSMA NSFVGTRSYM SPERLQGTHY SVQSDIWSMG LSLVEMAVGR YPIPPPDAKE LELLFGCHVE GDAAETPPRP RTPGRPLSSY GMDSRPPMAI FELLDYIVNE PPPKLPSGVF SLEFQDFVNK CLIKNPAERA DLKQLMVHAF IKRSDAEEVD FAGWLCSTIG LNQPSTPTHA ASI
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Dual specificity protein kinase which acts as an essential component of the MAP kinase signal transduction pathway. Binding of extracellular ligands such as growth factors, cytokines and hormones to their cell-surface receptors activates RAS and this initiates RAF1 activation. RAF1 then further activates the dual-specificity protein kinases MAP2K1/MEK1 and MAP2K2/MEK2. Both MAP2K1/MEK1 and MAP2K2/MEK2 function specifically in the MAPK/ERK cascade, and catalyze the concomitant phosphorylation of a threonine and a tyrosine residue in a Thr-Glu-Tyr sequence located in the extracellular signal-regulated kinases MAPK3/ERK1 and MAPK1/ERK2, leading to their activation and further transduction of the signal within the MAPK/ERK cascade. Activates BRAF in a KSR1 or KSR2-dependent manner; by binding to KSR1 or KSR2 releases the inhibitory intramolecular interaction between KSR1 or KSR2 protein kinase and N-terminal domains which promotes KSR1 or KSR2-BRAF dimerization and BRAF activation. Depending on the cellular context, this pathway mediates diverse biological functions such as cell growth, adhesion, survival and differentiation, predominantly through the regulation of transcription, metabolism and cytoskeletal rearrangements. One target of the MAPK/ERK cascade is peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARG), a nuclear receptor that promotes differentiation and apoptosis. MAP2K1/MEK1 has been shown to export PPARG from the nucleus. The MAPK/ERK cascade is also involved in the regulation of endosomal dynamics, including lysosome processing and endosome cycling through the perinuclear recycling compartment (PNRC), as well as in the fragmentation of the Golgi apparatus during mitosis.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- he Mek1(Y130C) mutation recapitulates major aspects of cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome. PMID: 29590634
- MEK1 does not act as a general tumor suppressor in leukemogenesis. Rather, its effects strongly depend on the genetic context (RAS versus MYC-driven leukemia) and on the cell type involved. PMID: 27741509
- data suggest that, although short-term suppression of Mek1/2 in ES cells helps to maintain an inner cell mass-like epigenetic state, prolonged suppression results in irreversible changes that compromise their developmental potential PMID: 28746311
- Cdk5 may play an important role in endoplasmic reticulum stress induced podocyte apoptosis through MEKK1/JNK pathway in diabetic nephropathy. PMID: 28024901
- High MEK1 expression is associated with Melanoma Metastasis. PMID: 28652244
- cartilage-specific inactivation of miR322 in mice linked the loss of miR-322 to decreased MEK1 levels and to increased RAF/MEK/ERK pathway activation. PMID: 28851708
- Lgr4 is a critical positive factor for skin tumorigenesis by mediating the activation of MEK1/ERK1/2 and Wnt/beta-catenin pathways. PMID: 27693558
- FGF2 is an extracellular inducer of COUP-TFII expression and may suppress the osteogenic potential of mesenchymal cells by inducing COUP-TFII expression prior to the onset of osteogenic differentiation PMID: 27404388
- REDD1 is required for normal insulin-stimulated signaling, and a subtle balance exists between MEK1/2, REDD1, and mTOR PMID: 27913296
- blood glucose levels are reduced by suppression of MEK1 expression in the liver of db/db mice PMID: 26839898
- MEK1 and MEK2 can substitute for each other but a minimum amount of MEK is critical for placenta development and embryo survival PMID: 26814233
- Aberrant phosphorylation of AKT and MEK signalling pathways was identified in cells carrying mutant huntingtin. PMID: 26660732
- An essential function for MEK1 in macrophages in regulating the ERK1/2 and STAT4 pathways in response to TLR4 activation. PMID: 26208884
- Nuclear enrichment of MEK1 physically sequesters peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma), inhibiting adipogenesis and disrupting ERK signaling. PMID: 24959884
- MEK1 is inhibited by phosphorylation at Thr-292/286 by Cdk5, ERK, and Cdk1. PMID: 25971971
- The effect of Akt1 and Mek1 on extracellular matrix synthesis was reconciled through the activation of p70 S6-kinase. PMID: 25843685
- Homologous recombination efficiency enhanced by inhibition of MEK and GSK3beta. PMID: 25196127
- Data show that Treg cell-specific expression of activated MAP Kinase Kinase 1 (MEK1) led to dysregulation of Treg function. PMID: 25361764
- Both ACE inhibition and MEK1/2 inhibition have beneficial effects on left ventricular function in Lmna(H222P/H222P) mice and both drugs together have a synergistic benefit when initiated after the onset of left ventricular dysfunction. PMID: 25218145
- both MEK1 and MEK2 have crucial roles in the integration of mesenchymal and epithelial signals essential for the development of the entire respiratory tract PMID: 25100655
- rapamycin treatment led to an increased MKP1 expression in BMDM from WT but failed to do so in BMDMs lacking the AKT1 isoform or MEK1 and MEK2. PMID: 24126911
- Identify MEK1 as an essential regulator of lipid/protein phosphatase PTEN, through which it controls phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate accumulation and AKT signaling. PMID: 23453810
- Up-regulation of MEK1 inhibits chronic post-myocardial infarction remodeling in mice. PMID: 22821618
- Inhibition of the MEK1/ERK pathway mediates the hypertrophy suppression and cardiac dysfunction caused by GSK-3alpha overexpression in cardiac myocytes. PMID: 22904158
- activation of the MEK1-ERK1/2 pathway leads to specific inhibition of PPARalpha transcriptional activity. PMID: 22723831
- review focuses on the role of the MEK1 and MEK2 kinases in the development of extraembryonic tissues and in the formation of the placenta PMID: 22561024
- AT(2)R-mediated eNOS NO production and vasorelaxation through a MEK pathway are enhanced in aortas from db/db mice. PMID: 22465219
- the proto-oncogenic property of the MEK/ERK pathway in hematopoietic cells can manifest in MDS/MPN development PMID: 22164275
- Crucial role of the ERK/MAPK cascade in the formation of extraembryonic structures. PMID: 22549869
- Mouse germline stem (GS) cell transfected with an activated form of Map2k1 have upregulated Etv5 and Bcl6b gene expression. PMID: 22491947
- Dox-induced up-regulation of IL-6 and GM-CSF was largely abolished after pretreatment of MTEC1 with MEK1/2 inhibitor U0126. PMID: 21439396
- MEK1 AND MEK2 are critical for maintaining a functional population of adult Leydig cells and for fertility PMID: 21527500
- MEK1 activated in differentiating myoblasts stimulates muscle differentiation by phosphorylating MyoD-Y156, which results in MyoD stabilization. PMID: 21454680
- KSR1 is a functional protein kinase, MEK1 is an in vitro substrate of KSR1, and the catalytic activities of both proteins are required for eliciting cell survival responses downstream of TNF. PMID: 21144847
- Novel changes in NF-{kappa}B activity during progression and regression phases of hyperplasia: role of MEK1,2, ERK1,2, and p38 PMID: 20710027
- Activation of the MEK/ERK signalling pathway by high serum concentration promoted PPARgamma expression and phosphorylation, and subsequently enhanced adipogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. PMID: 19243475
- Myogenic differentiation was inhibited if active MEK1 expression was induced earlier than day 1 in differentiation condition, but stimulated if induced after that, demonstrating that activated MEK1 plays differential roles depending on activation time. PMID: 19733237
- Requirement for a hsp90 chaperone-dependent MEK1/2-ERK pathway for B cell antigen receptor-induced cyclin D2 expression in mature B lymphocytes PMID: 11823472
- Results indicate that the phosphorylation of Ser(338) and Tyr(341) on Raf-1 exerts an important effect on reconfiguring the two MEK1-binding sites. PMID: 12244094
- activation of the MEK/ERK signaling pathway during the initial 12 h of adipogenesis enhances the activity of factors that regulate both C/EBPalpha and PPARgamma expression PMID: 12270934
- Data suggest that hydrogen peroxide regulates the activity of NF-kappaB by MEK1 activation through a MEKK1-dependent but Ras/Raf-independent mechanism. PMID: 12532330
- RafS259 mutants genetically separate MEK/ERK activation from the ability of Raf-1 to induce transformation and differentiation. The results further suggest that RafS259 mutants inhibit signaling pathways required to promote these biological processes. PMID: 12612072
- A selective inhibitor of MEK1 (PD 98059)blocked expression of galectin 3. PMID: 12788225
- MEKK1 is crucial for corneal development such that its ablation caused a reduction of ECM deposition in corneal stroma and disturbance of tight junctions in corneal epithelium PMID: 14627958
- Expression of a constitutively active mutant of MEK1 in chondrocytes of Fgfr3-deficient mice inhibited skeletal overgrowth, strongly suggesting that regulation of bone growth by FGFR3 is mediated at least in part by the MAPK pathway. PMID: 14871928
- mek1 has a role in cell cycle progression with activated PI3K/Akt oncoproteins PMID: 15004527
- Myogenic cells overexpressing activated Raf and kinase-defective MEKK1 remain differentiation-defective, suggesting that MEKK1 does not contribute to the inhibitory actions of Raf. PMID: 15159407
- activation of MEK1 downstream of beta1 integrins plays an important role in epidermal hyperproliferation and skin inflammation. PMID: 15304090
- there was no significant movement of MEK into the nucleus PMID: 15546878
- The ERK2 docking groove is more restrictive and selective for its tyrosine phosphatase inactivators than for MEK1/2 and indicate that distinct ERK2 residues modulate the docking interactions with activating and inactivating effectors. PMID: 16148006
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, spindle pole body. Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Membrane; Peripheral membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:Protein kinase superfamily, STE Ser/Thr protein kinase family, MAP kinase kinase subfamily
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:26395
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000005066
UniGene: Mm.248907
Most popular with customers
-
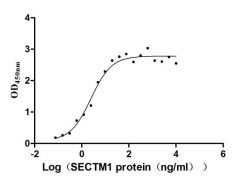
Recombinant Human Secreted and transmembrane protein 1 (SECTM1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human SARS coronavirus Spike glycoprotein (S), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Human SARS coronavirus (SARS-CoV) (Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus)
-
Recombinant Human CD226 antigen (CD226), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
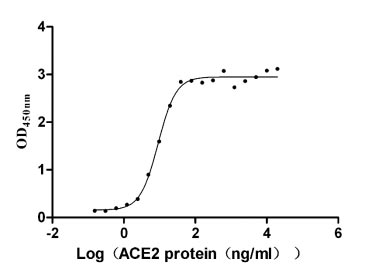
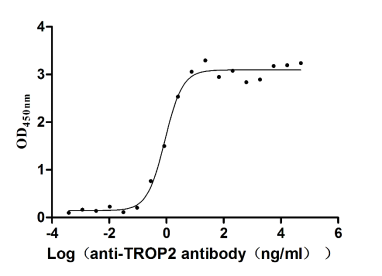
Recombinant Human Tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 (TACSTD2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
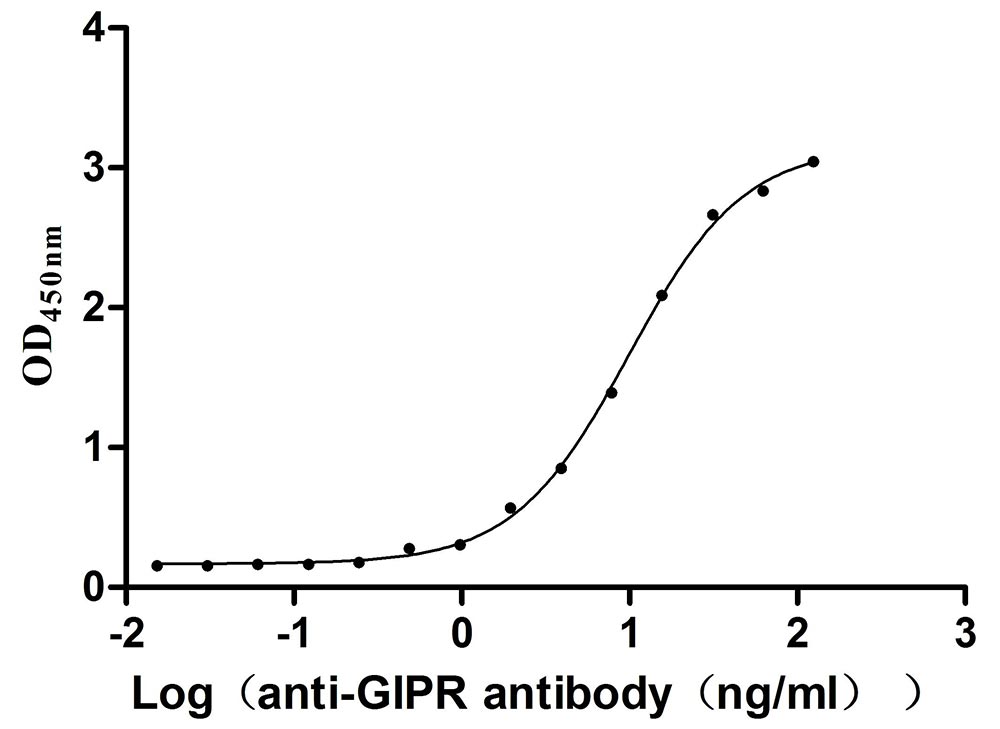
Recombinant Mouse Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor (Gipr), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
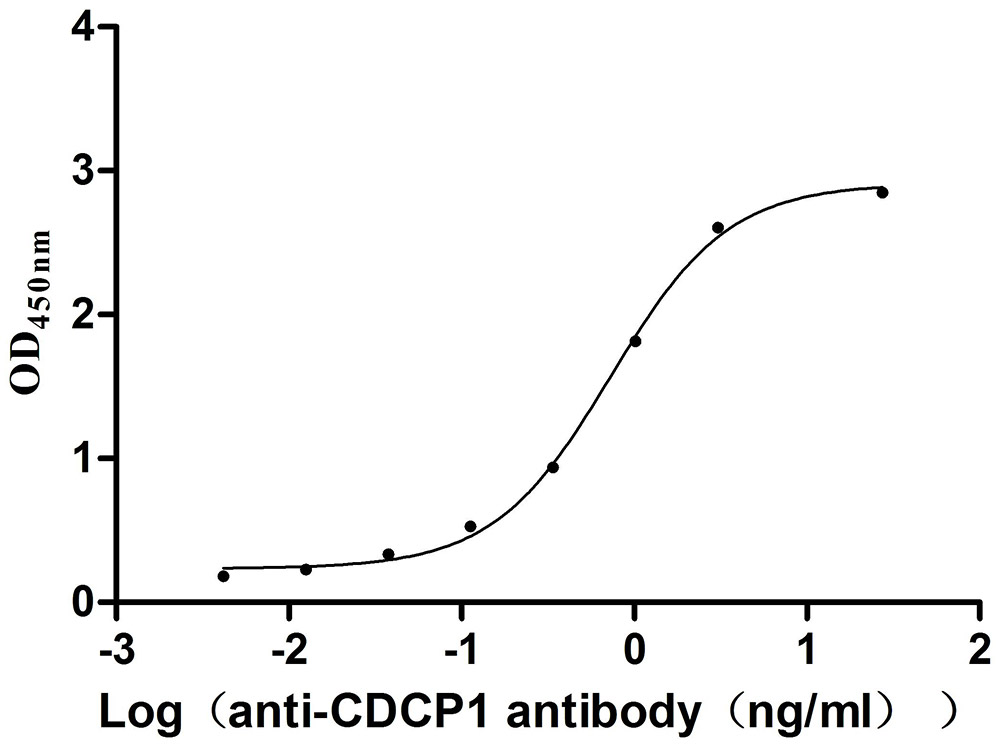
Recombinant Mouse CUB domain-containing protein 1 (Cdcp1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
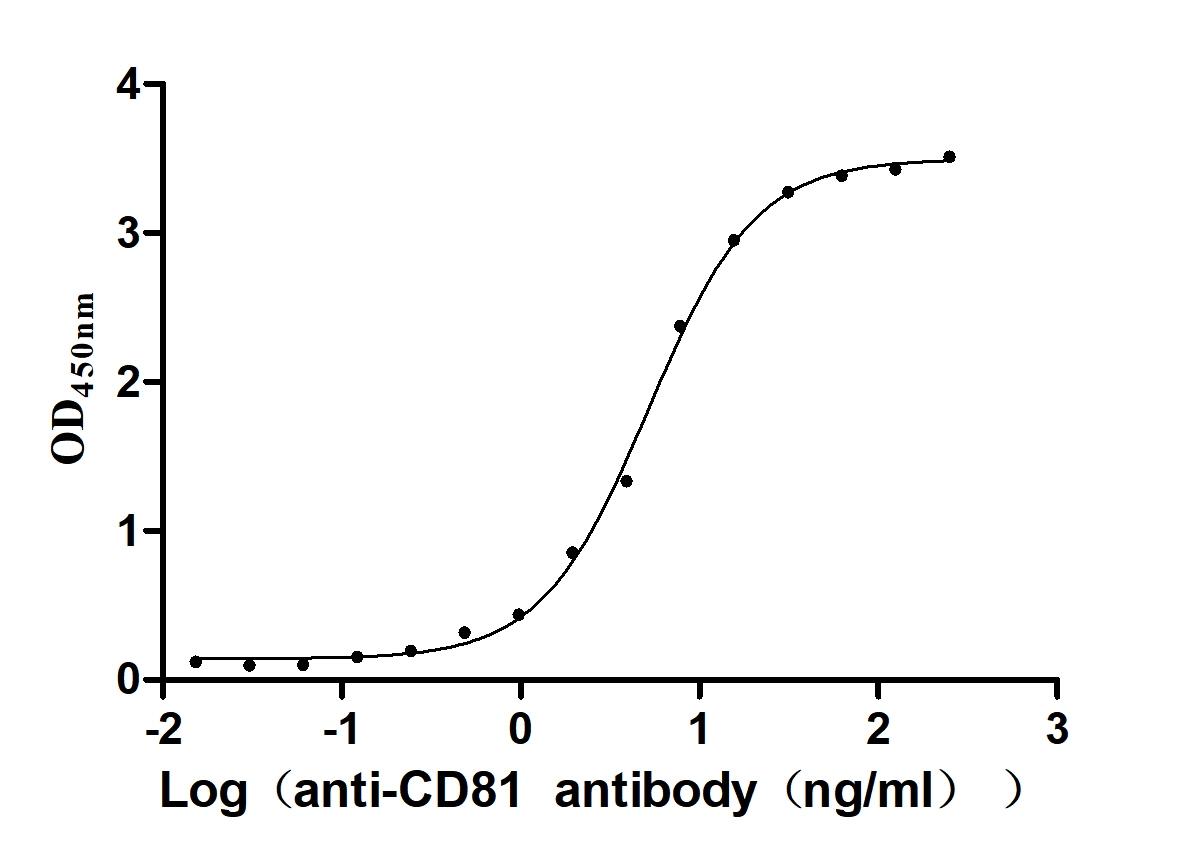
Recombinant Human CD81 antigen (CD81), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 15(TNFSF15) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)



-AC1.jpg)










