Recombinant Mouse Frizzled-4 (Fzd4), partial
-
货号:CSB-YP733770MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP733770MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP733770MO1-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP733770MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP733770MO1
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Fzd4; Frizzled-4; Fz-4; mFz4; CD antigen CD344
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Receptor for Wnt proteins. Most frizzled receptors are coupled to the beta-catenin (CTNNB1) canonical signaling pathway, which leads to the activation of disheveled proteins, inhibition of GSK-3 kinase, nuclear accumulation of beta-catenin (CTNNB1) and activation of Wnt target genes. Plays a critical role in retinal vascularization by acting as a receptor for Wnt proteins and norrin (NDP). In retina, it can be activated by Wnt protein-binding and also by Wnt-independent signaling via binding of norrin (NDP), promoting in both cases beta-catenin (CTNNB1) accumulation and stimulation of LEF/TCF-mediated transcriptional programs. A second signaling pathway involving PKC and calcium fluxes has been seen for some family members, but it is not yet clear if it represents a distinct pathway or if it can be integrated in the canonical pathway, as PKC seems to be required for Wnt-mediated inactivation of GSK-3 kinase. Both pathways seem to involve interactions with G-proteins. May be involved in transduction and intercellular transmission of polarity information during tissue morphogenesis and/or in differentiated tissues. Activation by Wnt5A stimulates PKC activity via a G-protein-dependent mechanism.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- NORRIN presented to FZD4 further increases cardiomyocyte output via proliferation through the canonical WNT pathway. PMID: 29249665
- results provide functional and biochemical dissection of Fzd4 in Norrin signaling. PMID: 30104375
- FZD4 was upregulated during cyclic mechanical stretch (CMS)-induced osteogenic differentiation, and the JNK signalling pathway was activated. FZD4 knockdown inhibited the mechanical stimuli-induced osteogenesis and JNK activity. PMID: 30007964
- These data expose a stromal component that regulates the earliest stages of tumorigenesis in the cerebellum, and a novel role for the Norrin/Fzd4 axis as an endogenous anti-tumor signal in the preneoplastic niche. PMID: 27823583
- Fzd4 and Fzd6 genes have a deep patterning effect on arterial vessel morphogenesis that may determine its functional efficiency PMID: 28253274
- Study identified a novel Wnt5a/Fzd4 signaling pathway that contributes to the regulation of dendrite morphogenesis PMID: 25424568
- These results question the conclusion that a dominant-negative mechanism would explain the dominance of the mutant L501fsX533 Fz4 allele in the transmission of a form of Familial exudative vitreoretinopathy. PMID: 25086772
- The data reveal both cell-autonomous and cell-nonautonomous effects, and they imply a central role for Norrin/Fz4 signaling in central nervous system vascular development and in the maintenance of the blood brain barrier/blood retina barrier state. PMID: 23217714
- Frizzled 4 regulates arterial network organization through noncanonical Wnt/planar cell polarity signaling. PMID: 22076635
- Frizzled4 wnt receptors are significantly increased in pathological neovascularization in a mouse model of oxygen-induced proliferative retinopathy. PMID: 21969016
- targeted inactivation of the TSK gene in mice causes expansion of the ciliary body and up-regulation of Wnt2b and Fzd4 expression in the developing peripheral eye PMID: 21856951
- These results demonstrate that FZD4 is required for physiological and pathologic angiogenesis in the retina and for regulation of retinal endothelial cell differentiation. PMID: 21743011
- A major role for frizzled 4 and frizzled 8 in controlling ureteric growth in the developing kidney. PMID: 21343368
- a Norrin-Fz4 signaling system plays a central role in vascular development in the eye and ear, and ligands unrelated to Wnts can act through Fz receptors PMID: 15035989
- Fzd4 appears to impact the formation of the corpus luteum PMID: 16093361
- Hyperosmotic sucrose and K(+) depletion increased the membrane localization of FZD(4)-GFP, and in parallel triggered fast and almost complete degradation of endogenous dishevelled PMID: 17428233
- sFRP-1 can interact with Wnt receptors Frizzled 4 and 7 on endothelial cells to transduce downstream to cellular machineries requiring Rac-1 activity in cooperation with GSK-3beta PMID: 18156211
- Loss of Fz4 in all endothelial cells disrupts the blood brain barrier in the cerebellum, whereas excessive Fz4 signaling disrupts embryonic angiogenesis. PMID: 19837032
- Data indicate that Norrin multimers and TSPAN12 cooperatively promote multimerization of FZD4 and its associated proteins to elicit physiological levels of signaling. PMID: 19837033
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:G-protein coupled receptor Fz/Smo family
-
组织特异性:Expressed in chondrocytes.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:14366
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000049852
UniGene: Mm.86755
Most popular with customers
-
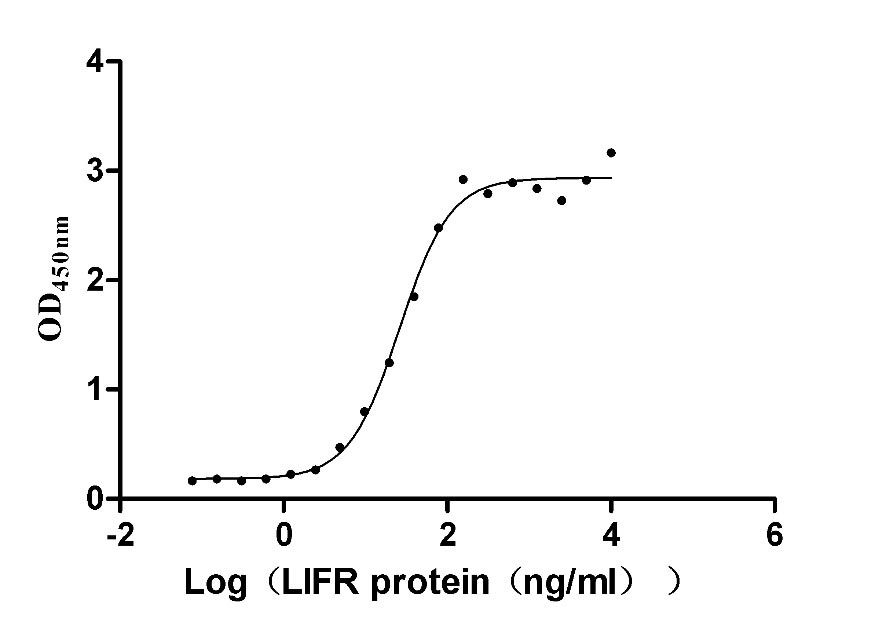
Recombinant Human Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
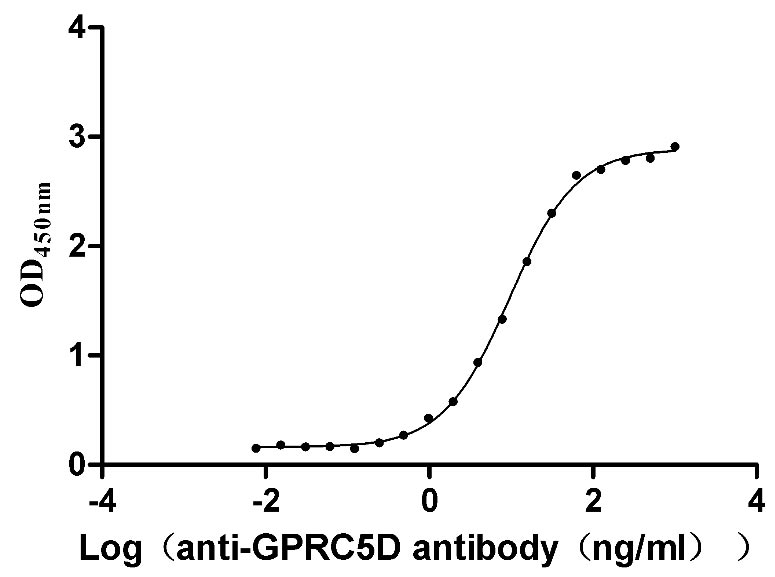
Recombinant Human G-protein coupled receptor family C group 5 member D (GPRC5D)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
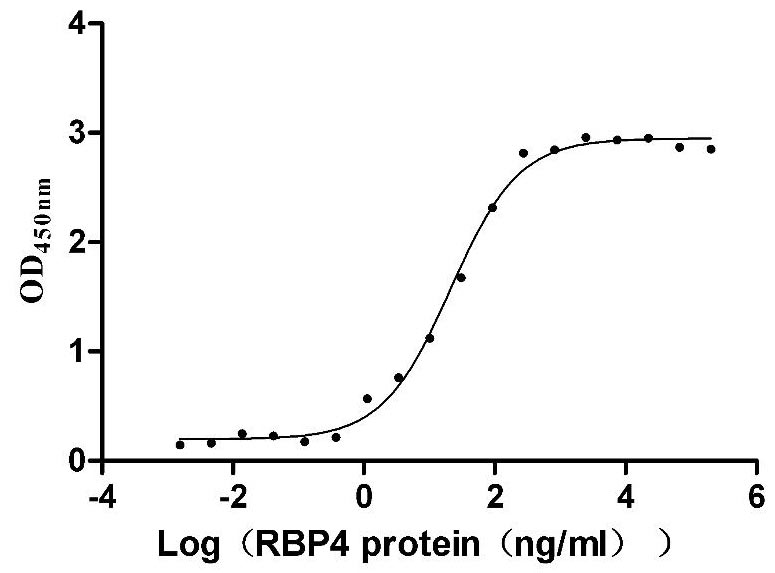
Recombinant Mouse Transthyretin (Ttr) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human Zymogen granule protein 16 homolog B (ZG16B) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
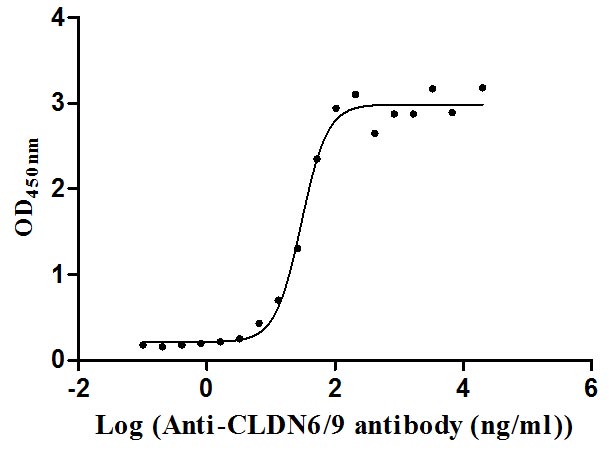
Recombinant Human Claudin-9 (CLDN9)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
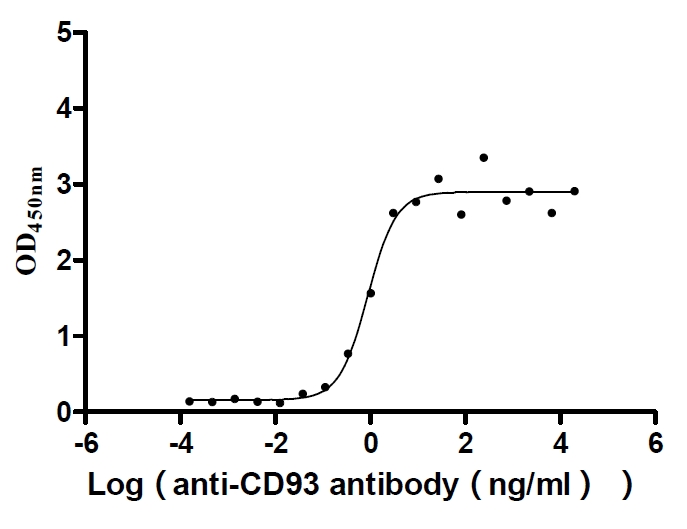
Recombinant Human Complement component C1q receptor (CD93), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Dickkopf-related protein 1 (DKK1) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
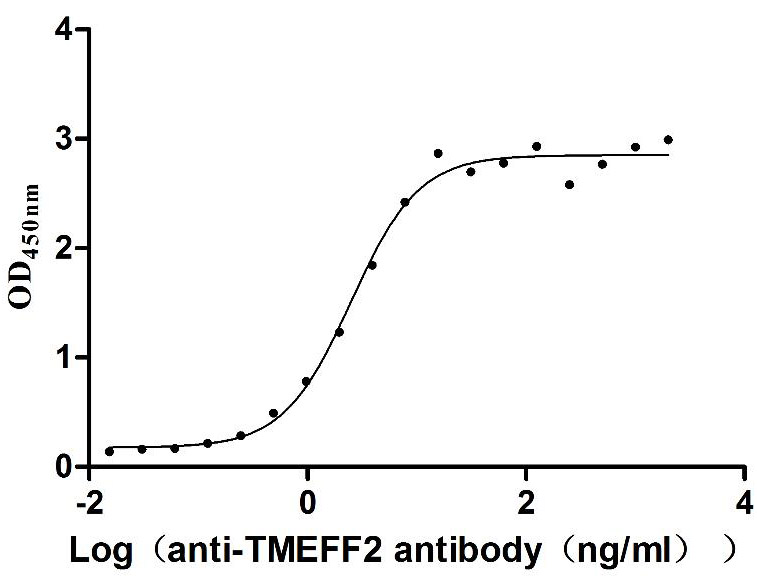
Recombinant Human Tomoregulin-2 (TMEFF2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)



-AC1.jpg)