Recombinant Mouse Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G (q) subunit alpha (Gnaq)
-
货号:CSB-YP009594MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP009594MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP009594MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP009594MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:GnaqGuanine nucleotide-binding protein G(q) subunit alpha; Guanine nucleotide-binding protein alpha-q
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Full length protein
-
表达区域:1-359
-
氨基酸序列MTLESIMACC LSEEAKEARR INDEIERQLR RDKRDARREL KLLLLGTGES GKSTFIKQMR IIHGSGYSDE DKRGFTKLVY QNIFTAMQAM IRAMDTLKIP YKYEHNKAHA QLVREVDVEK VSAFENPYVD AIKSLWNDPG IQECYDRRRE YQLSDSTKYY LNDLDRVADP SYLPTQQDVL RVRVPTTGII EYPFDLQSVI FRMVDVGGQR SERRKWIHCF ENVTSIMFLV ALSEYDQVLV ESDNENRMEE SKALFRTIIT YPWFQNSSVI LFLNKKDLLE EKIMYSHLVD YFPEYDGPQR DAQAAREFIL KMFVDLNPDS DKIIYSHFTC ATDTENIRFV FAAVKDTILQ LNLKEYNLV
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) are involved as modulators or transducers in various transmembrane signaling systems. Regulates B-cell selection and survival and is required to prevent B-cell-dependent autoimmunity. Regulates chemotaxis of BM-derived neutrophils and dendritic cells (in vitro). Transduces FFAR4 signaling in response to long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs).
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Repeated treatment with methamphetamine (METH)increased behavioral sensitization as well as Galphaq/11 protein expression and Galpha protein activity in the striata of mice, while a single treatment of METH at the same dose did not affect these parameters. Repeated intrastriatal injections of a Galphaq/11 inhibitor reduced behavioral sensitization and striatal dopamine level in response to METH. PMID: 29223637
- these data highlighted the critical role of Galphaq in regulating Th17 differentiation and multiple sclerosis pathogenesis PMID: 28216651
- Emergence of a malignant phenotype may therefore arise from both under- and overexpression of Galpha11/q signaling, implicating its upstream regulation as a potential therapeutic target in a host of pathologic conditions PMID: 28301547
- Galphaq regulates the development of rheumatoid arthritis by modulating Th1 differentiation PMID: 28197018
- Fluid shear stress acts on the Galphaq-ERK5 signaling pathway to upregulate Cyclin B1 and CDK1 expression, thereby resulting in MC3T3-E1 cell proliferation. PMID: 27115838
- cell-penetrating peptides should effectively inhibit active Galphaq in cells and that these and genetically encoded sequences may find application as molecular probes, drug leads, and biosensors to monitor the spatiotemporal activation of Galphaq in cells. PMID: 27742837
- The Galphas and Galphaq peptides adopt different orientations in beta2-AR and V1AR, respectively. The beta2-AR/Galphas peptide interface is dominated by electrostatic interactions, whereas the V1AR/Galphaq peptide interactions are predominantly hydrophobic. PMID: 27330078
- The betaARKrgs peptide, but not endogenous GRK2, interacted with Galpha(q) and interfered with signaling through this G protein. These data support the development of GRK2-based therapeutic approaches to prevent hypertrophy and heart failure. PMID: 27016525
- Galphaq/Galpha11 signaling pathways play a pivotal role in gene activity patterns during cardiac remodeling. PMID: 26476043
- Developmental AHR activation by pollutants, and other exogenous ligands, increases the likelihood that Gnaq knockout mice will develop autoimmune diseases later in life. PMID: 26363170
- demonstrate that the ability of an MC4R agonist delivered to PVN to inhibit food intake is lost in mice lacking G(q/11)alpha in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus but not in animals deficient for G(s)alpha PMID: 26595811
- In studies with Gnaq(-/-) mice, Galphaq inhibited the differentiation of Th17 cell via regulating the activity of ERK-1/2 to control the expression of STAT3 and RORalpha. PMID: 25732870
- results define specific modulation of spatial working memory and psychostimulant responses through disruptions in G(alphaq) signaling within cerebral cortical glutamatergic neurons PMID: 25963901
- Gnaq was selectively inactivated in GnRH neurons of global Gna11--null mice. Galphaq/11-coupled signaling is a major conduit of GnRH secretion, results with these mice showed a role for non-Galphaq/11-coupled signaling in reproductive development and function. PMID: 26377475
- Data show that the expression of the guanine nucleotide binding protein alpha q GNAQ(Q209L) allele induced causes the rapid development of uveal melanoma, with local invasion of blood vessels and multiple tumors developing in the lungs. PMID: 26113083
- Fluorosed mouse ameloblasts have increased SATB1 retention and Galphaq activity. PMID: 25090413
- Gq activation stimulated calcineurin activity, resulting in CN-dependent upregulation of TRPC6 in murine kidneys. PMID: 25844902
- activation of ERK5 MAPK by model Gq-coupled GPCRs does not depend on receptor internalization, beta-arrestin recruitment or receptor phosphorylation but rather is dependent on Galphaq-signalling. PMID: 24358341
- Precise temporal control of Gq signals in 5-HT2c-R domains in GABAergic neurons upstream of 5-HT neurons provides negative feedback regulation of serotonergic firing to modulate anxiety-like behavior in mice. PMID: 24733892
- Lack of TRPC4 potentiation in neurons in the lateral nucleus of the amygdala affects two Galphaq/11 protein-coupled signaling pathways, implicated in fear-related behavior. PMID: 24599464
- Galpha11 is essential for the development of cardiac hypertrophy in type I-diabetes. PMID: 22560942
- This is the first conclusive evidence for the physiological importance of the activation of Gq/11 by the LH receptor and for the involvement of Galphaq/11 in ovulation. PMID: 23836924
- Inhibition of Galphaq alters cell proliferation and is associated with decreased MMP-9 expression and activity PMID: 22595017
- Suggest the involvement of the Gnaq and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling cascades in mediating melatonin effects in pancreatic alpha-cells. PMID: 22672634
- Src family kinases, PI3 kinase and protein kinase C synergize to mediate Gq-dependent platelet activation PMID: 23066026
- PKCzeta is essential for Gq-dependent ERK5 activation in cardiomyocytes and cardiac fibroblasts and indicate a key cardiac physiological role for the Galpha(q)/PKCzeta/ERK5 signaling axis. PMID: 22232556
- Galpha(q) blockade abrogated the development of the heart failure phenotype in tetracycline-transactivating factor/V1A-transgenic mice. PMID: 21747049
- rat monoclonal antibodies, specifically recognizing the deamidated Galpha(q), to detect the actions of Pasteurella multocida toxin deamidated Galpha(q) only under reducing conditions. PMID: 21624053
- the Galpha(q) signal plays an inhibitory role in the PTH osteoanabolic action, suggesting that its suppression may lead to a novel treatment in combination with PTH against osteoporosis. PMID: 21345793
- study describe the structure of PLC-beta3 in an activated complex with Galphaq, which together with supporting biochemical and physiological analyses reveals its mechanism of transmembrane signaling PMID: 20966218
- Cellular G(i)-G(q) synergism derives from direct supra-additive stimulation of phospholipase C-beta3 by G protein subunits Gbetagamma and Galpha(q). PMID: 20579885
- Gnaq expression by B cells is necessary for normal peripheral B cell development and tolerance induction and also plays a role in preventing early onset mortality in mice. PMID: 20624888
- In Galphaq-induced cardiomyopathy, myocyte contractile dysfunction is mediated, at least in part, by 1 or more oxidative posttranslational modifications of SERCA. PMID: 20508180
- Both PKCzeta and MEK5 associate to G alpha(q) upon activation of GPCR, thus forming a ternary complex that seems essential for the activation of ERK5. PMID: 20200162
- In mouse pacreatic acini Galphaq links cholecystokinin stimulation to activation of Rac1, actin cytoskeletal reorganization and amylase secretion. PMID: 19940064
- Ca(2+)-mediated inhibition of AC5/6 is an important mechanism of purinergic receptor-induced decline of cAMP in vascular smooth muscle cells. PMID: 19889965
- MEKK1 is essential for cardiac hypertrophy and dysfunction induced by Gq PMID: 11891332
- Activation of Gq-coupled receptors on resident leukocytes in the lung elicits expression of GM-CSF, which in turn is required for allergen-induced pulmonary eosinophilia, identifying a novel pathway to pulmonary pathology in diseases such as asthma. PMID: 11907117
- pathway is involved in orphan G protein-coupled receptors MrgA1 and MrgC11 which are activated by RF-amide-related peptides PMID: 12397184
- The vesicular monoamine content regulates VMAT2 activity through Galphaq in mouse platelets. PMID: 12604601
- cholinergic receptor-mediated responses are dependent on Galphaq-mediated signaling events and Galphaq is a potential target of preventative/intervening therapies for lung dysfunction. PMID: 12611815
- antisense to Galpha(q/11) significantly inhibited IL-6 production compared to control PMID: 12829380
- an Akt-mediated cell survival pathway is compromised by the diminished availability of PIP2 elicited by pathological levels of Gq activity in cardiomyocytes PMID: 12900409
- These data suggest that slow myosin heavy chain 2 repression in innervated fast pectoralis major fibers is mediated by cell signaling involving muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, G(alpha)q, and protein kinase C. PMID: 12952937
- RGS proteins block Galpha(q)-mediated signal production by competing with downstream effectors for Galpha(q) binding. PMID: 14630933
- We identified three of four such mutations as hypermorphic alleles of Gnaq and Gna11, which encode widely expressed Galphaq subunits, act in an additive and quantitative manner, and require Ednrb. PMID: 15322542
- PC1 signaling elevates intracellular Ca(2+), activates Galpha(q) and PLC, which then activates calcineurin and NFAT PMID: 15466861
- prolonged activation of the Gq pathway desensitizes GnRH-induced signaling by selectively down-regulating the PLC-PKC-Ca2+ pathway, leading to reduced LHbeta synthesis and LH secretion PMID: 15878957
- the inhibitory effect of Galpha q on the cardiac LTCC is mediated by inhibition of PI3K PMID: 16186103
- activation of Galpha q in cardiac myocytes of adult mice causes a dilated cardiomyopathy that requires the activation of PLCbeta PMID: 16210321
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Lipid-anchor. Golgi apparatus. Nucleus. Nucleus membrane.
-
蛋白家族:G-alpha family, G(q) subfamily
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:14682
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000025541
UniGene: Mm.439701
Most popular with customers
-
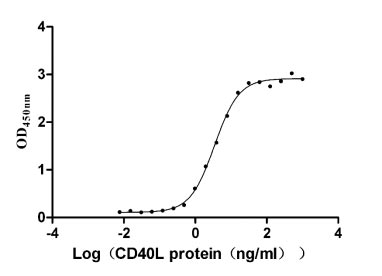
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 5 (CD40), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
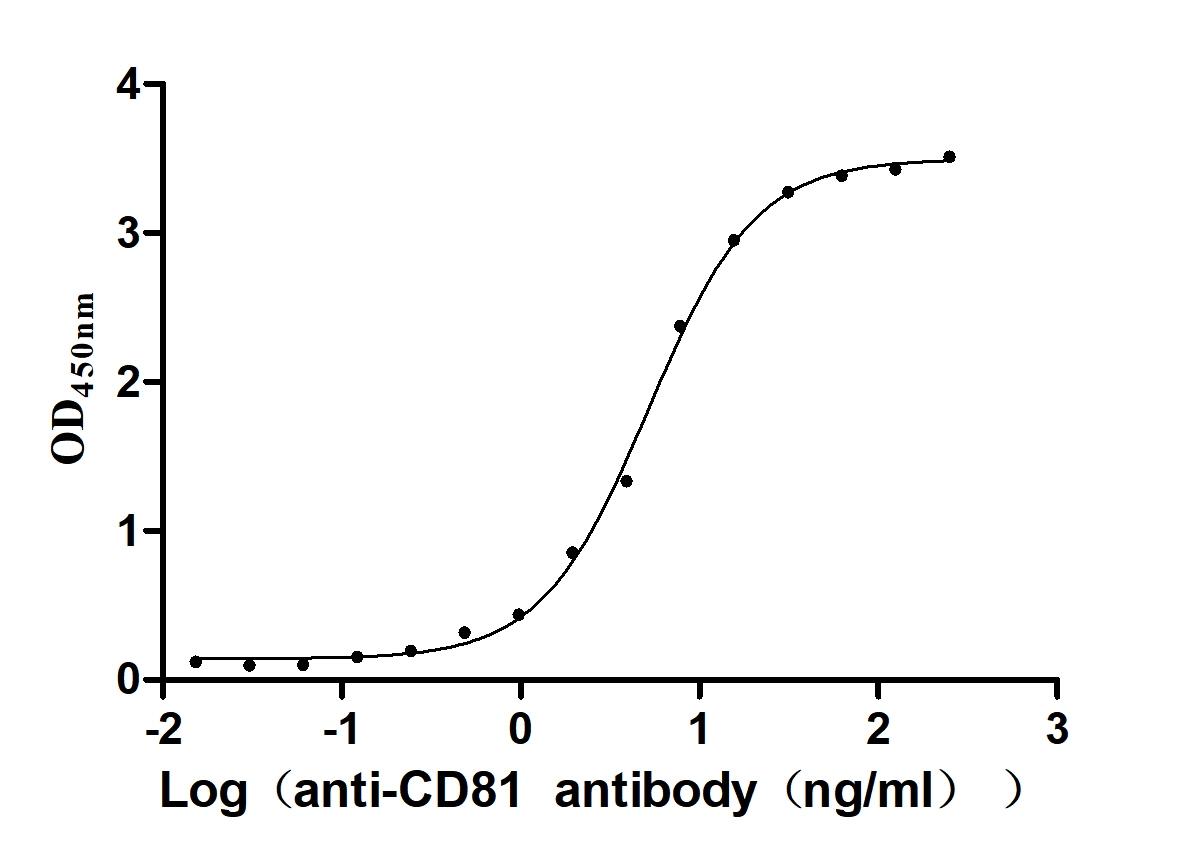
Recombinant Human CD81 antigen (CD81), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
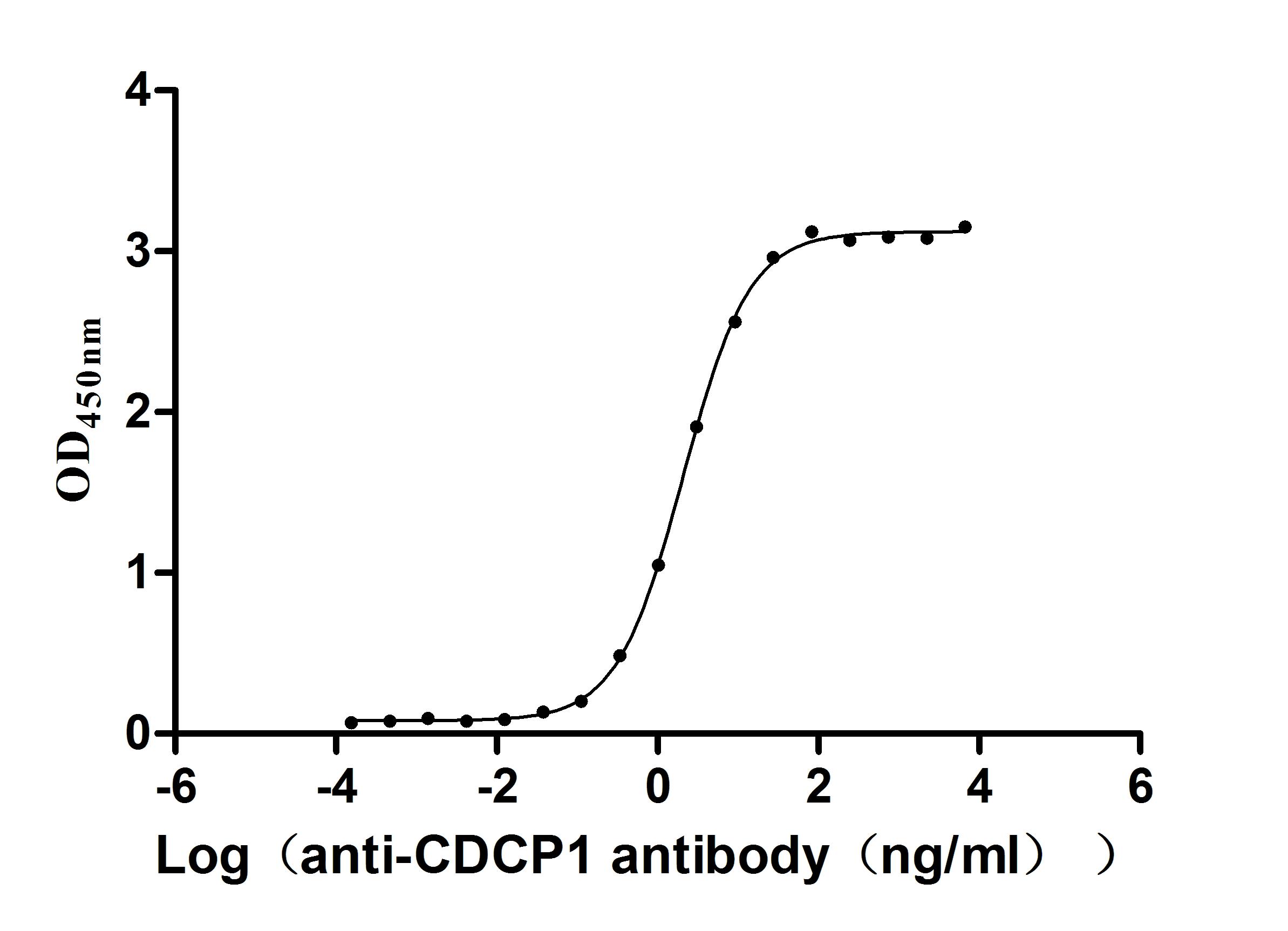
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis CUB domain containing protein 1 (CDCP1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
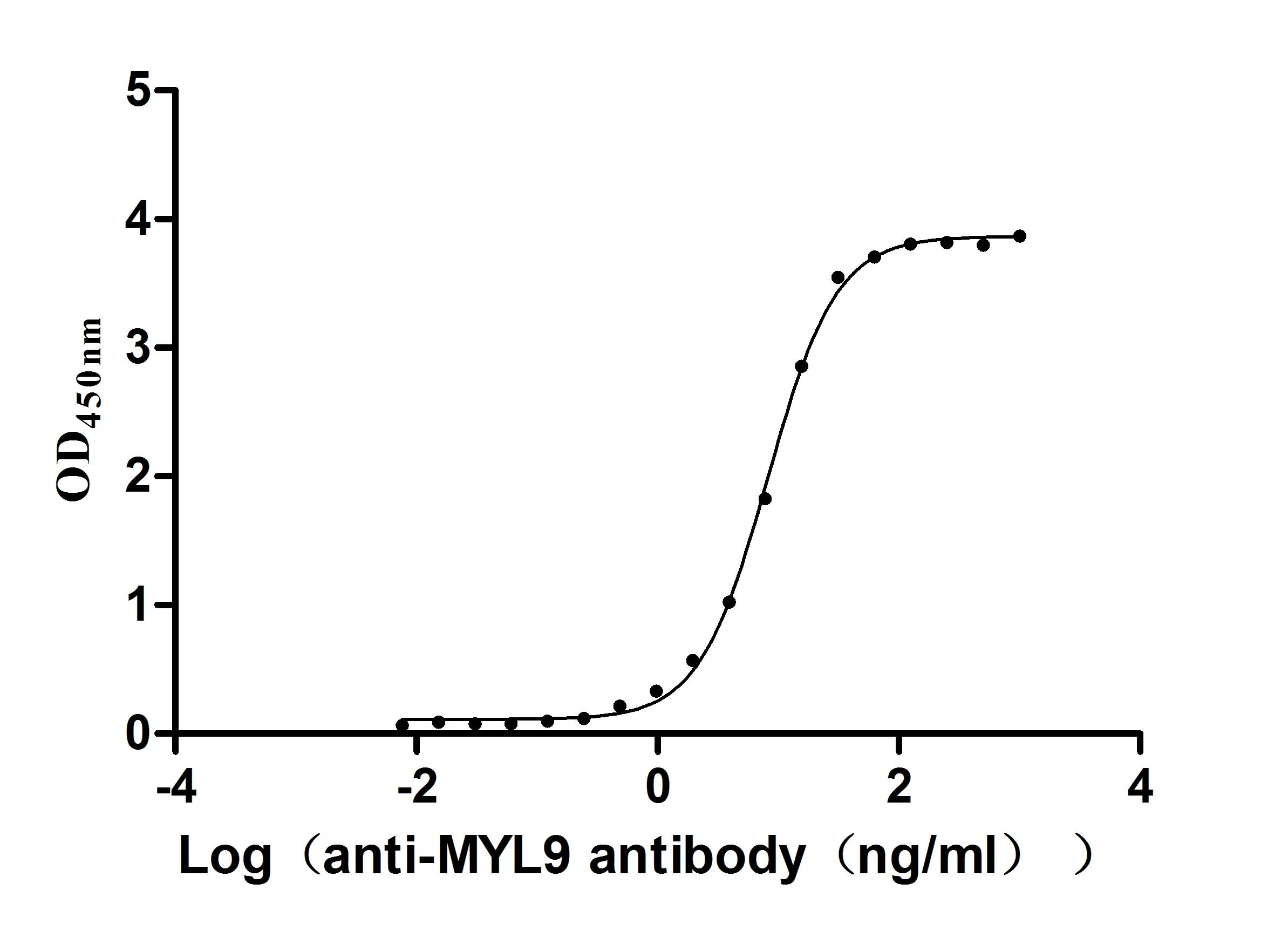
Recombinant Human Myosin regulatory light chain 12B(MYL12B) (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
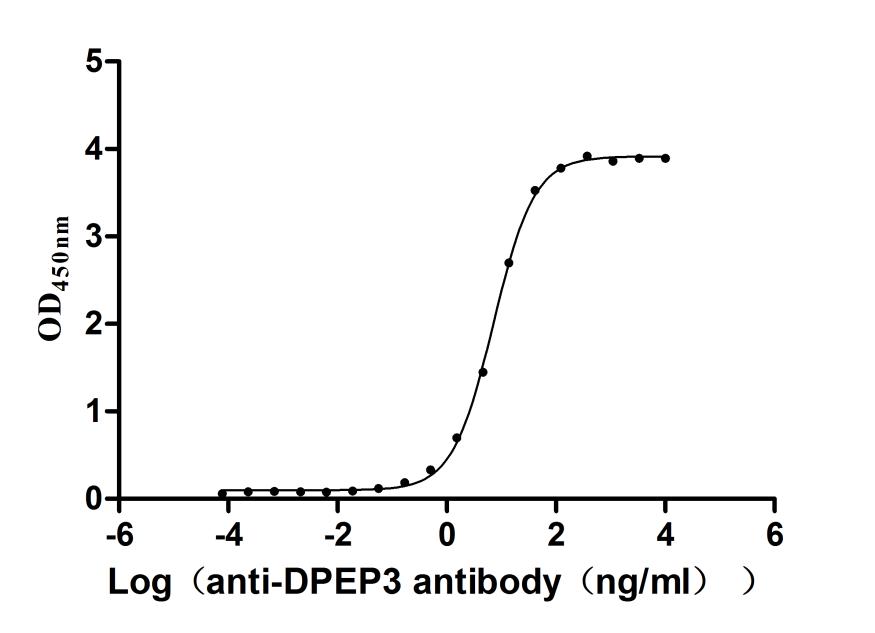
Recombinant Human Dipeptidase 3(DPEP3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
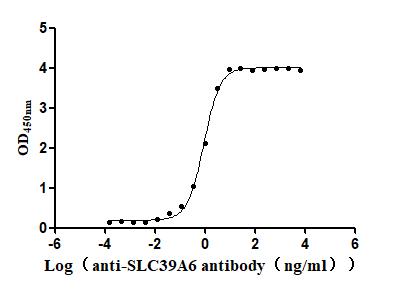
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Zinc transporter ZIP6 isoform X1(SLC39A6),partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque)
-
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 15(TNFSF15) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)










