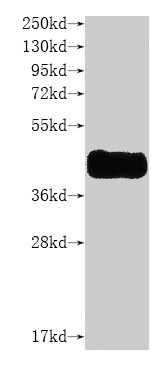
Recombinant Mouse Heparanase (Hpse), partial
-
货号:CSB-YP010716MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP010716MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP010716MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP010716MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP010716MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Hpse
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Hpse; Hpa; Heparanase; EC 3.2.1.166; Endo-glucoronidase) [Cleaved into: Heparanase 8 kDa subunit; Heparanase 50 kDa subunit]
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
表达区域:150-535aa
-
氨基酸序列KEFKNSTYSRSSVDMLYSFAKCSGLDLIFGLNALLRTPDLRWNSSNAQLLLDYCSSKGYN ISWELGNEPNSFWKKAHILIDGLQLGEDFVELHKLLQRSAFQNAKLYGPDIGQPRGKTVK LLRSFLKAGGEVIDSLTWHHYYLNGRIATKEDFLSSDVLDTFILSVQKILKVTKEITPGK KVWLGETSSAYGGGAPLLSNTFAAGFMWLDKLGLSAQMGIEVVMRQVFFGAGNYHLVDEN FEPLPDYWLSLLFKKLVGPRVLLSRVKGPDRSKLRVYLHCTNVYHPRYQEGDLTLYVLNL HNVTKHLKVPPPLFRKPVDTYLLKPSGPDGLLSKSVQLNGQILKMVDEQTLPALTEKPLP AGSALSLPAFSYGFFVIRNAKIAACI
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Endoglycosidase that cleaves heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) into heparan sulfate side chains and core proteoglycans. Participates in extracellular matrix (ECM) degradation and remodeling. Selectively cleaves the linkage between a glucuronic acid unit and an N-sulfo glucosamine unit carrying either a 3-O-sulfo or a 6-O-sulfo group. Can also cleave the linkage between a glucuronic acid unit and an N-sulfo glucosamine unit carrying a 2-O-sulfo group, but not linkages between a glucuronic acid unit and a 2-O-sulfated iduronic acid moiety. It is essentially inactive at neutral pH but becomes active under acidic conditions such as during tumor invasion and in inflammatory processes. Facilitates cell migration associated with metastasis, wound healing and inflammation. Enhances shedding of syndecans, and increases endothelial invasion and angiogenesis in myelomas. Acts as procoagulant by increasing the generation of activation factor X in the presence of tissue factor and activation factor VII. Increases cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix (ECM), independent of its enzymatic activity. Induces AKT1/PKB phosphorylation via lipid rafts increasing cell mobility and invasion. Heparin increases this AKT1/PKB activation. Regulates osteogenesis. Enhances angiogenesis through up-regulation of SRC-mediated activation of VEGF. Implicated in hair follicle inner root sheath differentiation and hair homeostasis.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- elevated expression of heparanase augmented both the innate and adaptive immune system and propagated inflammatory reactions in the murine rheumatoid arthritis model. PMID: 28401953
- These results show for the first time that HPSE regulates macrophage polarization as well as renal damage and repair after I/R. HPSE inhibitors could therefore provide a new pharmacologic approach to minimize acute kidney injury and to prevent the chronic profibrotic damages induced by I/R. PMID: 28970256
- Study reveals that HPSE stimulates the proliferation of ES cells as well as the expansion of emerging progenitors during neural differentiation. PMID: 27890389
- heparanase as a key mediator of macrophage activation and function in tumorigenesis and cross-talk with the tumor microenvironment. PMID: 27849593
- Results demonstrate that acute ischemic injury up-regulates renal heparanase expression and suggest that heparanase plays a deleterious role in the development of renal injury and kidney dysfunction. PMID: 28388547
- Heparanase has a role in upregulating platelet adhesion activity and thrombogenicity PMID: 27129145
- eNOS prevents heparanase induction and the development of proteinuria PMID: 27505185
- Data show that heparanase-1 (HPA-1) induced shedding of heparan sulfate chain from syndecan-1 (SDC-1) facilitated the release of vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C) from SDC-1/VEGF-C complex into the medium of hepatocarcinoma cell. PMID: 28209511
- the activation of intestinal heparanase contributes to intestinal injury during early sepsis by facilitating the destruction of mucosal epithelial glycocalyx and promoting inflammatory responses. PMID: 28170292
- Heparanase increases the inflammation in AGEs-stimulated macrophages through activating the RAGE-NF-kappaB pathway. Heparanase driven inflammation from AGEs-stimulated macrophages increases the adherence of glomerular endothelial cells (GEnCs) and augments the permeability of GEnCs. PMID: 28081450
- heparanase contributes to allergen-induced eosinophil recruitment to the lung. PMID: 26039697
- Unfractionated heparin inhibits heparanase, and reverses the activation of NF-kappaB and MAPK P38 signaling pathways to attenuate inflammatory responses induced by sepsis. These results suggest that UFH PMID: 26191183
- Results show a critical role for heparanase in regulating the branching and invasive behavior of normal mammary epithelia which could be the result of its mutually reciprocal feedback with MMP-14. PMID: 25735873
- Data suggest a potential mechanism of diabetic enteropathy, which is depending remarkably on syndecan-1 (Sdc1) and -beta-D-glucuronidase heparanase (HPSE). PMID: 25702768
- upregulated through NF-kB and translocated to the cell surface upon herpes simplex virus-1 infection for the removal of heparan sulfate to facilitate viral release PMID: 25912399
- Findings identify a dual function for HPSE in malignant melanoma with a protumorigenic extracellular activity and a tumor-suppressive nuclear action. PMID: 25745999
- Studies in heparanase-deficient mice established its contributions to autophagy. PMID: 26249176
- Heparanase is suggested to be a prognostic and diagnostic marker for oral premalignant lesions which could have a major impact on future prognosis and diagnosis of SCC of the oral cavity. PMID: 25189888
- Novel function of heparanase guides cancer-promoting action of TAM and heparanase expression status may be predictive of treatment potential, targeting TAM/IL-6/STAT3. PMID: 25326645
- Under diabetic conditions, latent heparanase, overexpressed by glomerular cells and posttranslationally activated by cathepsin L of tubular origin creates chronic inflammatory conditions and fosters macrophage-mediated renal injury. PMID: 25008182
- We found that heparanase induction is associated with decreased levels of CXCL10, suggesting that this chemokine exerts tumor-suppressor properties in myeloma. PMID: 24699306
- Because HS with unsubstituted glucosamine residues accumulates in heparanase-expressing breast cancer cells, we assumed that these HS structures are resistant to heparanase and can therefore be utilized as a heparanase inhibitor. PMID: 24753252
- Our findings indicated cell-autonomous HPSE1 modulates clonogenicity, proliferative potential and migration of BM-MSCs and suggested the HS-GAGs may contribute to the niche microenvironment of BM-MSCs PMID: 24624965
- Involvement of heparanase in the pathogenesis of psoriasis and a role for the enzyme in facilitating abnormal interactions between immune and epithelial cell subsets of the affected skin. PMID: 24169805
- Findings indicate an important role for heparanase in immunity and identify the enzyme as a potential target for regulation of an immune response. PMID: 24532362
- Heparanase has roles in lymphangiogenesis and tumor invasion in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors PMID: 23644656
- Cleavage of macromolecular heparin by heparanase accelerates the release of heparin and chymase from extracellular matrices. PMID: 24344642
- AGE-induced macrophage migration is dependent on HPA involving RAGE-HPA-PI3K/AKT pathway. Nonenzymatic activity of HPA may play a key role in AGE-induced macrophage migration associated with inflammation in diabetic vascular complication. PMID: 23442498
- heparanase is important for mouse palate formation because it mediates degradation of the ECM of palatal shelves PMID: 23509775
- Characterization of heparanase-induced phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-AKT activation and its integrin dependence. PMID: 23504323
- Heparanase activates macrophages, resulting in TLR2/3 mediated induction of cytokine expression associated with plaque progression toward vulnerability. PMID: 23162016
- heparanase acts as a negative modulator of AgRP signaling at MC4R, through cleavage of heparan sulfate chains presumably linked to syndecan-3 PMID: 22479599
- Together with CCR7 and its ligands, and probably MMP-14, heparanase controls DC trafficking. PMID: 22590508
- Cerebral ischemia markedly increased heparanase levels in endothelial cells and then in astrocytes. PMID: 22169133
- autoimmune destruction of islets in NOD mice was associated with production of catalytically active heparanase PMID: 22182841
- Crucial role of heparanase in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy(DN) and its potential as a highly relevant target for therapeutic interventions in patients with DN. PMID: 22106160
- Downregulating heparanase-1 with siRNA inhibits the invasiveness of mouse hepatoma cells. PMID: 20800024
- These findings reveal a novel function of heparanase in maintaining mast cell homeostasis PMID: 21575986
- Heparanase-mediated loss of nuclear syndecan-1 enhances histone acetyltransferase (HAT) activity to promote expression of genes that drive an aggressive tumor phenotype PMID: 21757697
- SST0001, a chemically modified heparin, inhibits myeloma growth and angiogenesis via disruption of the heparanase/syndecan-1 axis PMID: 21257720
- heparanase generates a vicious cycle that powers colitis and the associated tumorigenesis: heparanase, acting synergistically with the intestinal flora, stimulates macrophage activation PMID: 21490396
- Chronic skin barrier disruption activates heparanase and induces gene expression changes, leading to increased growth factor interaction between epidermis and dermis, and facilitating various cutaneous changes, including wrinkle formation. PMID: 20100191
- heparanase induces upregulation of Th2 cytokines, resulting in inhibition of the inflammatory lesion of experimental autoimmune encephalitis PMID: 20399501
- A full-length heparanase gene was cloned from a mouse embryo cDNA library and determined to encode a protein of 535 amino acids. The full-length mouse gene was stably expressed in NS0 myeloma cells. PMID: 12460766
- expression of heparanase mRNA and VEGF, and vessel formation in mouse fractured bone PMID: 14618334
- HPSE-1 likely plays important roles in regulating the in vivo growth and progression of melanoma PMID: 15645118
- heparanase is actively involved in embryo implantation. PMID: 15749484
- heparanase may have a role in lymph node metastatic dissemination PMID: 15799822
- By monitoring in vivo activation of luciferase gene driven by the heparanase promoter, we demonstrate activation of heparanase transcription at an early stage of DTH. PMID: 16384929
- HPSE is involved in the pathogenesis of proteinuria in overt diabetic nephropathy by degradation of heparan sulfates PMID: 17051139
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Lysosome membrane; Peripheral membrane protein. Secreted. Nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:Glycosyl hydrolase 79 family
-
组织特异性:Expressed in skin, mainly in the stratum granulosum and the first layer of the stratum corneum in the upper part of the epidermis. Also detected in hair follicles and in sebaceous glands.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:15442
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000044072
UniGene: Mm.265786
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Poliovirus receptor (PVR) (I340M), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
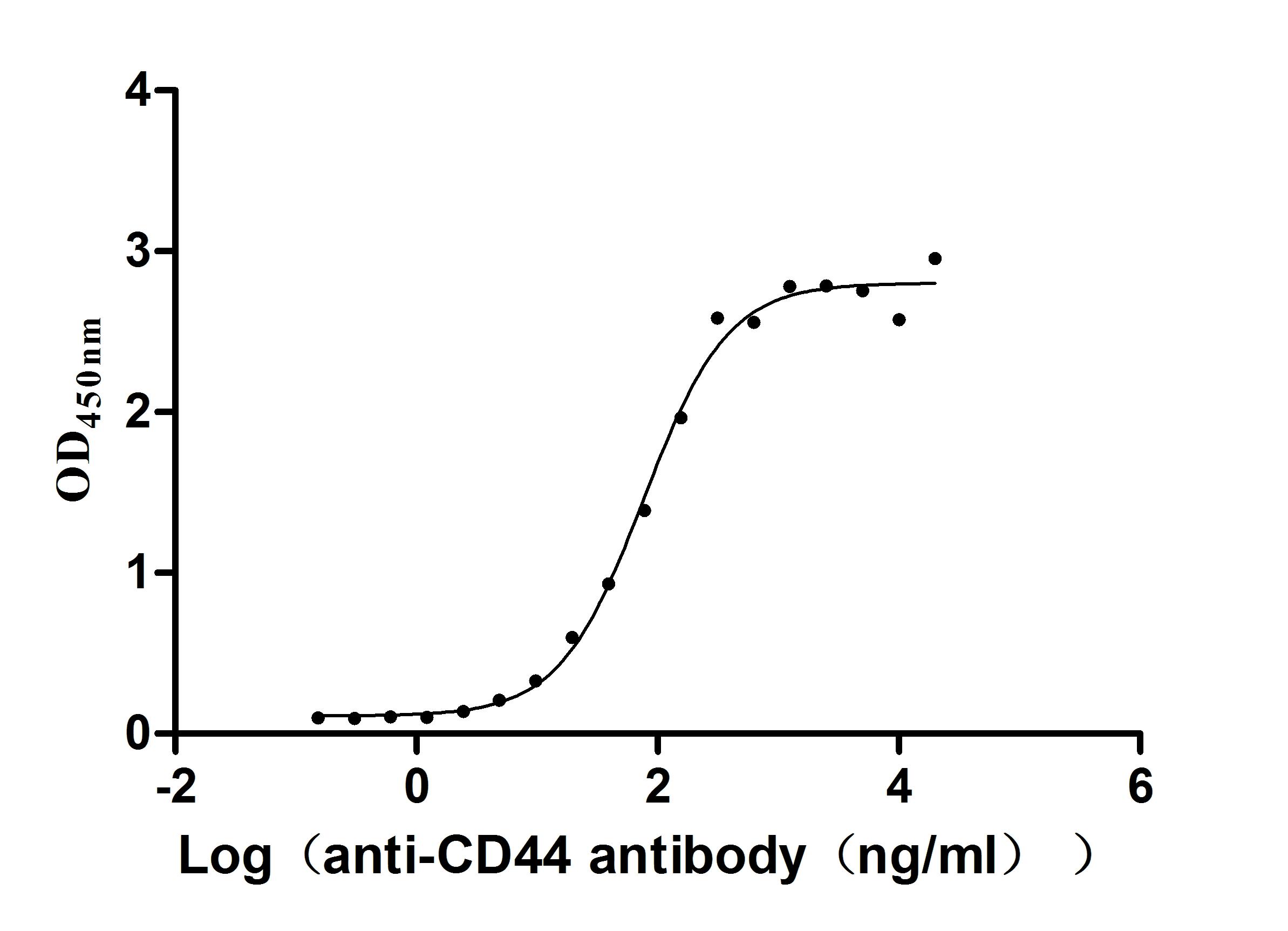
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis CD44 antigen (CD44), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
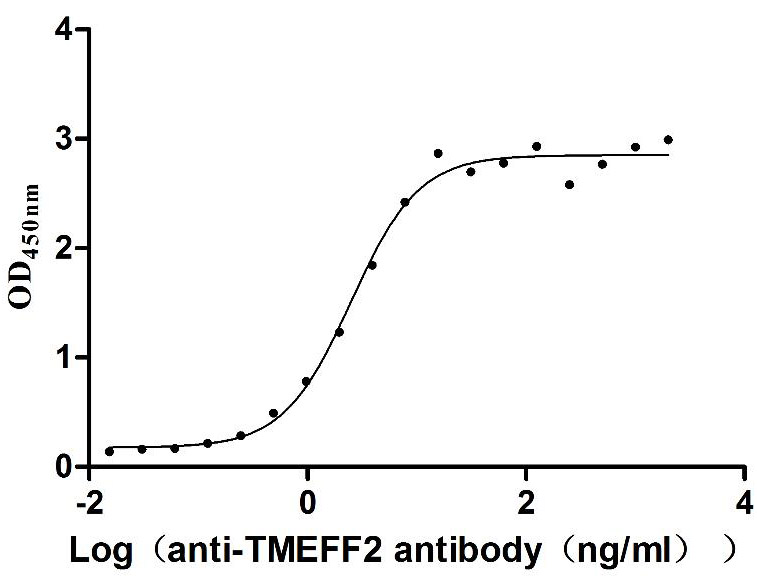
Recombinant Human Tomoregulin-2 (TMEFF2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
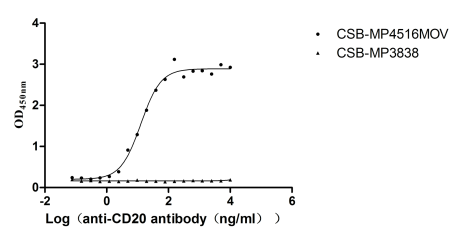
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Membrane spanning 4-domains A1 (MS4A1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 8 (CCR8)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Alkaline phosphatase, germ cell type (ALPG) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Myosin regulatory light polypeptide 9 (MYL9) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Dipeptidase 3(DPEP3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)