Recombinant Mouse Homeobox protein DLX-1 (Dlx1)
-
货号:CSB-YP731046MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP731046MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP731046MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP731046MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP731046MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Dlx1
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Dlx1Homeobox protein DLX-1
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:full length protein
-
表达区域:1-255
-
氨基酸序列MTMTTMPESL NSPVSGKAVF MEFGPPNQQM SPSPMSHGHY SMHCLHSAGH SQPDGAYSSA SSFSRPLGYP YVNSVSSHAS SPYISSVQSY PGSASLAQSR LEDPGADSEK STVVEGGEVR FNGKGKKIRK PRTIYSSLQL QALNRRFQQT QYLALPERAE LAASLGLTQT QVKIWFQNKR SKFKKLMKQG GAALEGSALA NGRALSAGSP PVPPGWNPNS SSGKGSGSSA GSYVPSYTSW YPSAHQEAMQ QPQLM
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Plays a role as a transcriptional activator or repressor. Inhibits several cytokine signaling pathways, such as TGFB1, activin-A/INHBA and BMP4 by interfering with the transcriptional stimulatory activity of transcription factors, such as MSX2, FAST2, SMAD2 and SMAD3 during hematopoietic cell differentiation. Plays a role in terminal differentiation of interneurons, such as amacrine and bipolar cells in the developing retina. Likely to play a regulatory role in the development of the ventral forebrain. May play a role in craniofacial patterning and morphogenesis and may be involved in the early development of diencephalic subdivisions.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Studies revealed that Dlx1/2 and Otp are required for the specification of growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH)- and AgRP-neurons, respectively. Dlx1/2 suppress agouti-related protein (AgRP)-neuronal fate by directly binding and repressing the Otp gene, uncovering a novel Dlx1/2-Otp gene regulatory axis critical for the segregation of GHRH- and AgRP-neuronal fates. PMID: 29795232
- GABA is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. We show that Dlx1/Dlx2 homeobox genes regulate GABA synthesis during forebrain development through direct activation of glutamic acid decarboxylase enzyme isoforms that convert glutamate to GABA. PMID: 28821666
- Dlx1 and Dlx2 function both downstream of ATOH7 and in parallel, but cooperative, pathways that involve regulation of Brn3b expression to determine retinal ganglion cell fate. PMID: 28356311
- Dlx1 specifically suppresses Npn-2 and PAK3 and induces characteristic morphology of interneuron dendrites. PMID: 24236816
- despite their redundant properties, Gsx1 and -2 have distinct interactions with Dlx1 and -2 PMID: 23042297
- Mice devoid of Dlx1as RNA are viable and fertile, and display a mild skeletal and neurological phenotype of a Dlx1 gain-of function phenotype, suggesting a role for this non-coding antisense RNA in modulating Dlx1 transcript levels and stability PMID: 23415800
- The functions of Dlx1 and Dlx2 are crucial for the initial formation of the posterior palatal shelves, and that the Dlx genes lie upstream of multiple signaling molecules and transcription factors important for later stages of palatogenesis. PMID: 22972697
- mice with a conditional deletion of Dlx1 have a chronic reduction in inhibition that reduces receptive field size in mouse auditory cortex PMID: 22753490
- A subtype-specific reduction of interneurons, particularly in the superficial layers, is found in the visual cortex of Dlx1 mutant mice; however, there is no evidence for altered properties of thalamic relay to visual cortex in Dlx1 mutant mice. PMID: 21666125
- Voltage-clamp recordings of interneurons in hippocampal slices prepared from Dlx1-deficient animals older than postnatal day 30 reveal significant reduction in excitatory postsynaptic current amplitude. PMID: 21325686
- Brn-3b suppresses the role of DLX1/2 through physical interaction and biases the competent precursors toward retinal ganglion cell fates. PMID: 21875655
- While Mash1 is required for early neurogenesis (E10.5), Dlx1 and Dlx2 are required to downregulate Notch signaling during specification and differentiation steps of 'late' progenitors (P3). PMID: 12397111
- Dlx1 has a role in deteriming mouse basal ganglia and neocortex axonal development PMID: 12421703
- Cross-talk between Msx/Dlx homeobox genes and vitamin D during tooth mineralization. Msx2 overexpression and vitamin D addition inhibited osteocalcin expression in immortalized MO6-G3 odontoblasts. PMID: 12489206
- Dlx-1 does not play a direct role in dopamine phenotypic differentiation and tyrosine hydroxylase gene regulation in adult olfactory bulb. Widespread expression of Dlx in adult brains suggests these genes may have additional roles in mature animals. PMID: 12722102
- genes act as forebrain-specific factors linking general neuron-inducing signals to region-specific neuron differentiation programs. PMID: 12799141
- The gene expresssion profile of Dlx1 mutant subpallium was studied at different embryonic days. PMID: 15376329
- early-born RGCs are Dlx1 and Dlx2 independent, but Dlx function is necessary for terminal differentiation of late-born retinal ganglion cell progenitors PMID: 15604100
- MSX and DLX have roles in contributing to spatiotemporal regulation of GnRH transcription during development PMID: 15743757
- Dlx1 mutant mice show generalized electrographic seizures and histological evidence of seizure-induced reorganization, linking the Dlx1 mutation to delayed-onset epilepsy associated with interneuron loss. PMID: 16007083
- DLX1 or DLX2 can function as transcriptional repressors PMID: 17259176
- Dlx-1 and -2 regulate parallel molecular pathways that are required for the generation of olfactory bulb interneurons. PMID: 17376983
- Analyses of protein-DNA interactions provide evidence of a direct role for MASH1 in Dlx1/2 regulation in the forebrain. PMID: 17409112
- These data suggest that interneuron subtypes use distinct combinations of Dlx1/Dlx2 enhancers from the time they are specified through adulthood. PMID: 17494687
- Dlx1 is required for coordinating programs of neurite maturation and migration. PMID: 17582329
- Dlx1&2 negatively regulate Olig2-dependant oligodendrocyte precursor cell formation. Role for Dlx genes as modulators of neuron versus oligodendrocyte development in ventral embryonic forebrain. PMID: 17678855
- DLX proteins the potential to stimulate osteoblastic differentiation and may compensate for the absence of this protein to produce normal osteoblastic differentiation in knockout mice. PMID: 18280462
- Data show that Cre-recombinase is active in a "Dlx-pattern" in the embryonic forebrain of transgenic mice, and suggest that both I12b and URE2 are direct targets of DLX2 and require Dlx1 and Dlx2 expression for proper activity. PMID: 19026749
- Results identify Dlx-dependent and Dlx-independent pathways, and show that the Dlx-independent pathway depends in part on the function of the Mash1 b-HLH transcription factor. PMID: 19030180
- These analyses define core transcriptional components that differentially specify the identity and differentiation of the globus pallidus, basal telencephalon, and pallial interneurons. PMID: 19386638
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:Distal-less homeobox family
-
组织特异性:Expressed in a restricted region of the developing brain, within the diencephalon and the adjacent telencephalic regions.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:13390
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000042413
UniGene: Mm.475101
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human IGF-like family receptor 1 (IGFLR1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
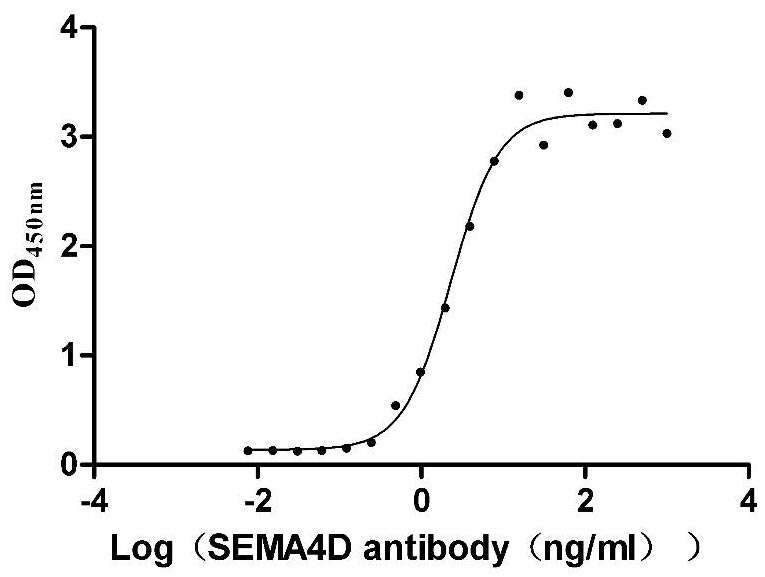
Recombinant Macaca mulatta Semaphorin-4D isoform 1 (SEMA4D), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque)
-
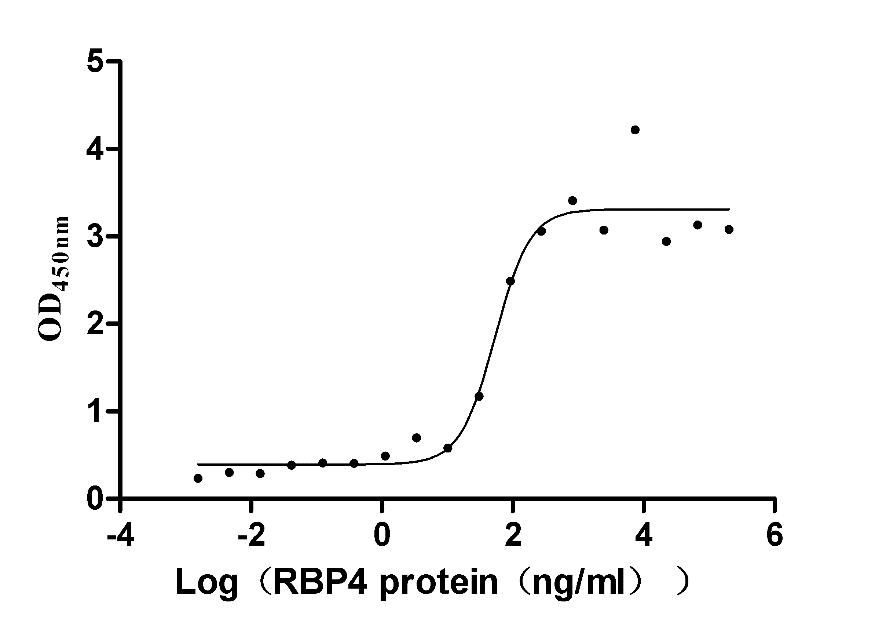
Recombinant Mouse Retinol-binding protein 4 (Rbp4) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Claudin (CLDN18)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human Dickkopf-related protein 1 (DKK1) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
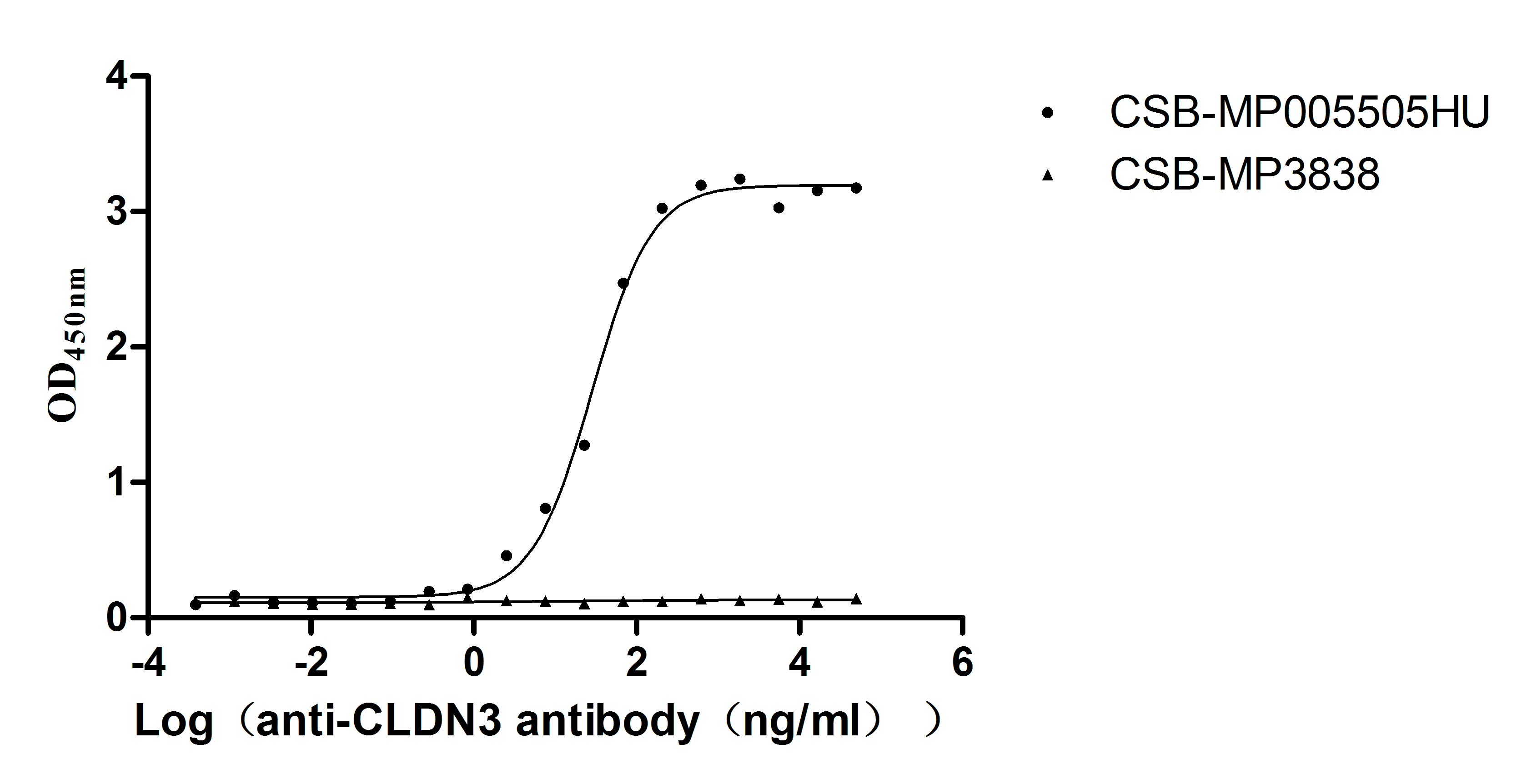
Recombinant Human Claudin-3 (CLDN3)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
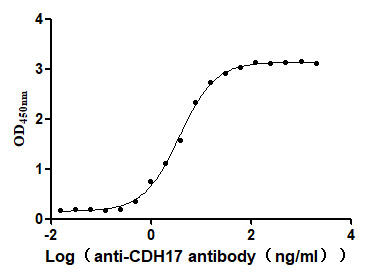
Recombinant Human Cadherin-17 (CDH17), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (CRTAM), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)



-AC1.jpg)