Recombinant Mouse Insulin-1 (Ins1)
In Stock-
货号:CSB-EP355623MO
-
规格:¥2328
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:Greater than 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
基因名:Ins1
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Ins1; Ins-1; Insulin-1 [Cleaved into: Insulin-1 B chain; Insulin-1 A chain]
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length of Mature Protein
-
来源:E.coli
-
分子量:14.5kDa
-
表达区域:25-108aa
-
氨基酸序列FVKQHLCGPHLVEALYLVCGERGFFYTPKSRREVEDPQVEQLELGGSPGDLQTLALEVARQKRGIVDQCCTSICSLYQLENYCN
Note: The complete sequence including tag sequence, target protein sequence and linker sequence could be provided upon request. -
蛋白标签:N-terminal 10xHis-tagged and C-terminal Myc-tagged
-
产品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:Tris-based buffer,50% glycerol
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:3-7 business days
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Insulin decreases blood glucose concentration. It increases cell permeability to monosaccharides, amino acids and fatty acids. It accelerates glycolysis, the pentose phosphate cycle, and glycogen synthesis in liver.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Impairment in the insulin-Snail1 axis may contribute to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in obesity. PMID: 30013137
- Feeding of high fat diet leads to impairment of brain insulin signaling linked with neuroinflammation. Insulin resistance due to high fat diet associated with biochemical changes in markers related with Alzheimer disease pathology. PMID: 27771511
- High INS1 expression is associated with weight gain and obesity. PMID: 29122848
- psychological stress impairs insulin signaling and results in hippocampal deficits. PMID: 29970188
- Our data shed light on the putative role of Kv1.3 in weight gain and insulin-dependent responses contributing to knowledge about adipocyte physiology. PMID: 29947924
- Data suggest that hybrid insulin peptides (HIPs), formed in insulin-secreting-cells by fusion of insulin C-peptide fragments to peptide fragments of chromogranin A or islet amyloid polypeptide, and reactivity of CD4+-T-lymphocytes to HIPs may act as biomarkers of autoimmunity in type 1 diabetes. PMID: 29976617
- Our findings, focusing on energy balance, provide a mechanistic understanding of the promising effect of early insulin initiation on lipotoxicity. Insulin, by recovering UCP3 activity, alleviated energy surfeit and potentiated AMPK-mediated lipid homeostasis in skeletal muscle cells following exposure to PA and in gastrocnemius of mice fed HFD. PMID: 29039450
- In the present study, the mRNA expression of the two mouse insulin genes Ins1 and Ins2 was investigated in MIN6 cells treated with different concentrations of melatonin, and insulin secretion was detected under the same conditions. Following the overexpression or silencing of MTNR1B, the activities of components of the MAPK signaling pathway PMID: 29207116
- diabetic gastroparesis was an aggressive process due to the successive damages of myenteric cholinergic neurones and ICC by impairing the insulin/InsR and IGF-1/IGF-1R signaling. Insulin therapy in the early stage may delay diabetic gastroparesis PMID: 28931726
- nNOS mediates insulin- and oxidative stress-induced glucose uptake in skeletal muscle myotubes. PMID: 28666850
- Data (including data from studies using knockout mice) suggest that Ins1 and Ins2 are required for pancreatic beta-cell maturation; thus, Ins1 and Ins2 are needed for normal beta-cell development and for maintenance of normal beta-cell function. PMID: 29029025
- Despite higher endogenous insulin concentrations following feeding, arcuate nucleus phosphorylation of Akt (pAkt) levels were significantly lower in the pregnant group compared with the nonpregnant group. PMID: 29029017
- Our current results reinforce the notion that the AT2R has a physiological role in the conservation of insulin action PMID: 27979738
- E4-ORF1 activation of PI3K in adipocytes recapitulates insulin regulation of FoxO1 but not regulation of Glut4. This uncoupling of PI3K effects occurs despite E4-ORF1 activating PI3K and downstream signaling to levels achieved by insulin PMID: 28009298
- These data support a role for islet NGF in fine-tuning insulin secretion. PMID: 27424144
- PDX1 and ISL1 regulation of insulin gene expression in pancreatic beta cells, was investigated. PMID: 26994512
- insulin and aPC converge on a common spliced-X-box binding protein-1 (sXBP1) signaling pathway to maintain endoplasmic reticulum (ER) homeostasis. PMID: 28687614
- Insulin stimulation of Akt1 and Akt2 signaling in Cystic fibrosis airway cells was diminished compared with that observed in airway cells expressing wild-type CFTR. PMID: 28213469
- These data implicate the insulin-FoxM1/PLK1/CENP-A pathway-regulated mitotic cell-cycle progression as an essential component in the beta cell adaptation to delay and/or prevent progression to diabetes. PMID: 28286049
- Rac1 activation is caused by membrane translocation of a guanine nucleotide exchange factor FLJ00068 in Akt2-mediated insulin signaling in mouse skeletal muscle. PMID: 27163697
- Netrin-1 enhanced insulin secretion by promoting beta-cell Ca(2+) influx and cAMP production. PMID: 27520508
- This study identifies AR as a novel receptor that enhances beta cell function. PMID: 27133133
- The effects were abolished by using pharmacological inhibition of PI3K/Akt with LY294002 and paralleled by transfecting DCs with klotho siRNA. In conclusion, the regulation of klotho sensitive DC function by IGF-1 or insulin is mediated through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in BMDCs. PMID: 27808000
- Overexpression of either ca-Nfatc2 or ca-Nfatc1 in mouse islets enhanced insulin secretion, whereas only ca-Nfatc2 was able to promote b-cell proliferation, suggesting distinct molecular pathways mediating insulin secretion vs. b-cell proliferation are regulated by NFAT PMID: 27935966
- BMP-7 therefore is an attractive candidate for tackling a multifaceted disease such as diabetes, since it not only reduces body fat, but also strengthens insulin signaling, causing improved glucose uptake and ameliorating peripheral insulin resistance. PMID: 28186649
- these findings demonstrate, for the first time, that miR-155 is a positive regulator of insulin sensitivity with potential applications for diabetes treatment. PMID: 27711113
- Maternal chromium restriction leads to glucose metabolism imbalance in mice offspring through insulin signaling and Wnt signaling pathways. PMID: 27782077
- Hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia blunts the Insulin-Inpp5f negative feedback loop in the diabetic heart. PMID: 26908121
- Data suggest that resveratrol acts on differentiating preadipocytes by inhibiting insulin signaling, mitochondrial biogenesis, and lipogenesis. PMID: 26968895
- elevating nuclear O-GlcNAc increases intracellular insulin levels and preserves glucose-stimulated insulin secretion during chronic hyperglycemia PMID: 26598517
- Data (including data from studies in knockout/transgenic mice) suggest INS is required for lipogenic effects of activation of LXRalpha in liver; INS is not required to down-regulate gene expression in ER stress or inflammation (as seen in diabetes). PMID: 26511317
- the insulin-InsR signaling drives multipotent progenitors differentiation into lymphoid lineages in early lymphopoiesis. PMID: 26573296
- The target miRNAs are closely associated with dysregulation of insulin/PI3K-AKT signaling, suggesting that the Cmah-null mice could be a useful model for studying diabetes. PMID: 25243123
- the inhibitory effect of CRFR2 signaling on insulin action is mediated by cAMP in a mammalian target of rapamycin-dependent manner. PMID: 25875045
- This study discloses age-dependent changes in insulin CSF/serum ratios in humans. In the elderly, cerebral insulin resistance might be partially attributed to an impaired transport of insulin into the central nervous system PMID: 25965336
- adiponectin. Taken together, our results show that adiponectin is stored in a unique vesicular compartment, and released through a regulated exocytosis pathway that is dependent on insulin signalling. PMID: 26330614
- LKB1 is essential for mitochondrial maintenance and negatively regulates a distal step of insulin secretion. PMID: 26139601
- ubiquitin-like protein 4A (Ubl4A) plays a crucial role in insulin-induced Akt plasma membrane translocation. PMID: 26195787
- synaptotagmin-7 is directly activated by GLP-1 signaling and may serve as a drug target for boosting insulin secretion. PMID: 26216970
- The paracrine actions of Ucn3 activate a negative feedback loop that promotes somatostatin release to ensure the timely reduction of insulin secretion upon normalization of plasma glucose. PMID: 26076035
- Tcf7l2 is regulating proinsulin expression directly via Isl1, Ins1 and indirectly via MafA, NeuroD1 and Pdx1. PMID: 25015099
- elevated adiponectin levels improve systemic lipid metabolism in the near absence of insulin. PMID: 25339419
- the RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway is involved in insulin release through the up-regulation of Cx36 expression in 3D-cultured MIN6 cells. PMID: 25129107
- Analyzed was insulin translation in islets and in INS-1 cells. Insulin translational levels were significantly increased in islets of mice fed a high-fat diet to meet systemic demand, without altering its transcriptional levels. PMID: 25686499
- Data indicate that Src homology-2 domain containing protein B (SHB) deficiency causes a chronic increase in beta-cell focal adhesion kinase (FAK) activity that perturbs the normal insulin secretory characteristics of beta-cells. PMID: 25274988
- The activation of Cav-1 during the adipocyte differentiation process could facilitate the maintenance of insulin sensitivity by mature adipocytes isolated from additional external stimuli. PMID: 24751908
- GX sPLA2 negatively regulated pancreatic insulin secretion by augmenting COX-2-dependent PGE2 production. PMID: 25122761
- Diet-induced obesity mice exhibited significant increases in body weight, plasma glucose, insulin, and IGF1. PMID: 24914941
- The over-expression of miR-200a in the hypothalamus of obese mice is linked to leptin and insulin signaling impairment. PMID: 24394757
- Mouse Ins2 and Ins1 promoters were transiently activated in mouse fetal hepatocytes of embryonic days 13.5 and 16.5, respectively. PMID: 24258027
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Secreted.
-
蛋白家族:Insulin family
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:16333
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000049095
UniGene: Mm.46269
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Mouse GDNF family receptor alpha-like (Gfral), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Dog Angiopoietin-2 (ANGPT2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris)
-
Recombinant Human Somatostatin receptor type 2 (SSTR2)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
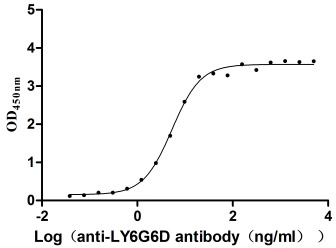
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis lymphocyte antigen 6 family member G6D (LY6G6D) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Mouse Cell adhesion molecule 1 (Cadm1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
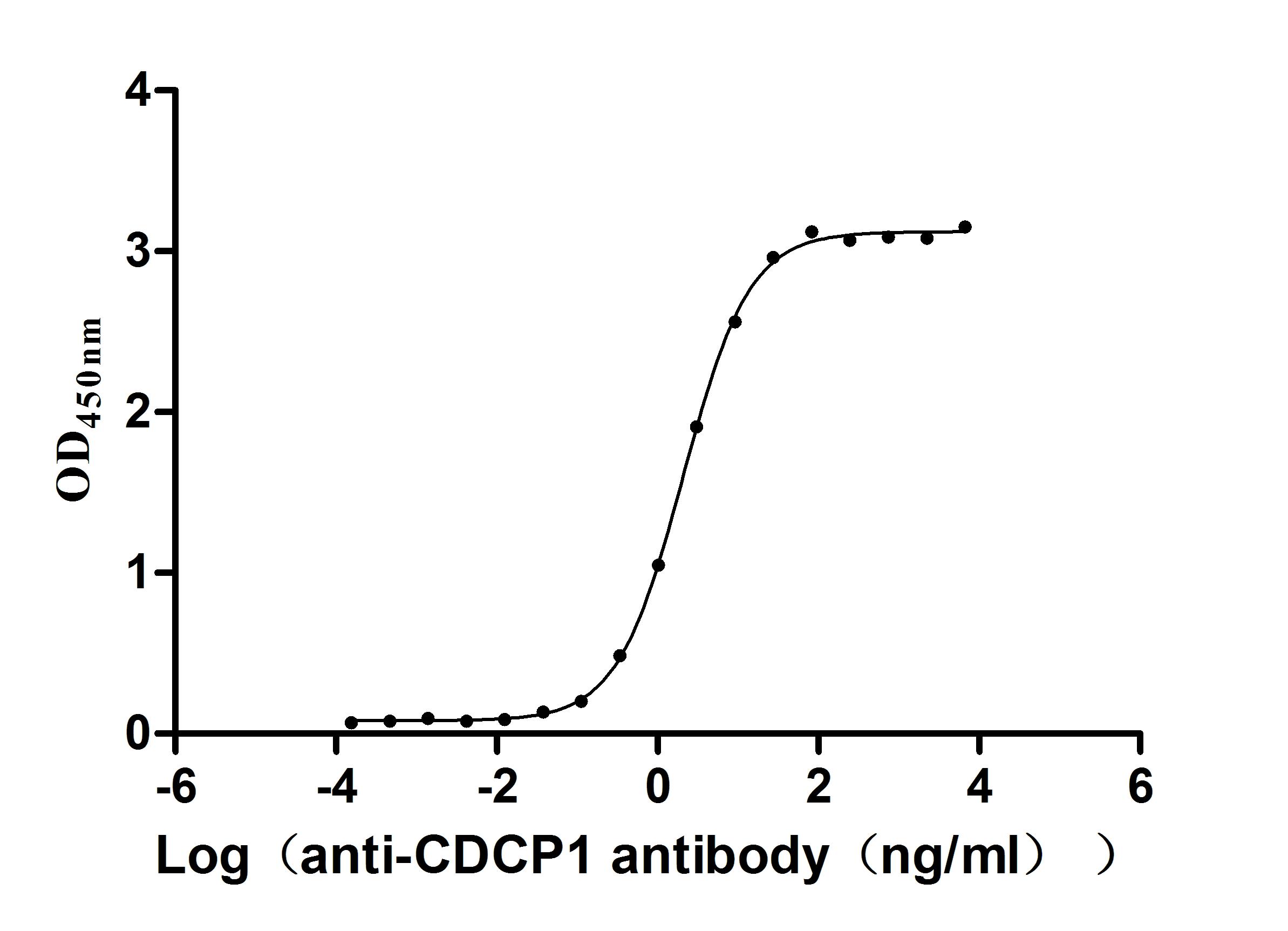
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis CUB domain containing protein 1 (CDCP1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
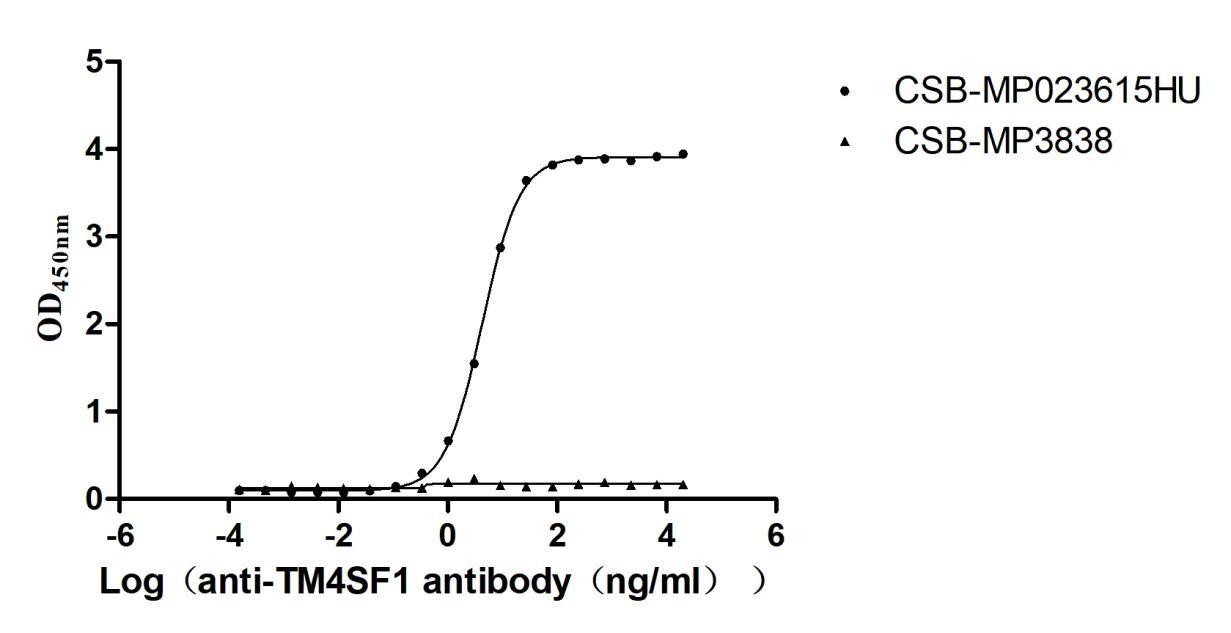
Recombinant Human Transmembrane 4 L6 family member 1(TM4SF1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)



-AC1.jpg)