Recombinant Mouse Interleukin-17 receptor A (Il17ra), partial
-
货号:CSB-YP736761MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP736761MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP736761MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP736761MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP736761MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Il17ra; Il17r; Interleukin-17 receptor A; IL-17 receptor A; IL-17RA; CD antigen CD217
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Receptor for IL17A and IL17F, major effector cytokines of innate and adaptive immune system involved in antimicrobial host defense and maintenance of tissue integrity. Receptor for IL17A. Receptor for IL17F. Binds to IL17A with higher affinity than to IL17F. Binds IL17A and IL17F homodimers as part of a heterodimeric complex with IL17RC. Also binds heterodimers formed by IL17A and IL17F as part of a heterodimeric complex with IL17RC. Cytokine binding triggers homotypic interaction of IL17RA and IL17RC chains with TRAF3IP2 adapter, leading to TRAF6-mediated activation of NF-kappa-B and MAPkinase pathways, ultimately resulting in transcriptional activation of cytokines, chemokines, antimicrobial peptides and matrix metalloproteinases, with potential strong immune inflammation. Involved in antimicrobial host defense primarily promoting neutrophil activation and recruitment at infection sites to destroy extracellular bacteria and fungi. In secondary lymphoid organs, contributes to germinal center formation by regulating the chemotactic response of B cells to CXCL12 and CXCL13, enhancing retention of B cells within the germinal centers, B cell somatic hypermutation rate and selection toward plasma cells. Plays a role in the maintenance of the integrity of epithelial barriers during homeostasis and pathogen infection. Stimulates the production of antimicrobial beta-defensins DEFB1, DEFB103A, and DEFB104A by mucosal epithelial cells, limiting the entry of microbes through the epithelial barriers. Involved in antiviral host defense through various mechanisms. Enhances immunity against West Nile virus by promoting T cell cytotoxicity. Contributes to influenza A virus (H1N1) clearance by driving the differentiation of B-1a B cells, providing for production of virus-specific IgM antibodies at first line of host defense. Receptor for IL17C as part of a heterodimeric complex with IL17RE.; (Microbial infection) Receptor for SARS coronavirus-2/SARS-CoV-2 virus protein ORF8, leading to IL17 pathway activation and an increased secretion of pro-inflammatory factors through activating NF-kappa-B signaling pathway.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Study shows that miR-215 regulates the Act1/IL-17RA pathway and represses the expression of Act1 protein in oxygen glucose deprivation/reperfusion-treated N2a cells and an middle cerebral artery occlusion mouse model of ischemic stroke. PMID: 29080697
- study provides insight regarding a novel antiviral role for IL-17A in the genital tract, in which IL-17A improves mucosal vaccination efficacy by mediating efficient Th1 cell immunity PMID: 28956763
- This study describes a previously unappreciated protective role for IL-17RA signaling in regulation of the skin barrier and maintenance of skin immune homeostasis. PMID: 28615416
- These data show that IL-17R signaling in the lung epithelium plays a critical role in establishing chemokine gradients that are essential for mucosal immunity against pulmonary bacterial pathogens. PMID: 27923703
- Thus, oral epithelial cells dominantly control IL-17R-dependent responses to oropharyngeal candidiasis through regulation of BD3 expression. PMID: 27923704
- this study showsthat the nature of the protective memory response depends closely on the route of infection and highlights the role of IFN-gamma-and IL-17RA-mediated responses in the control of mucosal infection by Brucella PMID: 27036913
- IL-17RA contributes to experimental glomerulonephritis, with IL-17RA expression on both leukocytes and stromal cells being required for the full expression of nephritogenic humoral immunity. PMID: 27941331
- genetic deletion results in earlier onset of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and worsened disease severity PMID: 26982366
- IL-17RA in non hematopoietic cells regulates recruitment of neutrophils to the lung during the adaptive phase of the immune response. PMID: 26871571
- IL-17 signaling through IL-17RA is an important driver of lung inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness. PMID: 25919006
- results suggest that the p38alpha-MKP-1 signaling axis links IL-17R signaling in tissue-resident cells to autoimmune inflammation dependent on infiltrating T(H)17 cells. PMID: 25737586
- There were no significant differences in clinical scores and numbers of infiltrating eosinophils among IL-25KO, TSLPR KO, and wild-type mice. PMID: 26244295
- promotes colorectal tumorigenesis in transformed enterocytes PMID: 25526314
- IL-17RA signaling is critical for the development of renal pathology in autoimmune glomerulonephritis.IL-17 enhanced the production of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines from tubular epithelial cells. PMID: 24935958
- Il17ra appears to be a novel modulator of monocyte phenotype and possible therapeutic target in renal fibrosis PMID: 24454873
- IL-17 expression is higher in C57BL/6 versus BALB/c cornea after infection and that the latter group has more MerTK+ cells. PMID: 25298414
- It was concluded that TLR signaling can directly stimulate the expression of IL-17RA, but not IL-17RC, in neuroglial cells, which functionally respond to IL-17A by secreting chemokines, and accelerating CD4 cell migration. PMID: 25076485
- Absence of IL-17RA leads to a Th2-like phenotype characterized by IL-4 production and suggests that IL-17RA signaling plays a critical role in the regulation of IL-4 in collagen-induced arthritis and development of autoimmune inflammation of the joint. PMID: 24504806
- IL-17RA is essential for optimal localization of follicular Th cells in the germinal center light zone to promote autoantibody-producing B cells. PMID: 23858031
- IL-17RA KO mice have a failure of resolution of inflammation. IL-17RA protects against infection-induced periapical inflammation & bone destruction via suppression of neutrophil & mononuclear inflammation. PMID: 23863904
- IL-17A receptor signaling regulates bacterial clearance as well as natural killer T (NKT) cell and gammadelta T cell infiltrates during Staphylococcus aureus-induced brain abscess formation. PMID: 22704602
- These data demonstrate PI3Kgamma-dependent signalling downstream of IL-17RA, which plays a pivotal role in regulating IL-17 production in T cells. PMID: 22930133
- IL-17RA signaling modulates IFN-gamma-mediated inflammatory responses during infections and recruitment of suppressive IL-10-producing neutrophils. PMID: 22577359
- Data show that deletion of the CC' loop from Act1 or IL-17RA abolished the interaction between both proteins. PMID: 22045852
- IL-17RA signaling plays a role as an amplifier of the effector phase of inflammatory arthritis PMID: 22028860
- mRNA levels of IL-17, IL-17R and MMP-9 were also higher in the invasive group than in the non-invasive group in human pituitary adenomas. PMID: 21279695
- TRAF3 is a negative regulator of IL-17R proximal signaling. PMID: 21078888
- an extended SEFIR domain is required for il-17RA-mediated signal transduction. PMID: 20729198
- Oral Toxoplasma gondii infection increases IL-17 expression via IL17RA and contributes to the inflammatory response, and IL-17 neutralization has a partial protective effect against fatal Toxoplasma gondii-associated inflammation. PMID: 20575661
- mouse IL-17Receptor may belong to a novel growth-receptor like molecule that has the capability to support cellular mitogenesis through RAS/MAPK pathway. PMID: 16310341
- In the absence of ligand, IL-17RA molecules exhibited significant specific FRET efficiency, demonstrating that they exist in a multimeric, preformed receptor complex. PMID: 16393951
- The biologic activity of IL-17 is dependent on a complex composed of receptors IL-17RA and IL-17RC. PMID: 16785495
- structure-function analysis of a IL-17 superfamily receptor reveals important differences in IL-17RA compared with IL-1/TLR receptors PMID: 17456598
- This study demonstrates a gender-dependent effect of IL-17 signaling and indicates that gender differences should be taken into account in the preclinical and clinical safety testing of anti-IL-17 biologic therapies. PMID: 18591228
- IL-17A controls the expansion of IL-17A-producing neutrophil-regulatory T cell populations through IL-17R PMID: 18606690
- IL-17F/IL-17R interaction stimulates granulopoiesis in mice. PMID: 18723265
- IL-25-mediated activities require both IL-17RB and IL-17RA in this example of an IL-17 family ligand that utilizes a heteromeric receptor complex. PMID: 18768888
- A role is supported for IL-17RA-independent mechanisms in the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. PMID: 19234160
- IL-17RA expression is significantly increased in the central nervous system of mice with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis compared to healthy mice PMID: 19400960
- our data suggest an important role for IL-17A-expressing T lymphocytes in eliminating Bacillus subtilis PMID: 19414809
- IL-17R-deficient mice, subjected to cecal ligation and puncture-induced non-severe sepsis PMID: 19494309
- signaling via the IL-17 receptor in bone marrow derived cells enhances the process of atherosclerosis. PMID: 19660432
- In contrast to many chronic inflammatory diseases in which IL-17RA signaling promotes an inflammatory response, IL-17RA signaling down-regulates the chronic mononuclear inflammation elicited by Helicobacter pylori infection. PMID: 19812196
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein.
-
组织特异性:Widely expressed. Highly expressed in T cells and macrophages. Highly expressed in B-1a B cells and at a lower extent in B-1b and B-2 B cells (at protein level).
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:16172
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000002976
UniGene: Mm.4481
Most popular with customers
-
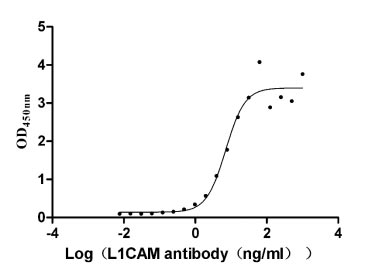
Recombinant Human Neural cell adhesion molecule L1 (L1CAM), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Glypican-3 (GPC3) (G537R), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
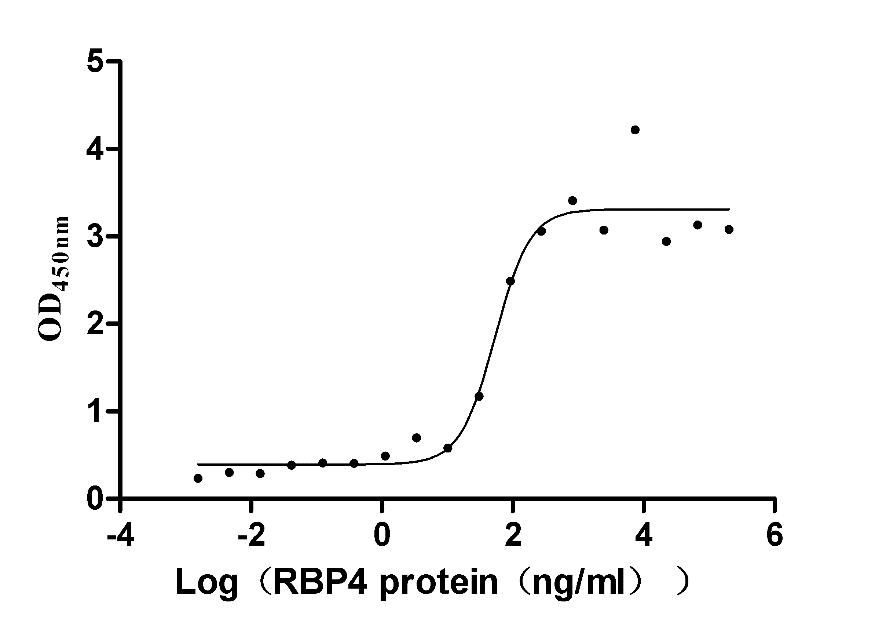
Recombinant Mouse Retinol-binding protein 4 (Rbp4) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
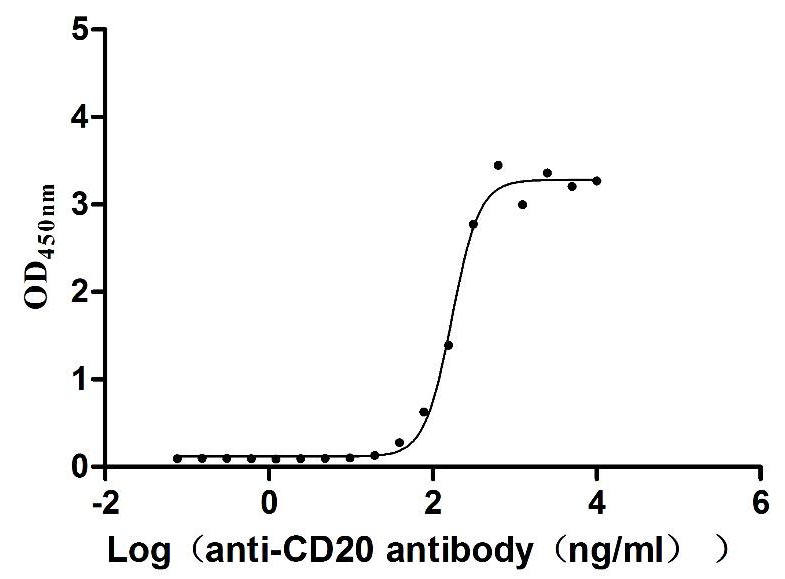
Recombinant Dog B-lymphocyte antigen CD20 (MS4A1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris)
-
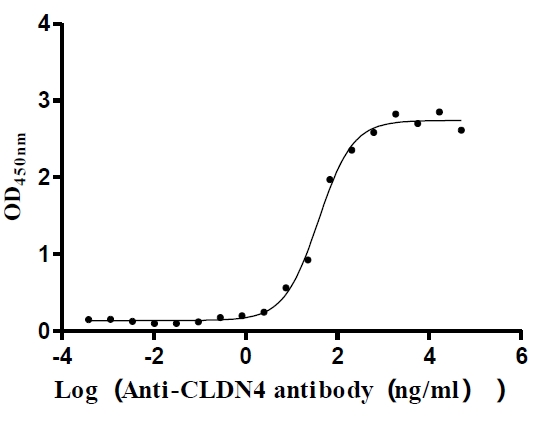
Recombinant Human Claudin-4 (CLDN4)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (CRTAM), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
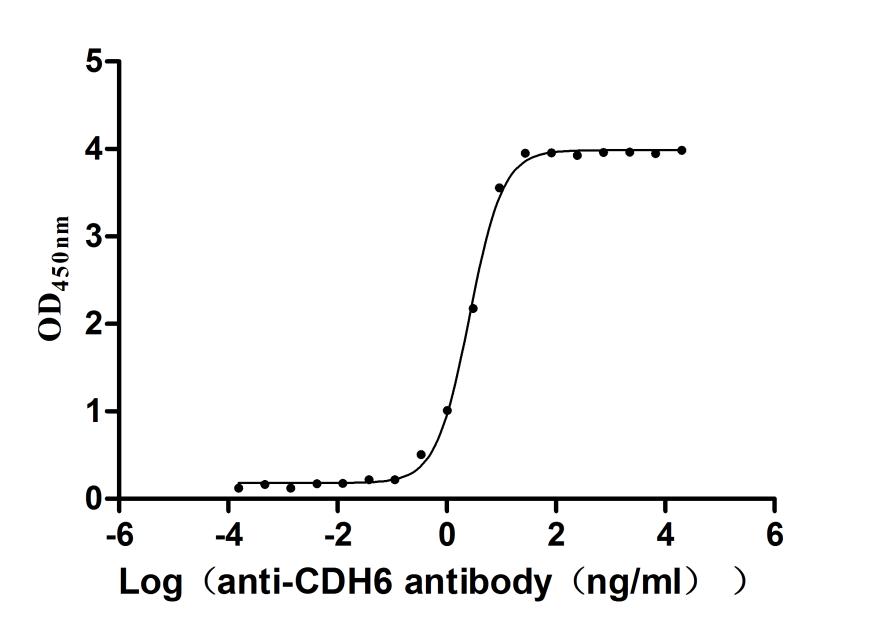
Recombinant Human Cadherin-6(CDH6),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
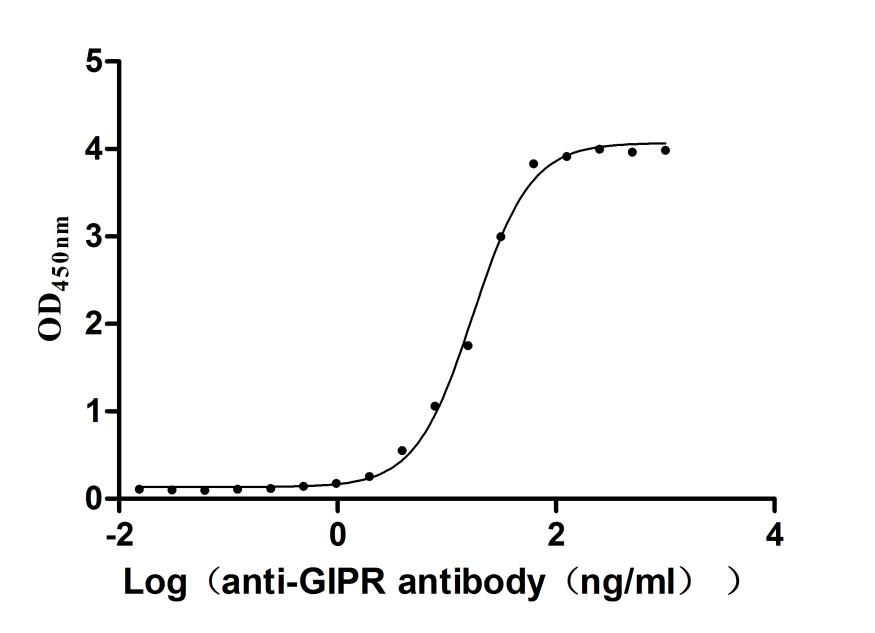
Recombinant Human Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor(GIPR),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)