Recombinant Mouse Lymphocyte cytosolic protein 2 (Lcp2)
-
货号:CSB-YP723341MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP723341MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP723341MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP723341MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP723341MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
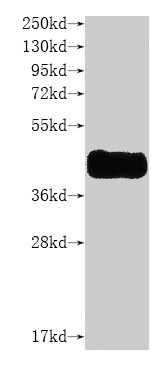
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Lcp2; Lymphocyte cytosolic protein 2; SH2 domain-containing leukocyte protein of 76 kDa; SLP-76 tyrosine phosphoprotein; SLP76
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:full length protein
-
表达区域:1-533
-
氨基酸序列MALKNVPFRS EVLAWNSDNL ADYFRKLNYR DCEKAVKKYH IDGARFLNLT ENDIQKFPKL RMPLLSKLSQ DINKNEERRS IFTRKPQIPR FLEETESHEE DDGGWSSFED DYESPNDDDP DGEDDGDYES PNEEEQALVD DAADYEPPPS NNEEALQSSI LPPNSFHNTN SMYIDRPPTG KVSQQPPVPP LRPKPALPPL PTGRNHSPLS PPHPNHEEPS RSGNNKTAKL PAPSIDRSTK PPLDRSLAPL DREPFILGKK PPFSDKPSAP LGREHLPKIQ KPPLPPAMDR HERNERLGPV TTRKPPVPRH GRGPDRREND EDDVHQRPLP QPSLPSMSSN TFPSRSVQPS SKNTFPLAHM PGAFSESNIG FQQSASLPPY FSQGPGNRPP LRSEGRNLPL PVPNRPQPPS PGEEETPLDE EWYVSYITRP EAEAALRKIN QDGTFLVRDS SKKTANNPYV LMVLYKDKVY NIQIRYQEES QVYLLGTGLR GKEDFLSVSD IIDYFRKMPL LLIDGKNRGS RYQCTLTHAA GCL
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Involved in T-cell antigen receptor mediated signaling.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Biochemical analyses revealed that mutant T cells were hypersensitive to TCR stimulation. Indeed, phosphorylation of several signaling proteins, including SLP76 itself, phospholipase Cgamma1 and the protein kinases AKT and ERK1/2, was increased PMID: 28107427
- slp-76 contributes to the regulation of the tissue distribution, PLZF, and cytokine expression of iNKT cells via ADAP-dependent and -independent mechanisms. PMID: 27349342
- findings identify ACK1 as a novel SLP-76-associated protein-tyrosine kinase that modulates early activation events in T cells. PMID: 28188290
- immune cell adaptor SLP-76 binds directly to SUMO-RanGAP1 of cytoplasmic fibrils of the nuclear pore complex, and this interaction is needed for optimal NFATc1 and NF-kappaB p65 nuclear entry in T cells PMID: 26321253
- these studies establish Slp-76 as a critical determinant of NK-cell development and NK cell mediated elimination of missing-self target cells in mice PMID: 25929249
- Data show that a splice variant of SLP-76 signal transducing adaptor protein (SLP-76 or Lcp2) reduced the amount of SLP-76 protein by ~90%, disrupting immunogenic and tolerogenic pathways to different degrees. PMID: 25662996
- A yopH mutant survived better in the absence of neutrophils, indicating that neutrophil inactivation by YopH by targeting PRAM-1/SKAP-HOM and SLP-76/Vav/PLCgamma2 signaling hubs may be critical for Yersinia survival. PMID: 24034616
- analysis of a costimulatory mechanism by which CXCL12 and antigen converge at SLP-76 microcluster formation to enhance T cell responses PMID: 23901140
- These findings reveal a novel role for SLP-76 in CXCR4-mediated T lymphocyte trafficking. PMID: 22806433
- a novel regulation mechanism of SLP-76 by ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of activated SLP-76, which is mediated by Ser-376 phosphorylation, leading to down-regulation of TCR signaling. PMID: 22902619
- Loss of SLP-76 has no effect on persistence of the antigen-specific CD4+ memory pool, suggesting that homeostatic turnover is not required for persistence of this population. PMID: 22956580
- SLP-76 and ADAP are involved in E-selectin-mediated integrin activation and neutrophil recruitment to inflamed kidneys, which may underlie the development of life-threatening ischemia-reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury in humans. PMID: 22291096
- Data show that development of the CD8+ ILLs present in SH2 domain-containing leukocyte protein, 76-kDa Y145F mice require Eomes and PLZF. PMID: 21383242
- Loss of Lcp2 leads to loss of tonic T-cell receptor signals altering the rate of memory versus effector cell differentiation independent of initial T-cell expansion. PMID: 20847203
- Loss of Lcp2 leads to loss of tonic T-cell receptor signals altering the generation but not the persistence of CD8+ memory T cells. PMID: 20884806
- HPK1 competes with ADAP for SLP-76 binding and via Rap1 negatively affects T-cell adhesion. PMID: 20957749
- A nonhemostatic pathway in which platelet CLEC-2 receptors bind lymphatic endothelial PDPN and activate SLP-76 signaling to regulate embryonic vascular development. PMID: 20363774
- Mice bearing membrane-targeted SLP-76 (MTS) have a partial T-cell lymphopenia and impaired signaling though the mature T-cell receptor. PMID: 20029045
- Deletion of SLP-76 in polyclonal memory CD4 T cells leads to impaired steady-state homeostasis as well as impaired homeostatic responses to IL-7. PMID: 20080760
- Differential role of SLP-76 domains in T cell development and function. PMID: 11792851
- SLP-76 is required for signaling via the T cell antigen receptor (TCR) and pre-TCR. Platelet activation downstream of GPVI and alphaIIbbeta3 shows a dependency on SLP-76 PMID: 11901197
- role of the adapter protein in GPVI-dependent platelet procoagulant responses to collagen PMID: 12351393
- results support a non-cell-autonomous mechanism in which SLP-76 and Syk signals are required in circulating cells to regulate separation of blood and lymphatic vascular networks PMID: 12522250
- Structural requirements of SLP-76 in signaling via the high-affinity immunoglobulin E receptor (Fc epsilon RI) in mast cells were elucidated PMID: 12640123
- Study provides the first data to address the mechanisms controlling SLP-76 transcription by providing evidence for several key cis-regulatory elements in the promoter region. PMID: 14662865
- bone marrow-derived macrophages mice lacking both SLP-76 and SLP-65 demonstrated normal FcgammaR-mediated activation PMID: 14694181
- N-terminal tyrosines as well as the central proline-rich region of SLP-76 are required for participation of SLP-76 in FcepsilonRI-mediated signaling and function. PMID: 15153494
- Results describe the effect of c-Cbl inactivation in mice deficient in the scaffolding molecule SLP-76. PMID: 15238603
- ADAP-SLP-76 binding as a signaling event that differentially regulates SMAC formation, and support a role for SMAC formation in T cell cytokine production. PMID: 15477347
- Tyr(145) of SLP-76 is the most critical tyrosine for both T cell function in vitro and T cell development in vivo PMID: 16456002
- Both SH2 domains and the kinase domain of Syk are required for immunoreceptor-dependent signaling and cellular response via integrins. The Gads-binding domain of SLP-76 is needed for immunoreceptor signaling, but dispensable for integrin signaling. PMID: 16943434
- Mouse embryos lacking Syk and Slp-76 develop abnormal blood-lymphatic endothelial connections. Expression of GFPSlp-76 rescues this phenotype, and that deficient cells confer focal vascular phenotypes in chimeric embryos. PMID: 16950126
- SLP-76-deficient BMDCs adhere poorly to fibronectin, suggesting impaired integrin function and manifest signaling defects following integrin ligation, including reduced global tyrosine phosphorylation and markedly impaired phosphorylation of p44/42 MAPK PMID: 17015703
- These data suggest that disruption of integrin signaling via loss of SLP-76 expression differentially impairs neutrophil functions in vivo. PMID: 17372019
- Low SLP-76 expression correlated with reduced CD5 on immature thymocytes & reduced TCR signaling potential. Maintenance of sufficient SLP-76 expression from the endogenous locus is a key element in the thymic selection process. PMID: 17965338
- SLP-76 acts as a dominant positive regulator for both NKG2D-mediated and YAC-1 cell-triggered IFN-gamma production PMID: 18203684
- N-terminal tyrosines of SLP76 are required for thymocyte selection but can function on separate molecules to support TCR signaling PMID: 18342008
- Using genetic complementation, all three phosphorylatable tyrosines are required within the same SLP76 molecule to support platelet activation by GPVI. PMID: 18663126
- Cbl suppresses activation of a bypass signaling pathway and thereby enforces SLP76 dependence of early T cell development. PMID: 19074136
- Fixed localization of SLP-76 reveals different requirements for subcellular localization of signal complexes downstream of the pre-T cell receptor (TCR) versus mature TCR; signaling requirements via pre-TCR and mature TCR overlap but are not identical. PMID: 19380761
- the sterile-alpha motif (SAM) domain is indispensable for optimal SLP-76 signaling PMID: 19401562
- SLP-76 is the dominant SLP family member in the osteoclast bone resorptive process cytoskeletal organization. SLP-76 is phosphorylated in a Syk-dependent manner PMID: 19592646
- Y145 is the most critical tyrosine supporting SLP-76 function in myeloid cells. PMID: 19895996
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm.
-
组织特异性:Highly expressed in spleen, thymus, and peripheral blood leukocytes.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:16822
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000126796
UniGene: Mm.265350
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Neural cell adhesion molecule L1 (L1CAM), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Intestinal-type alkaline phosphatase (ALPI) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Claudin-6 (CLDN6)-VLPs, Fluorescent (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 8 (CCR8)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
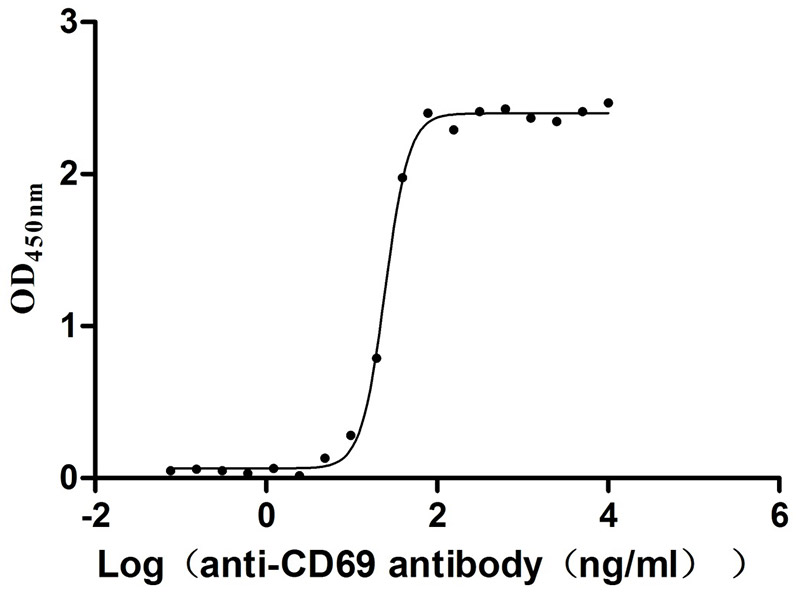
Recombinant Human Early activation antigen CD69 (CD69), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Cell adhesion molecule 1 (CADM1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
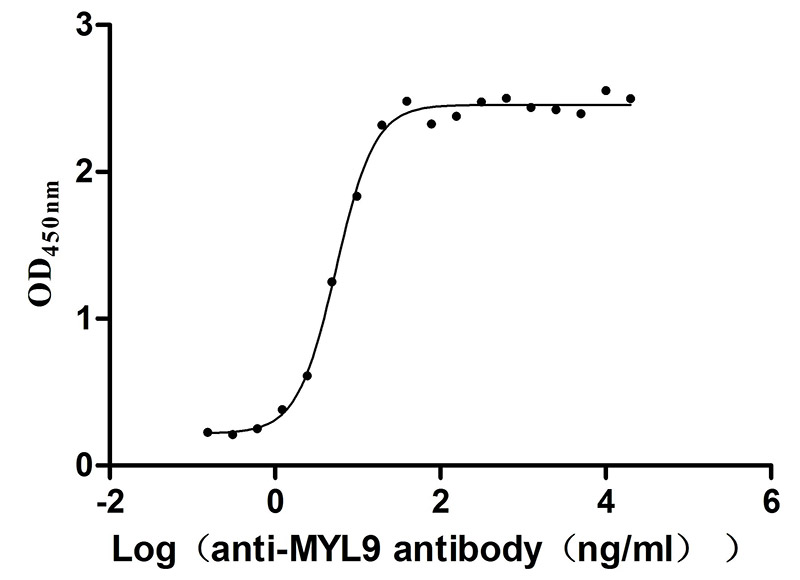
Recombinant Human Myosin regulatory light polypeptide 9 (MYL9) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)



f4-AC1.jpg)