Recombinant Mouse Moesin (Msn)
-
中文名称:小鼠Msn重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP015048MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Msn重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP015048MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Msn重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP015048MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Msn重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP015048MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Msn重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP015048MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Msn; Moesin; Membrane-organizing extension spike protein
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length of Mature Protein
-
表达区域:2-577
-
氨基酸序列PKTISVRVT TMDAELEFAI QPNTTGKQLF DQVVKTIGLR EVWFFGLQYQ DTKAFSTWLK LNKKVTAQDV RKESPLLFKF RAKFYPEDVS EELIQDITQR LFFLQVKEGI LNDDIYCPPE TAVLLASYAV QSKYGDFNKE VHKSGYLAGD KLLPQRVLEQ HKLNKDQWEE RIQVWHEEHR GMLREDAVLE YLKIAQDLEM YGVNYFSIKN KKGSELWLGV DALGLNIYEQ NDRLTPKIGF PWSEIRNISF NDKKFVIKPI DKKAPDFVFY APRLRINKRI LALCMGNHEL YMRRRKPDTI EVQQMKAQAR EEKHQKQMER ALLENEKKKR ELAEKEKEKI EREKEELMEK LKQIEEQTKK AQQELEEQTR RALELEQERK RAQSEAEKLA KERQEAEEAK EALLQASRDQ KKTQEQLASE MAELTARISQ LEMARKKKES EAVEWQQKAQ MVQEDLEKTR AELKTAMSTP HVAEPAENEH DEQDENGAEA SAELRADAMA KDRSEEERTT EAEKNERVQK HLKALTSELA NARDESKKTA NDMIHAENMR LGRDKYKTLR QIRQGNTKQR IDEFESM
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Ezrin-radixin-moesin (ERM) family protein that connects the actin cytoskeleton to the plasma membrane and thereby regulates the structure and function of specific domains of the cell cortex. Tethers actin filaments by oscillating between a resting and an activated state providing transient interactions between moesin and the actin cytoskeleton. Once phosphorylated on its C-terminal threonine, moesin is activated leading to interaction with F-actin and cytoskeletal rearrangement. These rearrangements regulate many cellular processes, including cell shape determination, membrane transport, and signal transduction. The role of moesin is particularly important in immunity acting on both T and B-cells homeostasis and self-tolerance, regulating lymphocyte egress from lymphoid organs. Modulates phagolysosomal biogenesis in macrophages. Participates also in immunologic synapse formation.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Collectively, these results implicate both moesin and myosin IIA in the regulation of phagolysosome biogenesis and in host defense against infections. PMID: 29247647
- these findings underscore the importance of moesin in IL-15-dependent CD8+ Treg cell homeostasis and the control of self-tolerance PMID: 28978692
- Moesin is an important regulator of the surface abundance and stability of TbetaRII and is important in facilitating the efficient generation of iTregs. PMID: 28287407
- The expression of moesin was upregulated in cardiomyocytes under inflammation, inducing protrusion formation in a phosphorylation-dependent fashion. PMID: 27342875
- These results of this study may pave the way for exploiting moesin as a novel target for intervention in muscular dystrophy. PMID: 28082118
- this study shows that low neutrophil rolling in inflamed venules was impaired in moesin-deficient mice PMID: 27131737
- High blood moesin levels were also observed in cecal ligation and puncture (CLP)-induced sepsis in mice. Administration of blocking moesin antibodies attenuated CLP-induced septic death. PMID: 25947626
- An increase in moesin expression may contribute to the increased expression of P-gp in blood brain barrier endothelial cells, leading to the development of morphine analgesic tolerance. PMID: 25048710
- phosphorylation-regulated interaction between the cytoplasmic tail of cell polarity protein crumbs and the actin-binding protein moesin PMID: 25792740
- both moesin-mediated inhibition and its localized deactivation by myosin phosphatase are essential for neutrophil polarization and effective neutrophil tracking of pathogens. PMID: 25601651
- A novel role for moesin in regulating clathrin-dependent S1PR1 internalization through clathrin-coated vesicles formation. PMID: 24358210
- Moesin may be a potential drug target for inhibiting corneal fibrosis, and the details of moesin-related signaling pathways would be critical for understanding corneal fibrosis. PMID: 23583046
- Findings indicate a function of moesin in lymphocyte homeostasis in regulating lymphocyte egress from lymphoid organs. PMID: 22875842
- A Pak1-PP2A-ERM signaling axis mediates F-actin rearrangement and degranulation in mast cells. PMID: 23063725
- the extracellular matrix molecule VN and its neuronal receptor TLCN play a pivotal role in the phosphorylation of ezrin/radixin/moesin proteins and the formation of phagocytic cup-like structures on neuronal dendrites PMID: 23019340
- Ezrin/radixin/moesin are required for the purinergic P2X7 receptor (P2X7R)-dependent processing of the amyloid precursor protein. PMID: 22891241
- increased moesin expression promotes EMT by regulating adhesion and contractile elements for changes in actin filament organization. PMID: 22031288
- biomarker for the assessment of genotoxic carcinogens in lymphoma PMID: 22358511
- Moesin is involved in AGE-induced retinal vascular endothelial dysfunction and the phosphorylation of moesin is triggered via ROCK and p38 MAPK activation. PMID: 21327982
- The ERM (ezrin, radixin, moesin) proteins are novel scaffolds at the level of SOS activity control, which is relevant for both normal Ras function and dysfunction known to occur in several human cancers. PMID: 22132106
- ezrin-radixin-moesin (ERM) proteins are induced in activated microglia/macrophages, whereas ERM molecules are only marginally expressed in quiescent microglia in the normal brain. PMID: 21451358
- Ezrin, radixin, and moesin are phosphorylated in response to 2-methoxyestradiol and modulate endothelial hyperpermeability. PMID: 21659656
- Results show that while CD43 binding to ezrin-radixin-moesin proteins is crucial for S76 phosphorylation, CD43 movement and regulation of T-cell migration can occur through an ERM-independent, phosphorylation-dependent mechanism. PMID: 21289089
- Data suggest that myosin-II and ERM proteins modulate mechanical properties in oocytes, contributing to cell polarity and to completion of meiosis. PMID: 20660156
- Data show that TNF-alpha induces the formation of fibrotic foci by cultured retinal pigment epithelial cells through activation of transforming growth factor-TGF-beta signaling in a manner dependent on hyaluronan-CD44-moesin interaction. PMID: 19965872
- cross talk between the blastocyst and uterus involving the ezrin/radixin/moesin (ERM) proteins and ERM-associated cytoskeletal cross-linker proteins CD43, CD44, ICAM-1, and ICAM-2. PMID: 14613898
- The study demonstrates a link between Galpha13 signaling that regulates differentiation of F9 cells through primitive to parietal endoderm and a moesin requirement for cell survival. PMID: 16860319
- Ezrin/radixin/moesin proteins are activated by osmotic shrinkage in a PtdIns(4,5)-P(2)-dependent manner. PMID: 17977945
- These data identify the ERM proteins, which cross-link the plasma membrane and actin, as major and stable cytoskeletal-associated proteins in lens fibers, and indicate a potential role(s) for the ERMs in fiber cell actin cytoskeletal organization. PMID: 18261459
- Hepatic stellate cell migration and fibrogenesis in moesin-deficient mice, is described. PMID: 18606220
- This is the first report of a functional involvement of moesin in the regulation of lung inflammation and repair, which regulates the preservation of alveolar structure and lung homeostasis. PMID: 18658275
- These studies identify a new ERM kinase of importance in lymphocytes and confirm the role of ezrin-radixin-moesin phosphorylation in regulating cell shape and motility. PMID: 19255442
- argue for ezrin-radixin-moesin proteins being both targets and modulators of parvovirus infection PMID: 19321616
- These results suggest a critical role of moesin phosphorylation in Advanced glycation end products-induced endothelial cell functional and morphological regulations PMID: 19395553
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Apical cell membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side. Cell projection, microvillus membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side. Cell projection, microvillus.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:17698
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000113071
UniGene: Mm.138876
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Glypican-3 (GPC3) (G537R), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Prolactin receptor (PRLR), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Claudin-6 (CLDN6)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
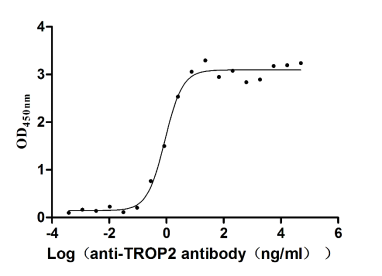
Recombinant Human Tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 (TACSTD2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
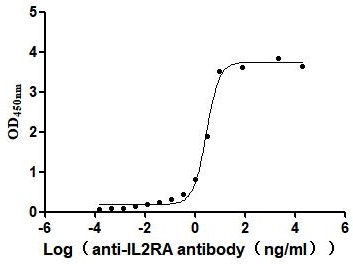
Recombinant Human Interleukin-2 receptor subunit alpha (IL2RA), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
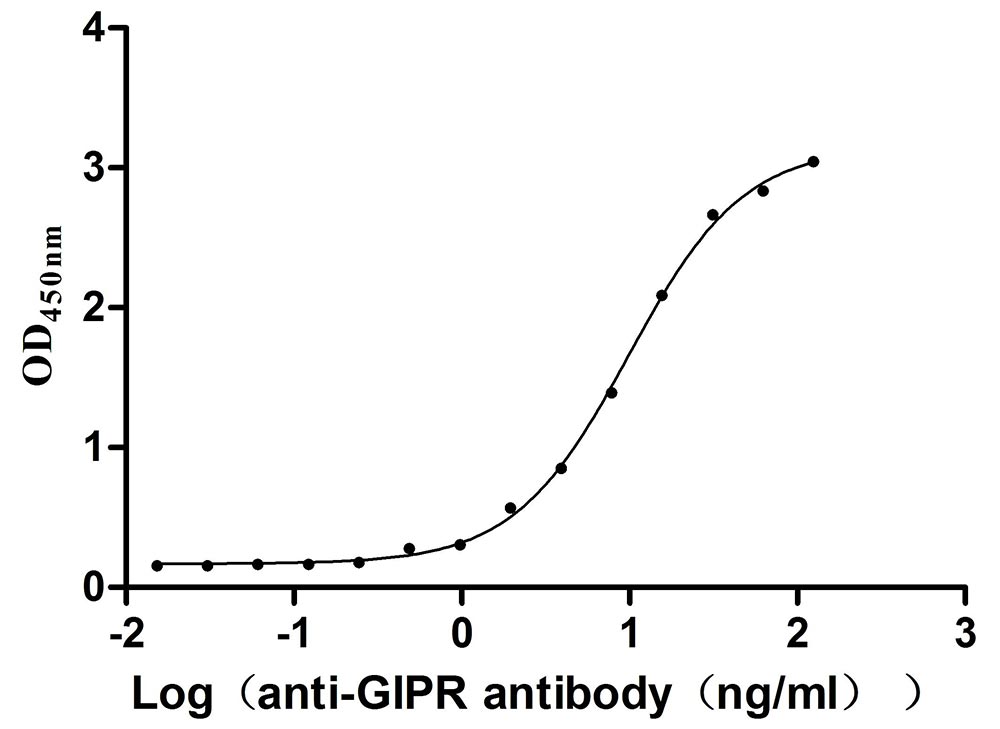
Recombinant Mouse Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor (Gipr), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
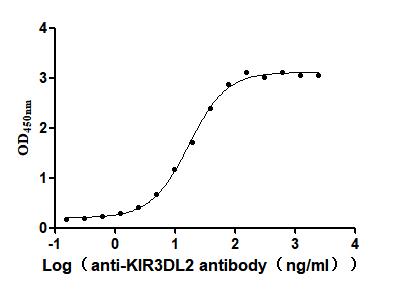
Recombinant Human Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 3DL2 (KIR3DL2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)
-AC1.jpg)
-AC1.jpg)