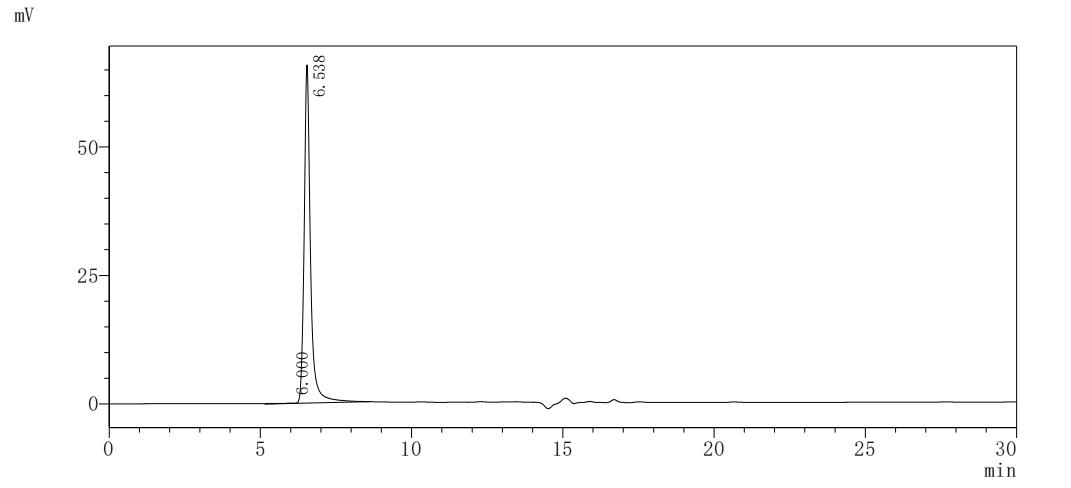
Recombinant Mouse NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-2 (Sirt2)
-
中文名称:小鼠Sirt2重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP851832MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Sirt2重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP851832MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Sirt2重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP851832MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Sirt2重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP851832MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Sirt2重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP851832MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Sirt2
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Sirt2; Sir2l2; NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-2; EC 2.3.1.286; Regulatory protein SIR2 homolog 2; SIR2-like protein 2; mSIR2L2
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length of Mature Protein
-
表达区域:2-389
-
氨基酸序列AEPDPSDPL ETQAGKVQEA QDSDSDTEGG ATGGEAEMDF LRNLFTQTLG LGSQKERLLD ELTLEGVTRY MQSERCRKVI CLVGAGISTS AGIPDFRSPS TGLYANLEKY HLPYPEAIFE ISYFKKHPEP FFALAKELYP GQFKPTICHY FIRLLKEKGL LLRCYTQNID TLERVAGLEP QDLVEAHGTF YTSHCVNTSC RKEYTMGWMK EKIFSEATPR CEQCQSVVKP DIVFFGENLP SRFFSCMQSD FSKVDLLIIM GTSLQVQPFA SLISKAPLAT PRLLINKEKT GQTDPFLGMM MGLGGGMDFD SKKAYRDVAW LGDCDQGCLA LADLLGWKKE LEDLVRREHA NIDAQSGSQA PNPSTTISPG KSPPPAKEAA RTKEKEEQQ
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:NAD-dependent protein deacetylase, which deacetylates internal lysines on histone and alpha-tubulin as well as many other proteins such as key transcription factors. Participates in the modulation of multiple and diverse biological processes such as cell cycle control, genomic integrity, microtubule dynamics, cell differentiation, metabolic networks, and autophagy. Plays a major role in the control of cell cycle progression and genomic stability. Functions in the antephase checkpoint preventing precocious mitotic entry in response to microtubule stress agents, and hence allowing proper inheritance of chromosomes. Positively regulates the anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) ubiquitin ligase complex activity by deacetylating CDC20 and FZR1, then allowing progression through mitosis. Associates both with chromatin at transcriptional start sites (TSSs) and enhancers of active genes. Plays a role in cell cycle and chromatin compaction through epigenetic modulation of the regulation of histone H4 'Lys-20' methylation (H4K20me1) during early mitosis. Specifically deacetylates histone H4 at 'Lys-16' (H4K16ac) between the G2/M transition and metaphase enabling H4K20me1 deposition by KMT5A leading to ulterior levels of H4K20me2 and H4K20me3 deposition throughout cell cycle, and mitotic S-phase progression. Deacetylates KMT5A modulating KMT5A chromatin localization during the mitotic stress response. Deacetylates also histone H3 at 'Lys-57' (H3K56ac) during the mitotic G2/M transition. During oocyte meiosis progression, may deacetylate histone H4 at 'Lys-16' (H4K16ac) and alpha-tubulin, regulating spindle assembly and chromosome alignment by influencing microtubule dynamics and kinetochore function. Deacetylates histone H4 at 'Lys-16' (H4K16ac) at the VEGFA promoter and thereby contributes to regulate expression of VEGFA, a key regulator of angiogenesis. Deacetylates alpha-tubulin at 'Lys-40' and hence controls neuronal motility, oligodendroglial cell arbor projection processes and proliferation of non-neuronal cells. Phosphorylation at Ser-368 by a G1/S-specific cyclin E-CDK2 complex inactivates SIRT2-mediated alpha-tubulin deacetylation, negatively regulating cell adhesion, cell migration and neurite outgrowth during neuronal differentiation. Deacetylates PARD3 and participates in the regulation of Schwann cell peripheral myelination formation during early postnatal development and during postinjury remyelination. Involved in several cellular metabolic pathways. Plays a role in the regulation of blood glucose homeostasis by deacetylating and stabilizing phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase PCK1 activity in response to low nutrient availability. Acts as a key regulator in the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) by deacetylating and activating the glucose-6-phosphate G6PD enzyme, and therefore, stimulates the production of cytosolic NADPH to counteract oxidative damage. Maintains energy homeostasis in response to nutrient deprivation as well as energy expenditure by inhibiting adipogenesis and promoting lipolysis. Attenuates adipocyte differentiation by deacetylating and promoting FOXO1 interaction to PPARG and subsequent repression of PPARG-dependent transcriptional activity. Plays a role in the regulation of lysosome-mediated degradation of protein aggregates by autophagy in neuronal cells. Deacetylates FOXO1 in response to oxidative stress or serum deprivation, thereby negatively regulating FOXO1-mediated autophagy. Deacetylates a broad range of transcription factors and co-regulators regulating target gene expression. Deacetylates transcriptional factor FOXO3 stimulating the ubiquitin ligase SCF(SKP2)-mediated FOXO3 ubiquitination and degradation. Deacetylates HIF1A and therefore promotes HIF1A degradation and inhibition of HIF1A transcriptional activity in tumor cells in response to hypoxia. Deacetylates RELA in the cytoplasm inhibiting NF-kappaB-dependent transcription activation upon TNF-alpha stimulation. Inhibits transcriptional activation by deacetylating p53/TP53 and EP300. Deacetylates also EIF5A. Functions as a negative regulator on oxidative stress-tolerance in response to anoxia-reoxygenation conditions. Plays a role as tumor suppressor.; Deacetylates alpha-tubulin.; Deacetylates alpha-tubulin.; Deacetylates alpha-tubulin.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- These findings indicate that the NAD(+)/SIRT2 pathway is an important mediator through which silybin prevents NLRP3 inflammasome activation during NAFLD PMID: 28970254
- both NAD and NADH significantly increased the intracellular ATP levels of BV2 microglia, which were attenuated by SIRT2 siRNA, the SIRT2 inhibitor AGK2, and the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt inhibitor LY294002. Results suggested that SIRT2 mediates the NAD-induced and NADH-induced increase in Akt phosphorylation in BV2 microglia. PMID: 29189472
- These findings suggest that SIRT2 inhibited atherosclerotic plaque progression and enhanced plaque stability in LDL receptor knockout mice by inhibiting macrophage polarization towards the M1 phenotype. PMID: 29145149
- Results provide a novel link between SIRT2 and physiological aging impacting the axonal compartment of the central nervous system, while supporting a major role for SIRT2 in orchestrating its metabolic regulation. PMID: 28984064
- CDK5-mediated phosphorylation of Sirt2 has a role in to depressive-like behavior induced by social defeat stress PMID: 29158185
- These results confirm that SIRT2 inhibition is able to reverse anhedonia in different animal models and highlight the need to further investigate the role of SIRT2 inhibitors as new antidepressant agents. PMID: 28778545
- SIRT2 knockout mice show marked up-regulation in AMPAR acetylation and protein accumulation, aberrant synaptic plasticity and impaired memory. PMID: 28793258
- SIRT2 inhibition may improve microtubule assembly thus representing a valid approach as disease-modifying therapy for Alzheimer's disease. PMID: 27311773
- s show that SIRT2 is downregulated in insulin-resistant hepatocytes and livers, and this was accompanied by increased generation of reactive oxygen species, activation of stress-sensitive ERK1/2 kinase, and mitochondrial dysfunction. PMID: 28973648
- Given the significance of KRAS activity as a driver in tumorigenesis, identification of K147 acetylation as a novel post-translational modification directed by SIRT2 in vivo may provide a better understanding of the mechanistic link regarding the crosstalk between non-genetic and genetic factors in KRAS driven tumors. PMID: 27637077
- SIRT2 modulates microvascular inflammation in sepsis and affects survival PMID: 28503576
- This study showed that Sirt2-dependent GKRP deacetylation improves impaired HGU and suggest that it may be a therapeutic target for type 2 diabetes. PMID: 29296001
- AMPK and Sirt2 control compensatory glucose uptake in metabolically arrested mitochondria. PMID: 27909079
- SIRT2 promotes AMPK activation by deacetylating the kinase LKB1. Loss of SIRT2 reduces AMPK activation, promotes aging-related and Ang II-induced cardiac hypertrophy, and blunts metformin-mediated cardioprotective effects. PMID: 28947430
- found a decreased ratio of dopaminergic neurons in primary midbrain cultures treated with the SIRT2 inhibitor AK-7 PMID: 28478325
- SIRT-2 regulates microvascular inflammation in obese mice with sepsis. PMID: 27500833
- Loss of SIRT2 expression is associated with breast Cancer. PMID: 27197174
- QKI directly plays a crucial role in the post-transcriptional regulation and expression of Sirt2 to facilitate oligodendrocyte differentiation. PMID: 28188285
- Sirt2-knockout mice were less susceptible to the development of hepatic fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride or thioacetamide. PMID: 27125275
- Results suggest a role for Hdac5 and Sirt2 in neuronal adaptations induced by chronic stress and antidepressant treatment and highlight the therapeutic potential of these targets in the treatment of depression PMID: 26433268
- Sirt2 deletion results in radiation-induced alteration of the mouse brain proteome. PMID: 26373435
- mechanisms of intramolecular inhibition of catalytic activity PMID: 26407304
- Sirt2 expression has a transitory effect in M. tuberculosis infection PMID: 26135889
- we postulate that Sirt2 mediates myelin-dependent neuronal dysfunction during the early phase after ischemic stroke PMID: 26219598
- The study reports the formation of a multiprotein complex at the G2-to-M transition in vitro and in vivo. Group IVA cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2-alpha) acts as a bridge in this complex to promote binding of SIRT2 to cyclin A-Cdk2. PMID: 26303530
- Lipopolysaccharide-induced increases in microglia NOS and cytokine mRNA were attenuated in the cells with SIRT2 silencing-produced decreases in the SIRT2 level. This suggests that SIRT2 is required for lipopolysaccharide-induced microglial activation PMID: 25536118
- Disruption of the SIRT2-beta-catenin interaction represents an endogenous therapeutic target to prevent transformation and preserve the integrity of aging cells against exogenous stressors such as reactive oxygen species. PMID: 24866770
- Tissue-specific deregulation of selected HDACs characterizes ALS progression in mouse models: pharmacological characterization of SIRT1 and SIRT2 pathways. PMID: 24946089
- long-term vitamin E-deficiency significantly decreased the expression of silent mating type information regulation (SIRT)-2 mRNA compared to short-term deficiency. PMID: 24568262
- data indicated that Sirt2 could enhance myoblast proliferation, shorten the G1 phase in murine C2C12 myoblasts by inducing cell cycle regulatory proteins cyclin D1 and cdk2 kinase, and suppressing p21 PMID: 24457518
- Results suggest a novel function of SIRT2 in cilia dynamics and centrosome function, and in ciliopathy-associated disease progression. PMID: 24203696
- data suggested that deficiency of SIRT2 ameliorates iNOS, NO expression and reactive oxygen species production with suppressing LPS-induced activation of NFkappaB in macrophages PMID: 25003320
- our results indicate that SIRT2 suppresses skin tumorigenesis and also suggest that SIRT2 promotes keratinocyte differentiation and suppresses tumor cell stemness in association with downregulating Keratin-19. PMID: 24438005
- the loss of BubR1 levels with age is due to a decline in NAD(+) and the ability of SIRT2 to maintain lysine-668 of BubR1 in a deacetylated state, which is counteracted by the acetyltransferase CBP. PMID: 24825348
- Results suggest that Fry plays a crucial role in promoting the level of microtubule acetylation in the mitotic spindle by inhibiting the tubulin-deacetylase activity of SIRT2. PMID: 23886946
- AKT also associated with a nuclear sirtuin, Sirt1; however, inhibition of PI3K resulted in dissociation from Sirt1 and increased association with Sirt2. PMID: 24446434
- Those findings strongly indicate Sirt2 as a considerably inhibitor of the development of arthritis. PMID: 24211200
- Collectively, our study has provided the first evidence suggesting a significant role of SIRT2 in the basal survival of microglia, as well as a mechanism accounting for the effects of SIRT2 on intracellular ATP levels. PMID: 23570735
- We established an essential role of SIRT1 and SIRT2 in nucleus accumbens in controlling both cocaine and morphine reward PMID: 24107942
- The NAD-dependent deacetylase sirtuin 2 is a suppressor of microglial activation and brain inflammation. PMID: 24013120
- Deletion of Sirt2 failed to affect the disease course, but also did not modify alpha-tubulin acetylation in a mouse model of ALS. PMID: 23364049
- SIRT2 directs replication stress responses by regulating the activity of cyclin-dependent kinase 9, a protein required for recovery from replication arrest. PMID: 23898190
- SIRT2 may be a potential therapeutic agent for various disorders related to ROS, including skin inflammation PMID: 23770196
- The sirtuin 2 inhibitor AK-7 is neuroprotective in Huntington's disease mouse models. PMID: 23200855
- report that SIRT2 increases protein accumulation in murine cholinergic SN56 cells and human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells under proteasome inhibition PMID: 22819792
- SirT2 loss in mice induces significant defects associated with defective H4K20me1-3 levels, genomic instability and chromosomal aberrations and are prone to tumorigenesis PMID: 23468428
- K8 acetylation at Lys-207, a highly conserved residue among type II keratins, is up-regulated upon hyperglycemia and down-regulated by SIRT2. PMID: 23358244
- Sirt2 enhances CG4 oligodendroglial differentiation and report a novel mechanism through which Nkx2.2 represses CG4 oligodendroglial differentiation via Sirt2. PMID: 21669943
- The results of this study indicated that the abundance of SIRT2 in myelin is dependent on PLP. PMID: 21948283
- by negatively regulating the Sirt2-Pgc1alpha regulatory axis, Hif1alpha negates adipocyte-intrinsic pathways of fatty acid catabolism, thereby creating a metabolic state supporting the development of obesity PMID: 22302938
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Cytoplasm, perinuclear region. Perikaryon. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Cell projection. Cell projection, growth cone. Myelin membrane. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle. Chromosome. Midbody. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome, centriole.
-
蛋白家族:Sirtuin family, Class I subfamily
-
组织特异性:Isoform 1 is weakly expressed in the cortex at postnatal(P) days P1, P3 and P7, and increases progressively between P17 and older adult cortex. Isoform 1 is also expressed in heart, liver and skeletal muscle, weakly expressed in the striatum and spinal co
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:64383
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000072732
UniGene: Mm.272443
Most popular with customers
-
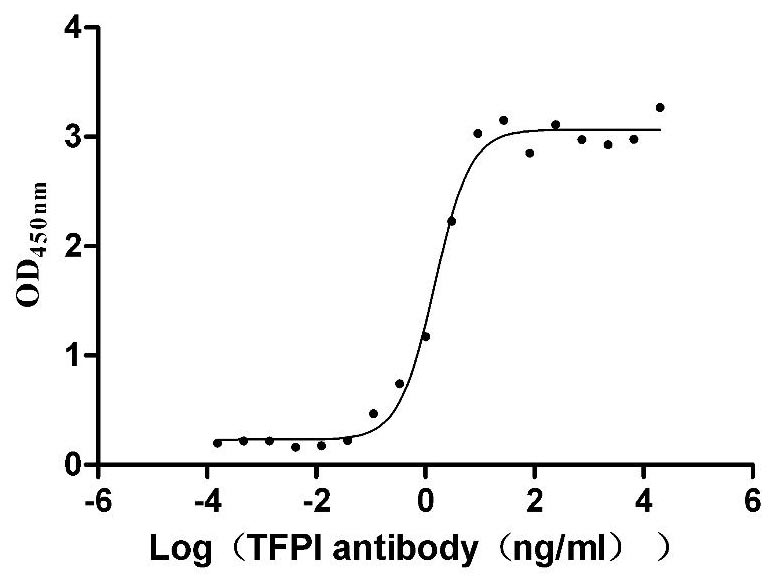
Recombinant Human Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
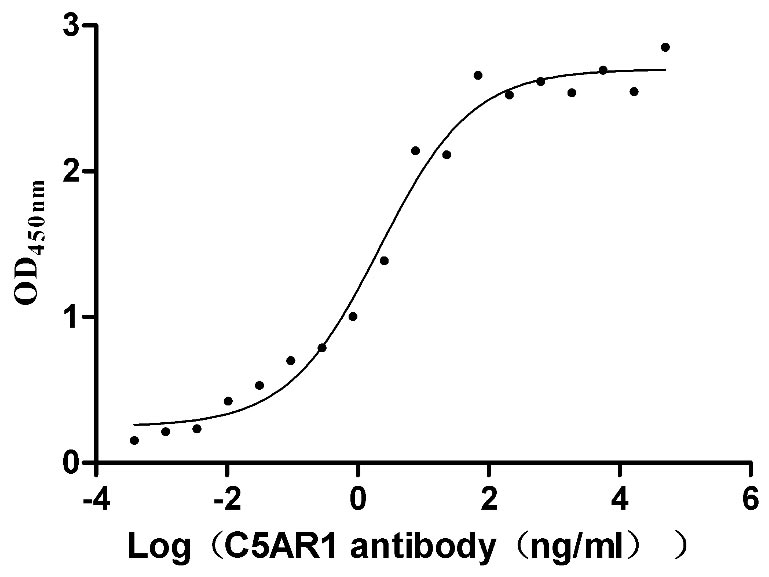
Recombinant Human C5a anaphylatoxin chemotactic receptor 1 (C5AR1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Claudin-6 (CLDN6)-VLPs, Fluorescent (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Dickkopf-related protein 1 (DKK1) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
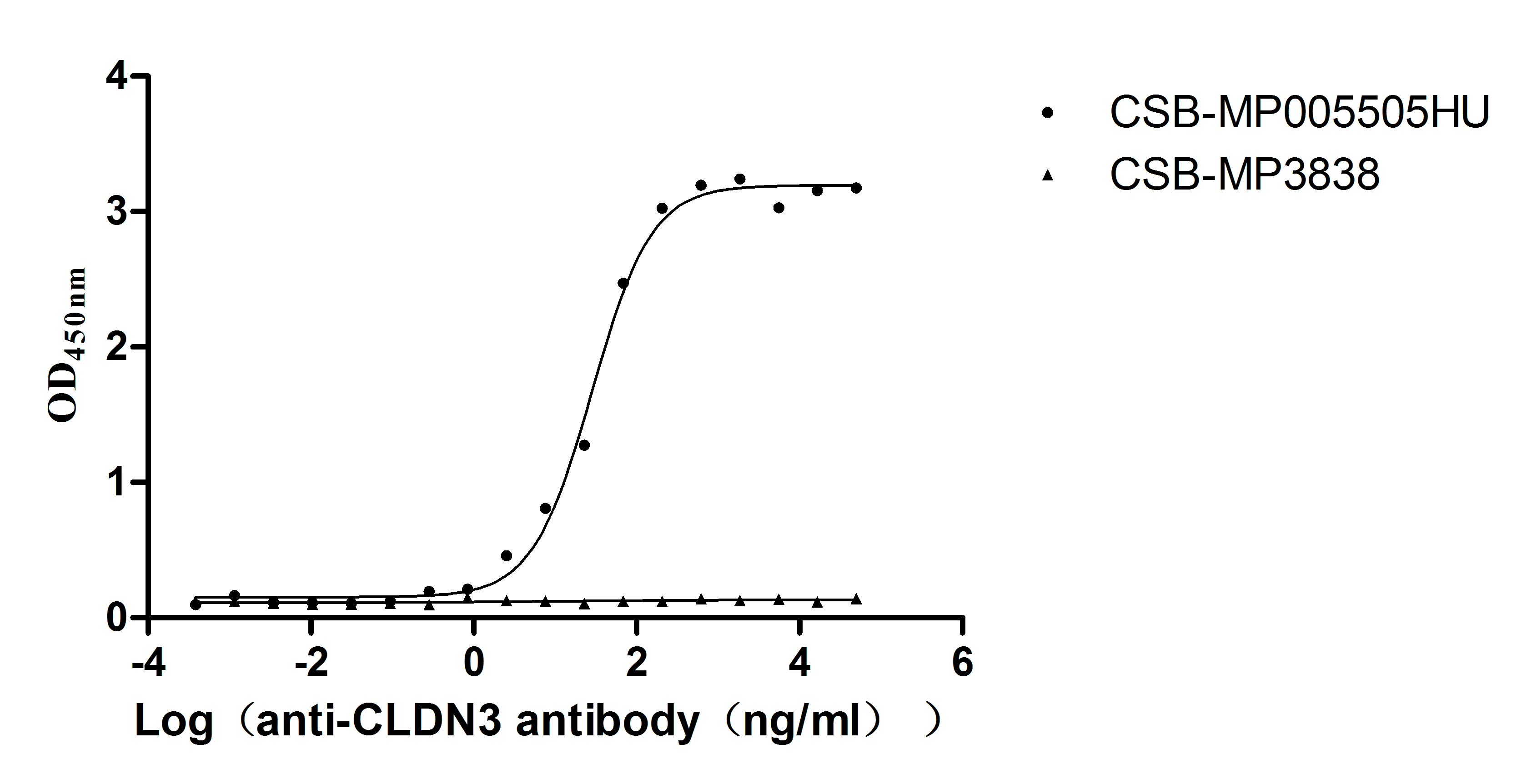
Recombinant Human Claudin-3 (CLDN3)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
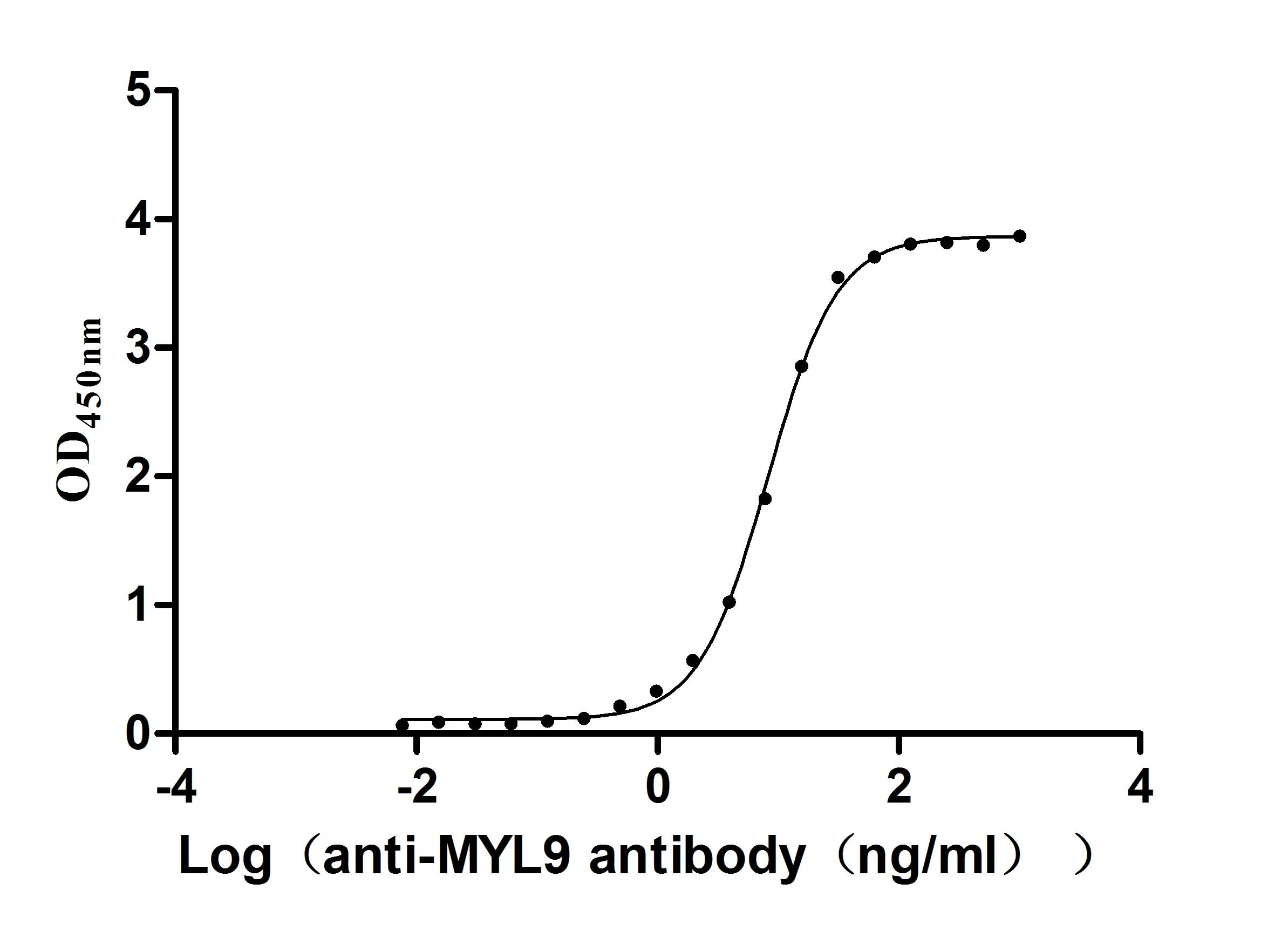
Recombinant Human Myosin regulatory light chain 12B(MYL12B) (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 9 (CCR9)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


f4-AC1.jpg)
-AC1.jpg)