Recombinant Mouse Platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase IB subunit alpha (Pafah1b1)
-
中文名称:小鼠Pafah1b1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP017383MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Pafah1b1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP017383MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Pafah1b1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP017383MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Pafah1b1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP017383MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Pafah1b1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP017383MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Pafah1b1
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Pafah1b1; Lis-1; Lis1; Pafaha; Platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase IB subunit alpha; Lissencephaly-1 protein; LIS-1; PAF acetylhydrolase 45 kDa subunit; PAF-AH 45 kDa subunit; PAF-AH alpha; PAFAH alpha
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Full length protein
-
表达区域:1-410
-
氨基酸序列MVLSQRQRDE LNRAIADYLR SNGYEEAYSV FKKEAELDMN EELDKKYAGL LEKKWTSVIR LQKKVMELES KLNEAKEEFT SGGPLGQKRD PKEWIPRPPE KYALSGHRSP VTRVIFHPVF SVMVSASEDA TIKVWDYETG DFERTLKGHT DSVQDISFDH SGKLLASCSA DMTIKLWDFQ GFECIRTMHG HDHNVSSVAI MPNGDHIVSA SRDKTIKMWE VQTGYCVKTF TGHREWVRMV RPNQDGTLIA SCSNDQTVRV WVVATKECKA ELREHEHVVE CISWAPESSY SSISEATGSE TKKSGKPGPF LLSGSRDKTI KMWDVSTGMC LMTLVGHDNW VRGVLFHSGG KFILSCADDK TLRVWDYKNK RCMKTLNAHE HFVTSLDFHK TAPYVVTGSV DQTVKVWECR
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Regulatory subunit (beta subunit) of the cytosolic type I platelet-activating factor (PAF) acetylhydrolase (PAF-AH (I)), an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolyze of the acetyl group at the sn-2 position of PAF and its analogs and participates in PAF inactivation. Regulates the PAF-AH (I) activity in a catalytic dimer composition-dependent manner. Positively regulates the activity of the minus-end directed microtubule motor protein dynein. May enhance dynein-mediated microtubule sliding by targeting dynein to the microtubule plus end. Required for several dynein- and microtubule-dependent processes such as the maintenance of Golgi integrity, the peripheral transport of microtubule fragments and the coupling of the nucleus and centrosome. Required during brain development for the proliferation of neuronal precursors and the migration of newly formed neurons from the ventricular/subventricular zone toward the cortical plate. Neuronal migration involves a process called nucleokinesis, whereby migrating cells extend an anterior process into which the nucleus subsequently translocates. During nucleokinesis dynein at the nuclear surface may translocate the nucleus towards the centrosome by exerting force on centrosomal microtubules. Also required for proper activation of Rho GTPases and actin polymerization at the leading edge of locomoting cerebellar neurons and postmigratory hippocampal neurons in response to calcium influx triggered via NMDA receptors. May also play a role in other forms of cell locomotion including the migration of fibroblasts during wound healing. Non-catalytic subunit of an acetylhydrolase complex which inactivates platelet-activating factor (PAF) by removing the acetyl group at the SN-2 position. Required for dynein recruitment to microtubule plus ends and BICD2-bound cargos. May modulate the Reelin pathway through interaction of the PAF-AH (I) catalytic dimer with VLDLR.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- This study examined the effect of Pafah1b1 overexpression on radial migration of cerebral cortical neurons and found that enhanced expression of Pafah1b1 caused over-migration of neurons into the marginal zone, and Pafah1b1-overexpressing neurons that entered the marginal zone were disoriented. PMID: 28836069
- Lis1 dysfunction reduces migration and traction force production in fibroblasts. PMID: 29470990
- findings suggest that Lis1 is required for germinal center (GC) B cell expansion, affinity maturation, and maintaining functional intact GC response, thus ensuring both the quantity and quality of Ab response PMID: 28446568
- Lis1 plays an important role in T cell homeostasis and the generation of memory T lymphocytes. PMID: 27029586
- This study demonstrated that LIS-1 regulate the septohippocampal cholinergic projection developmental. PMID: 26079645
- Lis1 is required for the expansion of FL-HSCs by ensuring their genomic stability and therefore promoting their survival. PMID: 24853954
- Results show that LIS1 acts via the LIS1-NDEL1-dynein complex to regulate astral microtubule MT plus-ends dynamics and establish proper contacts of MTs with the cell cortex to ensure precise cell division. PMID: 24030547
- Conditional deletion of Lis1 in the hematopoietic system led to a severe bloodless phenotype, depletion of the stem cell pool and embryonic lethality. PMID: 24487275
- Rab6a mediates LIS1 release from a LIS1-dynein complex followed by dynein activation. PMID: 23783758
- LIS1 plays prominently in filopodia dynamics and dendritic spine turnover. PMID: 23483716
- Nde1 and Lis1 regulate central nervous system development by interpreting midline signals differentially. PMID: 23673330
- Lis1 mediates planar polarity of auditory hair cells through regulation of microtubule organization. PMID: 23533177
- We have investigated the mouse PAFAH1B subunit genes during brain development PMID: 22522921
- Lis1 is required for the dorsally directed tangential migration of many sympathetic and parasympathetic preganglionic neurons and a subset of somatic motor neurons. PMID: 21935943
- findings indicate that disruption of LIS1 has direct effects on excitatory synaptic transmission independent of laminar disorganization. PMID: 22973010
- results indicate that LIS1 is a previously unrecognized regulator of osteoclast formation, microtubule organization, and lysosomal secretion by virtue of its ability to modulate dynein function and Plekhm1 PMID: 22073305
- A three-dimensional regulation of radial glial cells' cytoarchitecture by the Lis1-Nde1-DGC complex determines the number and spatial organization of cortical neurons as well as the size and shape of the cerebral cortex. PMID: 22028625
- Lis1 overexpression stimulated retrograde transport in axons, while a Lis1 dynein-binding mutant severely disrupted transport. PMID: 22114287
- Mutually exclusive cytoplasmic dynein regulation by NudE-Lis1 and dynactin. PMID: 21911489
- Data show that overexpression of Lis1 in different stages of spermatogenesis could not rescue the infertility phenotype of homozygous gene trap males. PMID: 21734362
- Lis1 is essential for cortical microtubule organization and desmosome stability in the epidermis. PMID: 21844209
- Endogenous PAF-AH plays a protective role in the development of necrotizing enterocolitis, and because preterm neonates have endogenous PAF-AH deficiency, this may place them at increased risk for disease. PMID: 20531249
- These data highlight a role for Lis1, acting through the PAF pathway, in leading process branching and microtubule stabilization. PMID: 19861636
- The combined effects of Lis1 haploinsufficiency and Dcx knock-out lead to more severe neuronal migration and proliferation phenotypes in the Lis1(+/ko);Dcx(ko/Y) male double mutant compared with the single mutants, resulting in cortical disorganization. PMID: 20181597
- Compound Pafah1b1(+/-);Apoer2(-/-) mutant mice exhibit a reeler-like phenotype in the forebrain consisting of the inversion of cortical layers and hippocampal disorganization, whereas double Pafah1b1(+/-);Vldlr(-/-) mutants do not. PMID: 17330141
- Lis1 and Ndel1 are essential for normal cortical neuronal migration, neurite outgrowth, and function of the microtubule organizing center in a dose-dependent manner. PMID: 20007476
- LIS1 has a principle role in brain development.Hemizygote mutations result in a severe brain malformation known as lissencephaly. It is a WD repeat protein involved in several protein complexes that may play a functional role in brain development. PMID: 11803439
- LIS1 influences generation and survival of cortical ventricular zone neuroblasts; dose-dependent defects in neuronal migration were found; position and number of ventricular zone mitotic cells were more abnormal as LIS1 levels decreased PMID: 12629176
- role in spermatogenesis PMID: 12775763
- Migration of cerebellar granule cells is regulated by PAF through receptor-dependent and receptor-independent pathways. LIS1 links PAF action and neuronal cell migration. PMID: 12911752
- results show that LIS1 expression is required for the continued normal development of the ICM (inner cell mass)and optimal trophoblast giant cell formation PMID: 12950100
- Lis1 protein has a role in spermatogenesis, particularly in the differentiation of spermatids into spermatozoa PMID: 13129914
- A role for Lis1 protein in neuronal motility by promoting actin polymerization through the regulation of Rho GTPase activity was noted. This effect of Lis1 on GTPases does not appear to occur through direct Lis1 binding of Rho PMID: 14507966
- dynein and its regulators dynactin and LIS1 localize to the leading cell cortex during wound healing. PMID: 14691133
- the 1.75 A resolution crystal structure of the N-terminal domain of mouse LIS1 shows that the LisH motif is a novel, thermodynamically very stable dimerization domain PMID: 15274919
- structure of LIS1 in complex with the alpha2/alpha2 PAF-AH homodimer; data suggest that the LIS1 molecule undergoes major conformational rearrangement when switching from a complex with the acetylhydrolase to the one with Ndel1. PMID: 15572112
- Platelet-activating factor plays a dual role in the pathology of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the induction and chronic phases through the T cell-independent pathways. PMID: 16172262
- Lis1 thus is a key component of neuronal motility signal transduction that regulates the cytoskeleton PMID: 16369480
- Data show that dimerization of Lis1 is dependent on both the LisH motif and the residues downstream of it, including the first few turns of the helix. PMID: 16445939
- Lis1 stimulates the activity of a subset of motors, which could be particularly important during neuronal migration and long-distance axonal transport. PMID: 16481446
- Pafah1b1 may not be a candidate gene of the diabetes susceptibility Idd4.1 locus. PMID: 17130546
- Thus, LIS1 haploinsufficiency can lead to abnormal cell proliferation, migration and differentiation in the adult dentate gyrus. PMID: 17148952
- The neurons ofP7 and P30 Lis1/sLis1 mice was detected a lower frequency and slower decay phase of mIPSCs, and at P30 the mIPSCs amplitude and the action potential duration were reduced. PMID: 17433713
- A novel function for mammalian nudC-like genes as anti-inflammatory proteins. PMID: 17555748
- Lis1 mutant mice shows malformed hippocampus and inhibitory circuits. PMID: 17881479
- over-expression of the PAF-AH (I) catalytic subunits induces centrosomal amplification and microtubule disorganization by disturbing intracellular localization of LIS1 PMID: 17903175
- Together, these results confirm that the LCS contributes pyramidal neurons to ventral forebrain structures and reveals that DCX and LIS1 have important functions in this major migratory pathway in the developing forebrain. PMID: 18075262
- Together, our findings point to a previously unknown interaction between APC and Lis1 during mammalian brain development. PMID: 18075263
- Study reports that Lis1 is essential for precise control of mitotic spindle orientation in both neuroepithelial stem cells and radial glial progenitor cells. PMID: 18267077
- LIS1 mutants exhibit abnormal cell positioning and aberrant hippocampal neurogenesis, but maintain relatively normal fiber termination patterns. PMID: 18446829
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle. Nucleus membrane.
-
蛋白家族:WD repeat LIS1/nudF family
-
组织特异性:Highly expressed in brain, particularly the hippocampus and the olfactory bulb. Also highly expressed in testis, including all seminiferous tubule cell types, all types of spermatogenic and Sertoli cells, and meiotically dividing and elongating spermatids
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:18472
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000021091
UniGene: Mm.397111
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human CD226 antigen (CD226), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
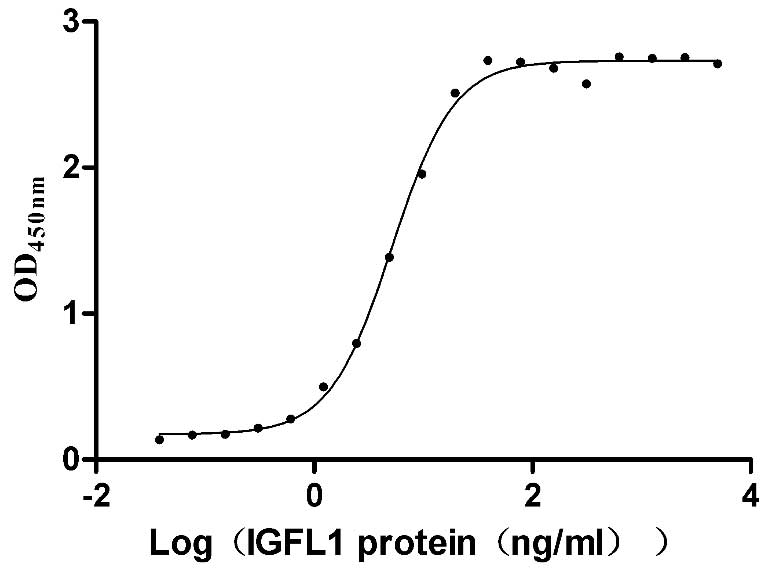
Recombinant Human IGF-like family receptor 1 (IGFLR1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
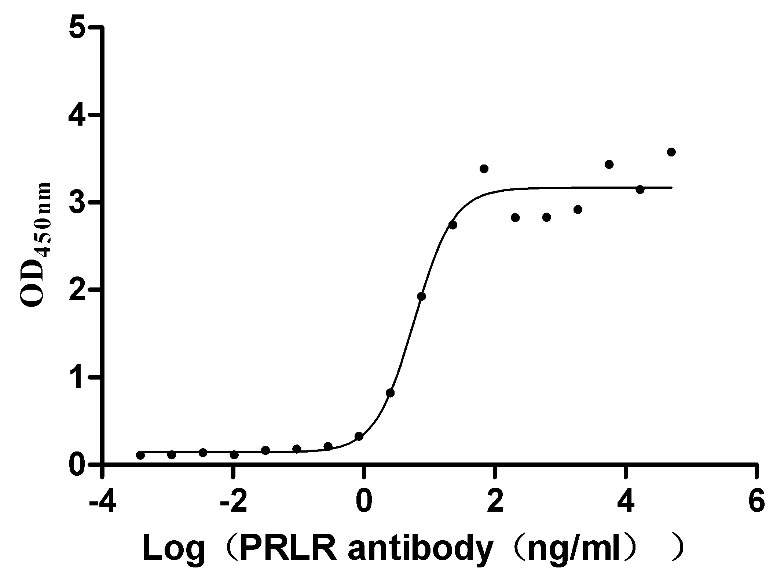
Recombinant Mouse Prolactin receptor (Prlr), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
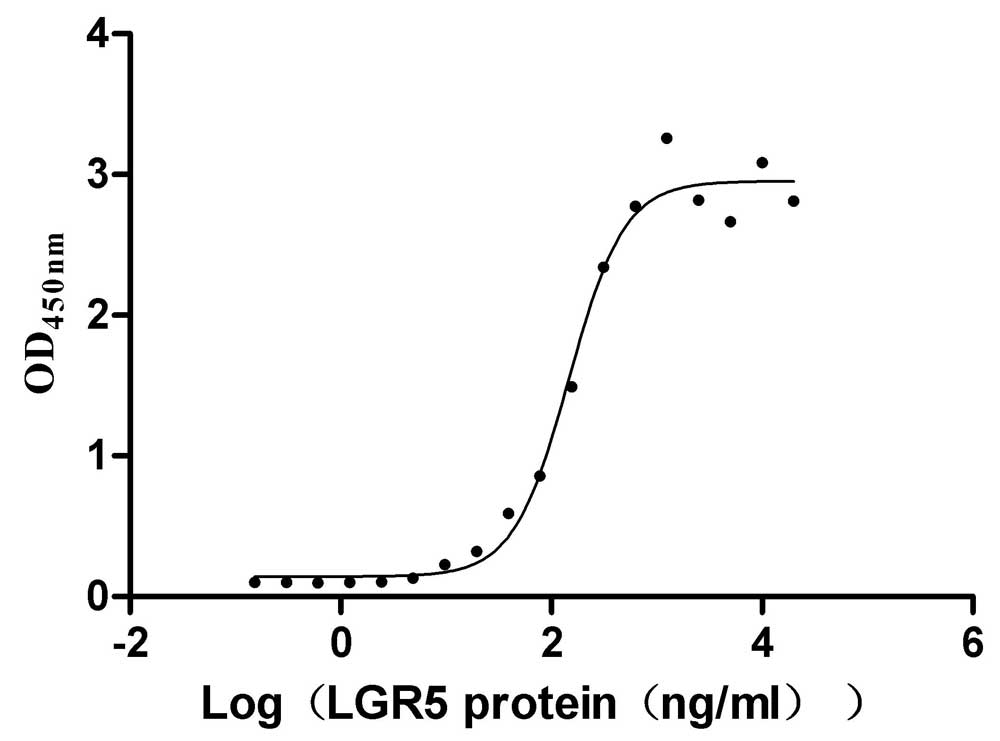
Recombinant Human R-spondin-1 (RSPO1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
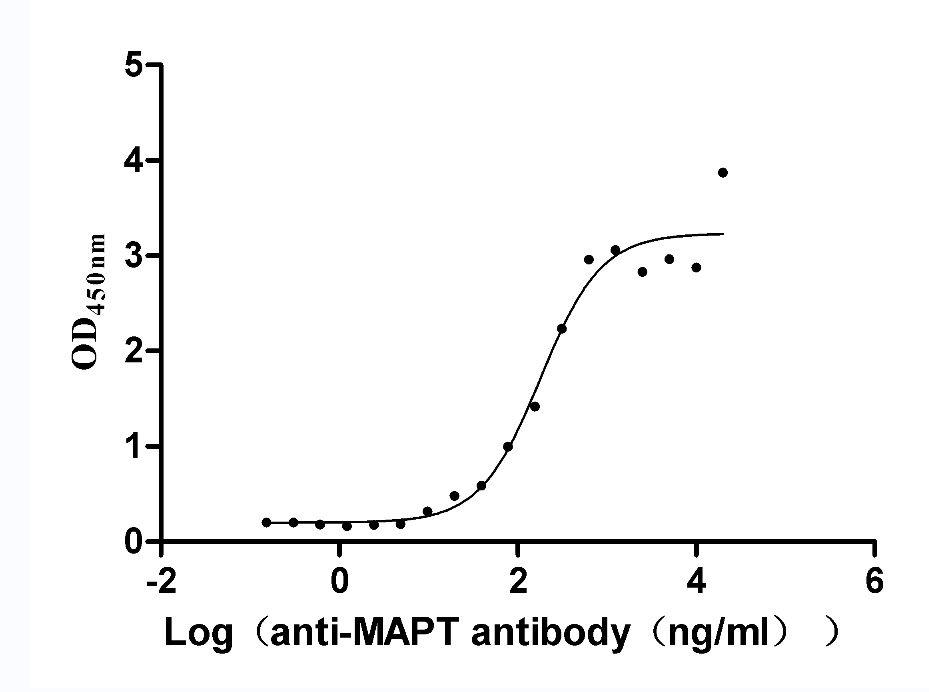
Recombinant Rat Microtubule-associated protein tau (Mapt) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
Recombinant Human Mucin-17 (MUC17), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Complement component C1q receptor (Cd93), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human Desmoglein-3 (DSG3), partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)