Recombinant Mouse SH2 domain-containing protein 1A (Sh2d1a)
-
货号:CSB-YP021209MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP021209MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP021209MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP021209MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP021209MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Sh2d1a; Xlp; SH2 domain-containing protein 1A; Signaling lymphocytic activation molecule-associated protein; SLAM-associated protein; T-cell signal transduction molecule SAP
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Full length protein
-
表达区域:1-126
-
氨基酸序列MDAVTVYHGK ISRETGEKLL LATGLDGSYL LRDSESVPGV YCLCVLYQGY IYTYRVSQTE TGSWSAETAP GVHKRFFRKV KNLISAFQKP DQGIVTPLQY PVEKSSGRGP QAPTGRRDSD ICLNAP
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Cytoplasmic adapter regulating receptors of the signaling lymphocytic activation molecule (SLAM) family such as SLAMF1, CD244, LY9, CD84, SLAMF6 and SLAMF7. In SLAM signaling seems to cooperate with SH2D1B/EAT-2. Initially it has been proposed that association with SLAMF1 prevents SLAMF1 binding to inhibitory effectors including INPP5D/SHIP1 and PTPN11/SHP-2. However, by simultaneous interactions, recruits FYN which subsequently phosphorylates and activates SLAMF1. Positively regulates CD244/2B4- and CD84-mediated natural killer (NK) cell functions. Can also promote CD48-, SLAMF6 -, LY9-, and SLAMF7-mediated NK cell activation. In the context of NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity enhances conjugate formation with target cells. May also regulate the activity of the neurotrophin receptors NTRK1, NTRK2 and NTRK3.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- naive T cells regulate B cell survival in a SAP-dependent manner PMID: 28904129
- SAP-dependent activating SFR signaling is essential for NKT cell selection. PMID: 28049627
- SAP differentially regulates the late-stage lineage decisions of iNKT cell subsets. These results also provide evidence that iNKT1, iNKT2, and iNKT17 cells are differentially regulated by SAP. SAP-dependent signals are essential for the fate decisions that drive the differentiation of iNKT2 but not iNKT1 and NKT17 cells. PMID: 27338553
- SAP is an essential molecule for autoimmune antibody production. PMID: 26501485
- In addition to their role in NK cell activation by hematopoietic cells, the SLAM-SAP-SHP1 pathways influence responsiveness toward nonhematopoietic targets by a process akin to NK cell 'education'. PMID: 26878112
- SLAM-SAP signaling promotes differentiation of IL-17-producing T cells and progression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. PMID: 25362182
- these data suggest that SAP is critical for regulating type II NKT cell responses. PMID: 25236978
- functional analysis in vitro indicates that SAP-2 is a non-functional isoform due to decreased protein stability PMID: 24369347
- Here we report that B cell intrinsic responses to haptenated protein antigens are impaired in SAP-/- mice and in Rag-/- mice into which B cells derived from SAP-/- mice together with wt CD4+ T cells had been transferred. PMID: 23806511
- SAP plays an essential role in CIA because of Fyn-independent and Fyn-dependent effects on TFH cells and, possibly, other T cell types. PMID: 24045941
- SAP was required not only for the initiation but also for the progression of primary T cell-driven B cell responses to haptens. PMID: 23319045
- Loss of SAP expression is associated with invariant NKT cell cytotoxicity and defective lytic synapse formation. PMID: 23430111
- SAP is required for the development of innate phenotype in H2-M3--restricted Cd8(+) T cells. PMID: 23041566
- In the absence of SAP, several routes of natural killer cell-mediated antibody production are still accessible. PMID: 22613797
- SAP(-) cytotoxic lymphocytes had defects in synapse organization with B-cell & low-avidity T-cell targets. SAP & SLAM receptors regulate positive & negative signals for synapse organization & cytotoxicity thresholds for distinct targets. PMID: 22683123
- SAP secures NK cell activation in 2 ways. It couples SLAM receptors to Fyn, triggering Vav-1. It coupled SLAM family receptors to the kinase Fyn, which triggered the exchange factor Vav-1 and augmented NK cell activation. PMID: 22683124
- Overexpression of SAP in T cells increases and sustains protein kinase C-theta recruitment to the immune synapse and elevated IL-4 production, in response to T cell receptor (TCR)- plus SLAM-mediated stimulation. PMID: 20668219
- showed that Id3(-/-) CD8(+) T cells had an innate-like phenotype and required SAP for their development PMID: 20674402
- SAP is not required for T follicular helper (TFH) cell differentiation but is required for germinal center TFH cell differentiation and the resultant interleukin (IL)-4 production. PMID: 20525889
- PLZF acts independently of SAP- and Fyn-mediated signaling pathways. PMID: 20495068
- critical for T cell:B cell adhesion required for productive humoral immunity PMID: 20153220
- Review. Knockout mouse models of X-linked lymphoproliferative disease feature Sh2d1a gene disruption of the SLAM binding site or exon 1 or the intron 1/exon 2 junction. PMID: 12152986
- has a role in murine CD150 (SLAM)-mediated T-cell proliferation and interferon gamma production PMID: 12351401
- Mice lacking expression of SAP generate strong acute IgG antibody responses after viral infection, but show a near complete absence of virus-specific long-lived plasma cells and memory B cells, despite the presence of virus-specific memory CD4+ T cells PMID: 12529646
- results describe a biologically important signalling mechanism in which an adaptor molecule composed only of an SH2 domain links a receptor devoid of intrinsic catalytic activity to the kinase required for its function. PMID: 12545173
- Sap-deficient mice exhibit increased susceptibility to murine gammaherpesvirus-68 and manifest hypogammaglobulinemia prior to and after murine gammaherpesvirus-68 infection PMID: 12966553
- SAP increases FynT kinase activity and is required for phosphorylation of SLAM and Ly9. PMID: 15096483
- SH2D1A regulates T-dependent humoral autoimmunity PMID: 15263031
- SAP/Fyn-mediated pathway enhances PKC-theta/NF-kappaB1 activation and suggesting a role for this pathway in T(H)2 regulation. PMID: 15539155
- SAP is necessary for T(H)2 cytokine regulation primarily as a result of its capacity to recruit FynT. PMID: 15539156
- crucial role during the development of natural killer T cells PMID: 15711562
- SAP is a potent regulator of NKT cell development PMID: 15738056
- SAP is expressed in B cells and this expression is down-regulated after stimulation; B cells from Sap-deficient mice exhibit reduced IgG and IgA production in vitro and a defective Ig switch recombination PMID: 15941917
- SAP is a general negative regulator of the CD8+ T (CTL) cell response; CTL responses to viruses are augmented in the absence of SAP. PMID: 16081788
- SAP may serve as a negative regulator of Trk receptor activation and downstream signaling PMID: 16223723
- Ligation of the CD244 receptor by the CD48 ligand on B cells via signaling pathways depends upon expression of SAP (SLAM-associated protein, or SAP) in natural killer (NK) cells. PMID: 16493031
- germinal center formation was extremely defective in chronically infected knockout animals and hypogammaglobulinemia was observed. PMID: 16788096
- Data show that the interaction of the FynT SH3 domain with SLAM-SAP is strictly inducible, and is dependent on engagement of SLAM by extracellular ligands. PMID: 16847311
- distinct SAP signaling pathway regulates follicular helper CD4 T cell differentiation, separate from the SLAM-SAP-Fyn signaling pathway regulating Th1/Th2 differentiation PMID: 17202343
- despite SAP-associated defects in germinal center and memory B cell formation, latency was established and maintained in memory B cells at comparable frequencies to wild-type mice PMID: 17237419
- Deficiency results in increased proliferation of CD8-posotive t-cells and impaired activation-induced cell death. PMID: 17266174
- Ly108-triggered protein tyrosine phosphorylation was due to the capacity of SAP to recruit FynT PMID: 18482989
- SAP forms a ternary complex with the kinase Lyn and the inhibitory IgG Fc receptor FcgammaRIIB to regulate B cell proliferation and survival. PMID: 18662772
- Signaling properties of signaling lymphocytic activation molecule-associated protein (SAP) in natural killer (NK) T cells is differentially required for SAP-Fyn proto-oncogene protein interaction during ontogeny vs activation. PMID: 18684920
- SAP is necessary for very late stages of differentiation or, most likely, for allowing T helper cells to communicate during cognate T-B lymphocyte interactions. PMID: 18768854
- SAP deficiency selectively impairs the ability of CD4(+) T cells to stably interact with cognate B cells but not antigen-presenting dendritic cells PMID: 18843362
- The effect of sap deletion on the T dependent and T independent as well as on anti-nuclear antibody production was investigated. PMID: 18845419
- SAP plays a role in CD4-positive T-cell dependent antibody responses that is at least partially or completely independent of inducible T-cell co-stimulator (ICOS). PMID: 19050242
- SAP in the development of innate-like T-cell lineages, including natural killer T cells, and in the regulation of the interactions between B cells and T cells that are required for germinal-centre formation and long-term humoral immunity. Review. PMID: 19079134
- SAP is expressed endogenously in mouse splenic B cells and co-localizes and interacts with CD22. SAP binding to the inhibitory immunoreceptor CD22 regulates calcium mobilization in B cells. PMID: 19150402
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm.
-
组织特异性:T-cells.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:20400
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000005839
UniGene: Mm.441197
Most popular with customers
-
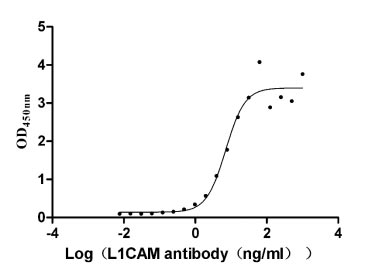
Recombinant Human Neural cell adhesion molecule L1 (L1CAM), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
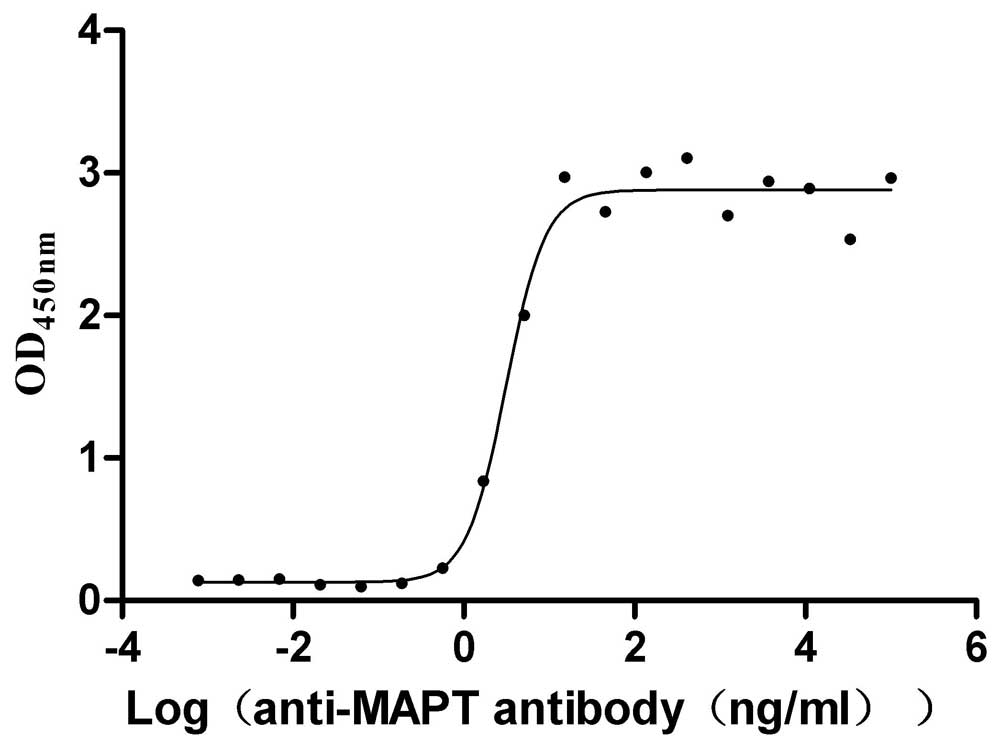
Recombinant Macaca mulatta Microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque)
-
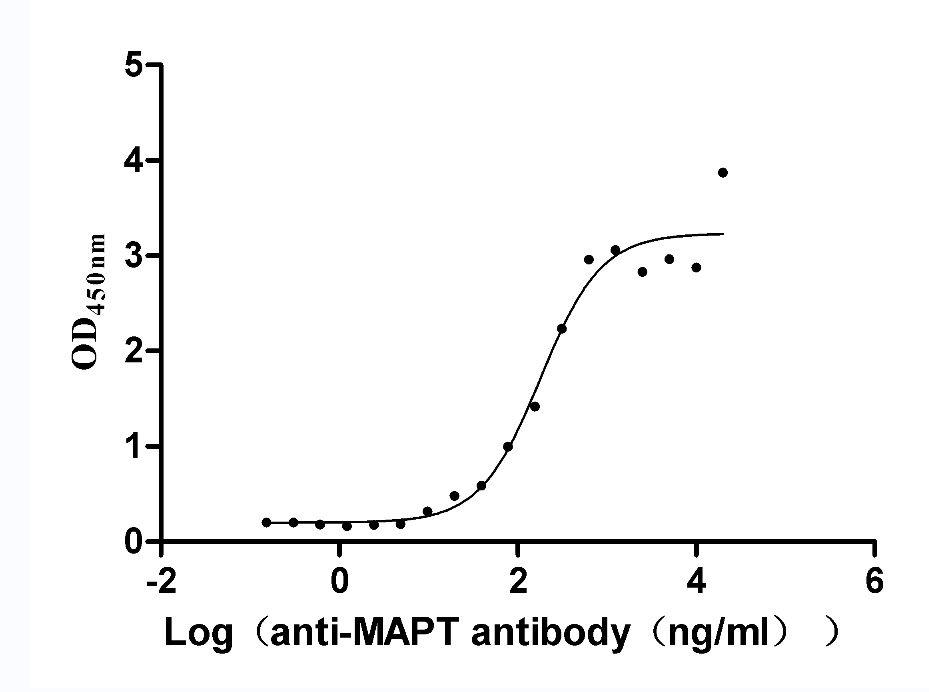
Recombinant Rat Microtubule-associated protein tau (Mapt) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
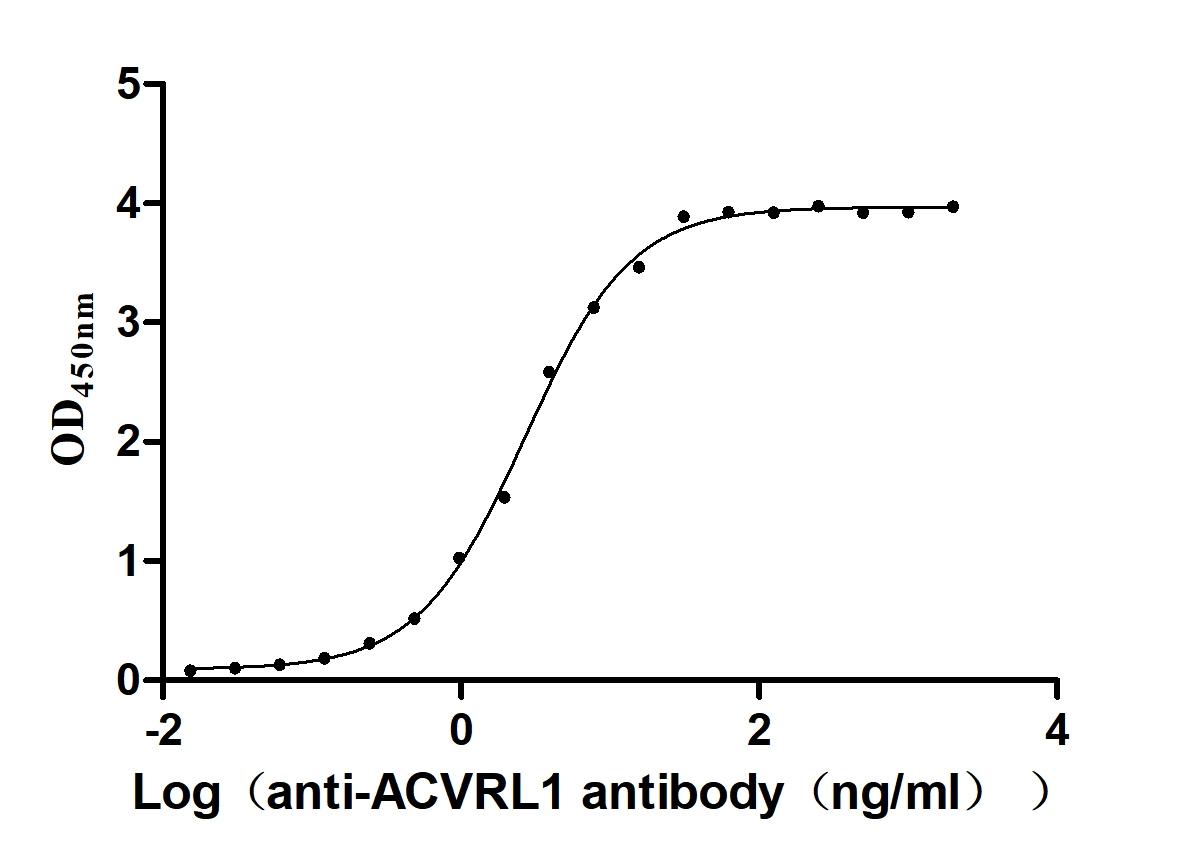
Recombinant Human Serine/threonine-protein kinase receptor R3 (ACVRL1), partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)