Recombinant Mouse Serum response factor (Srf)
-
中文名称:小鼠Srf重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP881354MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Srf重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP881354MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Srf重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP881354MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Srf重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP881354MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Srf; Serum response factor; SRF
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:full length protein
-
表达区域:1-504
-
氨基酸序列MLPSQAGAAA ALGRGSALGG NLNRTPTGRP GGGGGTRGAN GGRVPGNGAG LGQSRLEREA AAAAAPTAGA LYSGSEGDSE SGEEEELGAE RRGLKRSLSE MELGVVVGGP EAAAAAAGGY GPVSGAVSGA KPGKKTRGRV KIKMEFIDNK LRRYTTFSKR KTGIMKKAYE LSTLTGTQVL LLVASETGHV YTFATRKLQP MITSETGKAL IQTCLNSPDS PPRSDPTTDQ RMSATGFEEP DLTYQVSESD SSGETKDTLK PAFTVTNLPG TTSTIQTAPS TSTTMQVSSG PSFPITNYLA PVSASVSPSA VSSANGTVLK STGSGPVSSG GLMQLPTSFT LMPGGAVAQQ VPVQAIHVHQ APQQASPSRD SSTDLTQTSS SGTVTLPATI MTSSVPTTVG GHMMYPSPHA VMYAPTSGLA DGSLTVLNAF SQAPSTMQVS HSQVQEPGGV PQVFLTAPSG TVQIPVSAVQ LHQMAVIGQQ AGSSSNLTEL QVVNLDATHS TKSE
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:SRF is a transcription factor that binds to the serum response element (SRE), a short sequence of dyad symmetry located 300 bp to the 5' of the site of transcription initiation of some genes (such as FOS). Together with MRTFA transcription coactivator, controls expression of genes regulating the cytoskeleton during development, morphogenesis and cell migration. The SRF-MRTFA complex activity responds to Rho GTPase-induced changes in cellular globular actin (G-actin) concentration, thereby coupling cytoskeletal gene expression to cytoskeletal dynamics. Required for cardiac differentiation and maturation.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- The results demonstrate an unexpected function of Srf via a mechanism by which extracellular stimuli actively destabilize cell identity and suggest Srf involvement in a wide range of diseases. PMID: 29643333
- Forebrain-specific serum response factor deletion decreased acute stress-mediated immediate early gene induction. PMID: 27914009
- this study uncovered an SRF contribution to several processes of epileptogenesis in the pilocarpine model. PMID: 28716058
- these data indicate that Emerin, a conserved nuclear lamina protein, couples extracellular matrix mechanics and SRF-Mkl1-dependent transcription. PMID: 28576971
- findings reveal for the first time that SM22 is expressed in the nucleus in addition to the cytoplasm of VSMCs to regulate the transcription of Nik and its downstream proinflammatory NF-kB signal pathways as a modulator of SRF during vascular inflammation PMID: 29284006
- Cigarette smoke is one of the major causes for COPD pathogenesis, inducing COPD-associated skeletal muscle atrophy which is closely related to decreasing SRF nucleic translocation, and down-regulation of SRF target genes involved in muscle growth and nutrition. PMID: 28260872
- Synergy between TAZ and SRF in regulating smooth muscle gene activation was observed in primary aortic vascular smooth muscle cells. This novel signalling pathway links TGFbeta signalling to induction of smooth muscle genes through a mechanism involving regulation of TAZ and SRF proteins. PMID: 28342289
- Modifications at most transcription start sites are dependent on the TCF family of ERKregulated SRF cofactors. PMID: 28286024
- Blood pressure-associated polymorphism controls ARHGAP42 expression via serum response factor DNA binding PMID: 28112683
- regulates smooth muscle contractility via myotonic dystrophy protein kinases and L-type calcium channels PMID: 28152551
- knockdown of MKL1 induces a significant increase in the transcriptional activity of PPARgamma target genes and MKL1 interacts with PPARg, suggesting that SRF and MKL1 independently inhibit brown adipogenesis and that MKL1 exerts its effect mainly by modulating PPARgamma activity PMID: 28125644
- Our results elucidate the specific role of the transcription factors CREB, SRF, and MEF2 in the depression and potentiation components of ODP in vivo, therefore better informing future attempts to find therapeutic targets for diseases where activity-dependent plasticity is disrupted. PMID: 28607167
- The actin cytoskeleton regulatory pathway, MAPK and dilated cardiomyopathy signaling pathways, as well as CFL1 and ITGB6 genes, may be regulated by Srf to serve important roles in the progression of corneal disease. PMID: 27922676
- The inducible and conditional deletion of SRF in the adult mouse hippocampus increases the epileptic phenotype in the kainic acid model of epilepsy. There was a robust decrease in activity-induced gene transcription in SRF knockout mice. SRF target genes are associated with synaptic plasticity and epilepsy. PMID: 25636686
- the controlled and timely activation of SRF is essential for the coordinated growth of neuronal processes. PMID: 26638868
- Increased serum response factor activity provokes podocytes' epithelial-mesenchymal transition and dysfunction in diabetic nephropathy. PMID: 26408645
- A role for SRF in the transcriptional regulation of DUSP5 PMID: 26691724
- Exploration of the molecular causes of enhanced cardiac hypertrophy revealed significant activation of beta-catenin/GSK-3beta signaling, whereas MAPK and MKL1/serum-response factor pathways were inhibited. PMID: 26719331
- these findings reveal a key role of the SRF/CTGF/miR-133a axis in the regulation of cardiac fibrosis PMID: 26440278
- Study uncovered important roles of neurons and neuronally expressed SRF in multiple sclerosis associated de- and remyelination PMID: 25639799
- These data support a central role of the SRF/MRTF pathway in the pathobiology of lung fibrosis. PMID: 25681733
- the actin, myocardin-related transcription factors and serum response factor (actin-Mrtf-Srf) pathway is specifically downregulated in the muscle atrophy that is induced through disuse in mice. PMID: 25344251
- These results identify SRF and its MRTF cofactors as major transcriptional regulators of endothelial cell junctional stability, guaranteeing physiological functions of the cerebral microvasculature. PMID: 26221020
- Silencing Malat1 inhibits myocyte differentiation and decreases Srf at RNA and protein levels. Srf silencing decreases Malat1 expression. Malat1 contains an miR-133 functional target site, and the interplay between Malat1 and Srf is miR-133 dependent. PMID: 25868726
- SRF cooperated with MEF2 to sustain the expression of LMOD3 and other components of the contractile apparatus, thereby establishing a regulatory circuit to maintain skeletal muscle function. PMID: 25774500
- results indicate that Foxf2 signaling in smooth muscle cells is essential for intestinal development and serum response factor signaling PMID: 25631042
- Identified a set of direct SRF target genes acting in posterior nascent mesoderm which are enriched for transcripts associated with migratory function. We further show that cell migration is impaired in Srf mutant embryos. PMID: 25020278
- SRF-VP16iHep murine hepatocellular carcinoma reveal convergent Ras/MAPK and Rho/actin signaling as a highly oncogenic driver mechanism for hepatocarcinogenesis PMID: 25266280
- leading to a PDGF-responsive SRF-driven transcriptional program in the midface PMID: 25453829
- Increased SRF negatively affects transcription of SRF gene targets. PMID: 24550211
- Data show that the binding of WIP to actin controls the actin dynamics MRTFA-SRF-Focal adhesion assembly signaling cascade. PMID: 24797074
- MKL1/2 and ELK4 co-regulate distinct serum response factor (SRF) transcription programs in macrophages. PMID: 24758171
- Data indicate that despite normal neutrophil numbers, neutrophil function is severely impaired in serum response factor (SRF) knockout (KO) neutrophils. PMID: 24574460
- SRF-dependent miR-210 expression may operate as a novel silencer of the Shh signaling pathway. PMID: 23818299
- Our findings reveal a novel phosphorylation and activation of SRF by GSK-3 that is critical for SRF-dependent axon growth in mammalian central neurons. PMID: 24623780
- Serum response factor indirectly regulates type I interferon-signaling in macrophages. PMID: 23705899
- Data indicate that interferon regulatory factor 8 (IRF8) inhibited smooth muscle cells (SMCs) marker gene expression through regulating serum response factor (SRF) transactivation in a myocardin-dependent manner. PMID: 24248596
- sustained Akt1-induced alphaSMA synthesis markedly decreased upon RNA silencing of SRF and myocardin. PMID: 24106278
- Overexpression of transcription factors MYOCD and SRF alone or in conjunction with Mesp1 and SMARCD3 enhanced the basal but necessary cardio-inducing effect of the previously reported GATA4, TBX5, and MEF2C. PMID: 23704920
- Foxf1 also directly binds to serum response factor (SRF) and myocardin-related transcription factors (MRTFs). PMID: 23946491
- these results strongly support a role for -mediated alternative splicing in the regulation of contractile gene expression, achieved in part through modulating the activity of SRF, a key cardiac transcription factor. PMID: 23437181
- Lamin A/C and emerin regulate MKL1-SRF activity by modulating actin dynamics PMID: 23644458
- SRF is selectively required for endothelial filopodia formation and cell contractility during sprouting angiogenesis, but seems dispensable for vascular remodeling PMID: 23674601
- angiogenic homeostasis is ensured by differential stage-specific functions of SRF target gene products in the developing versus the mature retinal vasculature PMID: 23563308
- Serum response factor controls transcriptional network regulating epidermal function and hair follicle morphogenesis. PMID: 23151848
- Activated mDia promoted rapid and reversible nuclear actin network assembly, subsequent MAL nuclear accumulation, and SRF activity. PMID: 23558171
- SRF-related decreases in vasomotor tone and cell-matrix attachment increase arterial elasticity in large arteries. PMID: 23426017
- Data suggest that in mouse liver SRF is regulated via dramatic diurnal changes of actin dynamics, leading to the rhythmic translocation of the SRF coactivator Myocardin-related transcription factor-B (MRTF-B) into the nucleus. PMID: 23374345
- SRF has a major part to play in the control of local blood flow via its central role in pressure-induced myogenic tone in resistance arteries. PMID: 23264443
- SRF plays a key role in the modulation of cardiac fibrosis through repression of cardiomyocyte CTGF expression in a paracrine fashion. PMID: 22563064
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:20807
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000015749
UniGene: Mm.45044
Most popular with customers
-
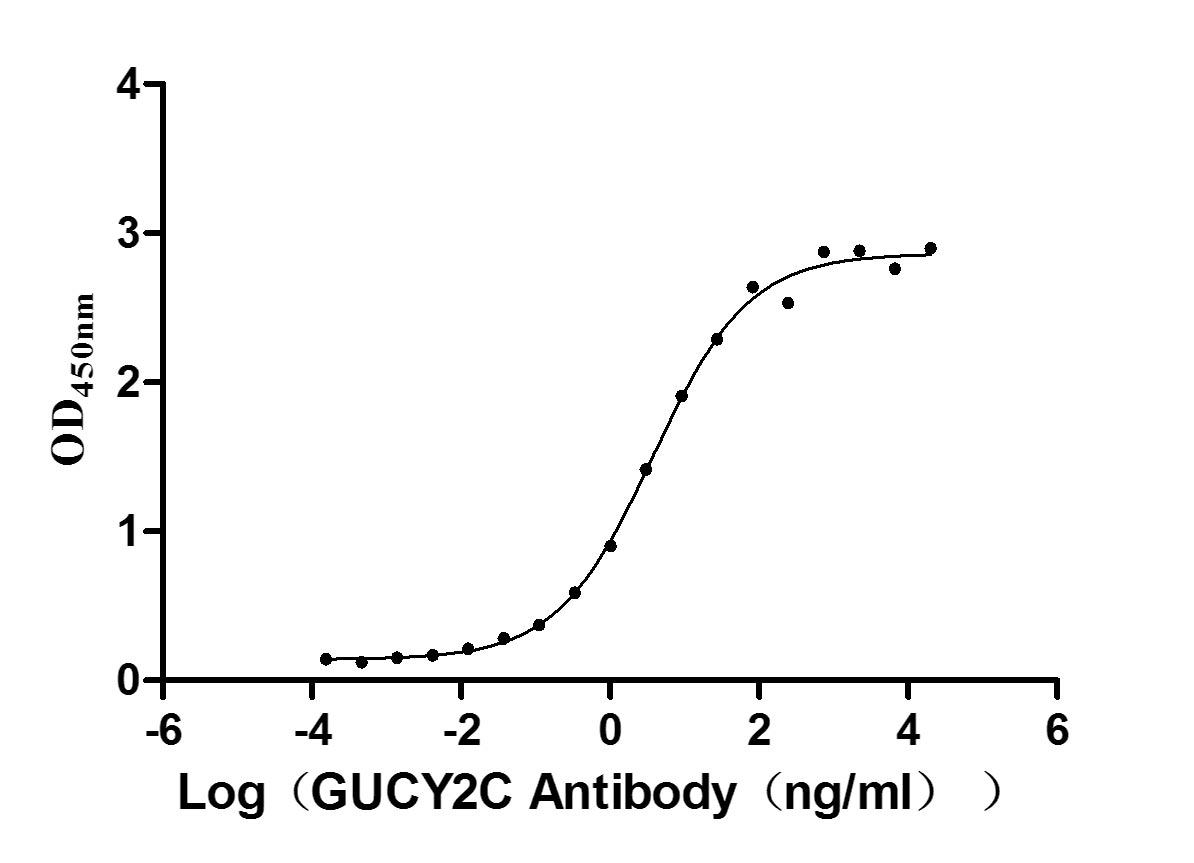
Recombinant Human Heat-stable enterotoxin receptor (GUCY2C), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse GDNF family receptor alpha-like (Gfral), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
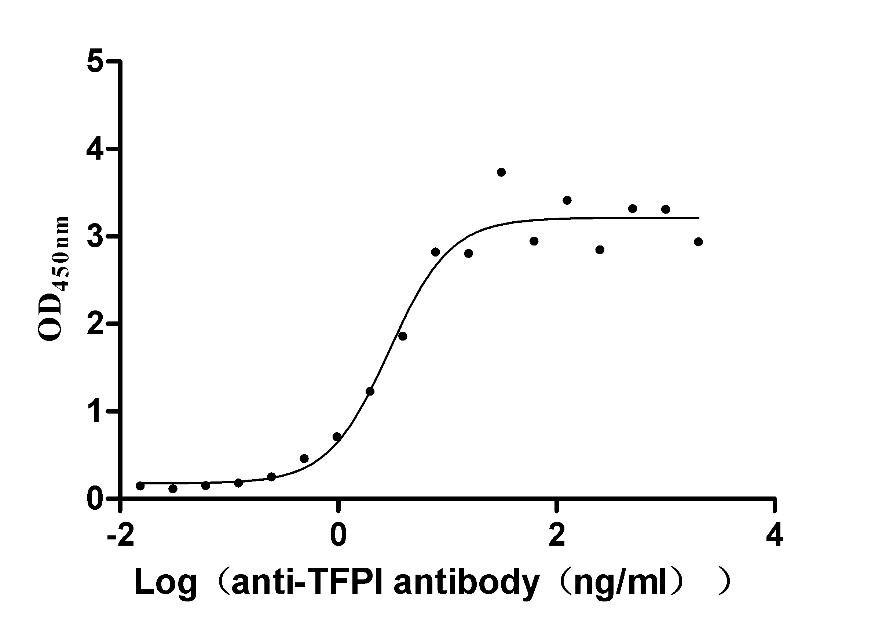
Recombinant Rabbit Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Oryctolagus cuniculus (Rabbit)
-
Recombinant Mouse Transthyretin (Ttr) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
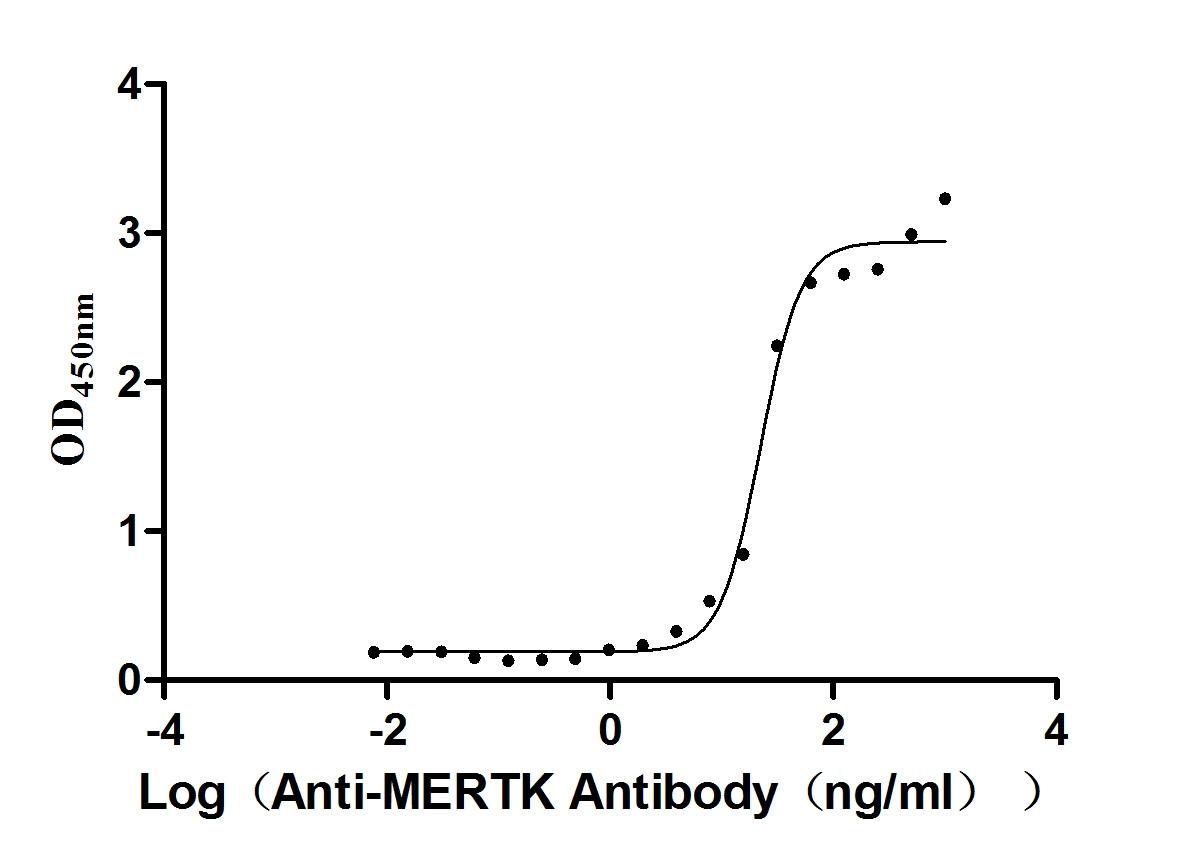
Recombinant Mouse Tyrosine-protein kinase Mer (Mertk), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
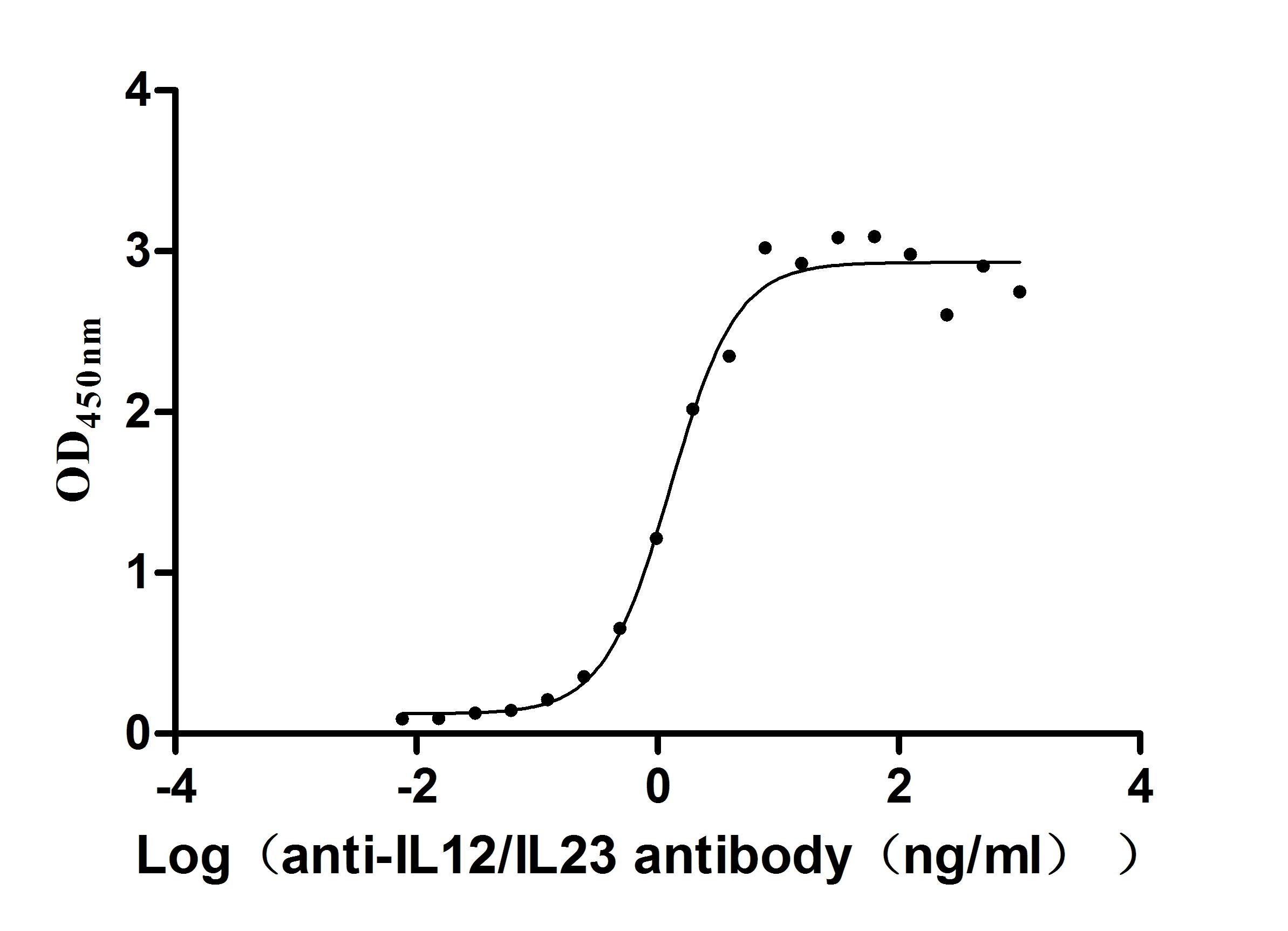
Recombinant Human IL12B&IL12A Heterodimer Protein (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
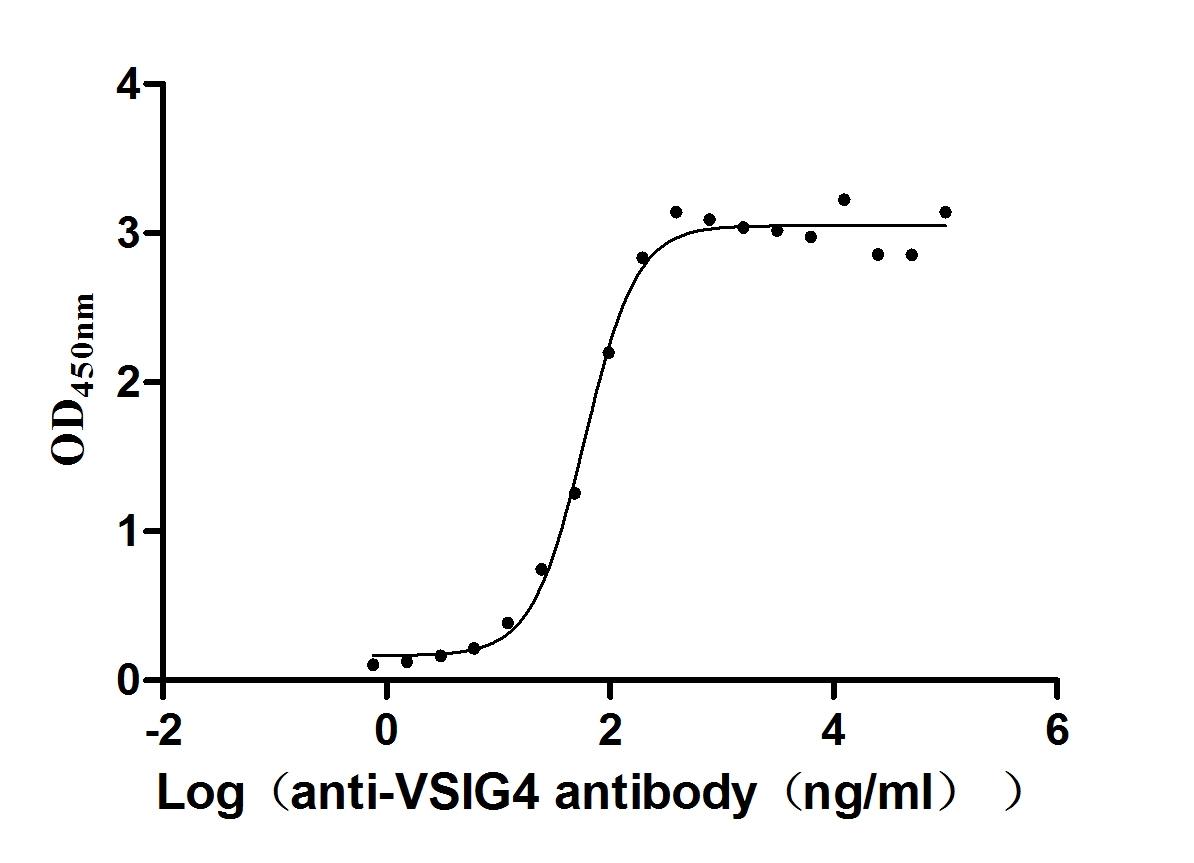
Recombinant Human V-set and immunoglobulin domain-containing protein 4 (VSIG4), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
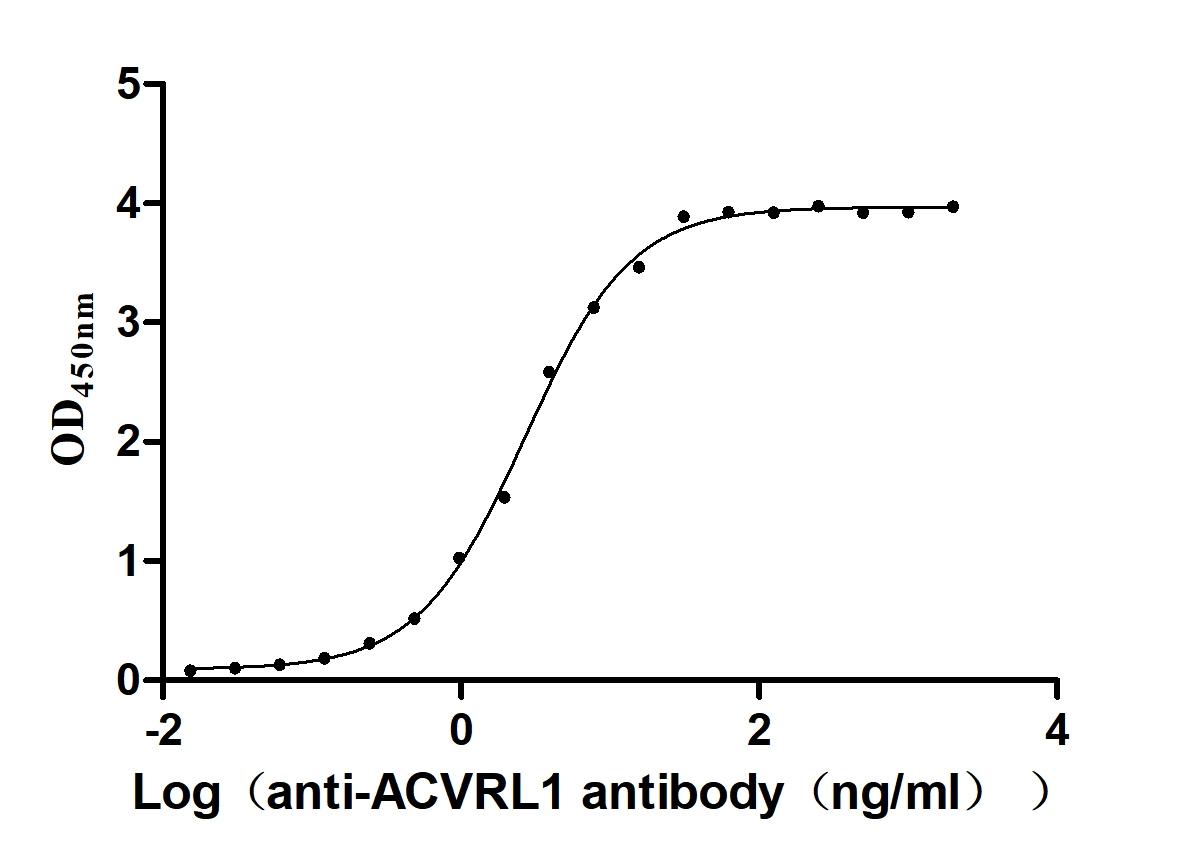
Recombinant Human Serine/threonine-protein kinase receptor R3 (ACVRL1), partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)