Recombinant Mouse Transcription factor jun-B (Junb)
-
货号:CSB-YP011973MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP011973MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP011973MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP011973MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP011973MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Junb; Jun-b; Transcription factor jun-B; MyD21
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Full length protein
-
表达区域:1-344
-
氨基酸序列MCTKMEQPFY HDDSYAAAGY GRSPGSLSLH DYKLLKPTLA LNLADPYRGL KGPGARGPGP EGSGAGSYFS GQGSDTGASL KLASTELERL IVPNSNGVIT TTPTPPGQYF YPRGGGSGGG TGGGVTEEQE GFADGFVKAL DDLHKMNHVT PPNVSLGASG GPQAGPGGVY AGPEPPPVYT NLSSYSPASA PSGGSGTAVG TGSSYPTATI SYLPHAPPFA GGHPAQLGLS RGASAFKEEP QTVPEARSRD ATPPVSPINM EDQERIKVER KRLRNRLAAT KCRKRKLERI ARLEDKVKTL KAENAGLSSA AGLLREQVAQ LKQKVMTHVS NGCQLLLGVK GHAF
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Transcription factor involved in regulating gene activity following the primary growth factor response. Binds to the DNA sequence 5'-TGA[CG]TCA-3'.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Data show that JunB is a nonredundant regulator of transcriptional programs that support Th17 cell identity and restrain alternative Th1 and Treg cell fates. PMID: 28824171
- the present data demonstrates for the first time that JunB plays an important role in the formation of embryonic vascular networks. PMID: 28096474
- JUNB is a significant modulator of both classical and alternative macrophage activation. PMID: 25472994
- Study shows that myeloid deletion of JUNB dampens immune polarization and reshapes disease outcomes during infection with both P. berghei and N. brasiliensis by limiting type 1 and type 2 responses, respectively. Thus, JUNB is an important regulator of myeloid responses to both type 1 and type 2 infections in vivo. PMID: 26178310
- Loss of JunB expression led to increased proliferation and decreased senescence, likely owing to decreased p16(Ink4a) and p21(CIP1) in epithelial cells. PMID: 25526087
- JunB controls epidermal growth, barrier formation, and proinflammatory responses through direct and indirect mechanisms, pinpointing SQSTM1 as a key mediator of JunB suppression of NF-kappaB-dependent inflammation PMID: 25501661
- our results suggest a functional cooperation between NFAT1 and JunB in mediating IL-31 gene expression in CD4(+) T cells PMID: 25595785
- an important role of the A2B receptor-dependent upregulation of JunB in VEGF production and possibly other AP-1-regulated events. PMID: 24136993
- In experimental hepatitis, the absence of JUNB in immune cells decreased IFN-gamma expression and secretion from NK & NKT cells, leading to reduced STAT1 pathway activation. PMID: 24200694
- The results show that the junb gene is organized in a nuclear chromatin loop bringing into close spatial proximity the upstream promoter region and the downstream enhancer and that this configuration permits immediate RNA Pol II release on the junb body on binding of LPS-activated NF-kappaB to the enhancer. PMID: 23921639
- Data suggest that JunB contributes to Id2 repression and provides important input in setting the transcriptional program of the EMT and profibrotic responses to TGF-beta. PMID: 22391036
- Wwp1 induces JunB ubiquitination and degradation. PMID: 21809421
- investigation of role of JunB: growth retardation of JunB-deficient mice correlates with strongly reduced fat mass (and is also associated with high lethality); in white adipose tissue, TNFalpha is up-regulated and perilipin is down-regulated PMID: 21540289
- T cell receptor signaling together with TGF-beta/IL-2 stimulation cooperatively enhance Foxp3 gene expression by maintaining accessible chromatin structure and by actively recruiting key transcription factors JunB and c-Rel. PMID: 21371435
- JunB is important not only in dividing populations but also in adult muscle, where it is required for the maintenance of muscle size and can induce rapid hypertrophy and block atrophy. PMID: 20921137
- Smurf1 negatively regulates mesenchymal stem cell proliferation and differentiation by controlling JunB turnover through an ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. PMID: 20200942
- Data show that Dmp1 directly bound to the genomic loci of Areg, Tsp-1, JunB and Egr1. PMID: 19816943
- expression of JunB protein has a negative effect on malignant tumor cell proliferation in part through its ability to inhibit AP-1 transactivation PMID: 11862466
- Transcriptional regulation of JunB, a myeloid differentiation primary response (MyD) gene, during myeloid differentiation is mediated by nuclear factor Y. PMID: 12070012
- Jun B controls cyclin A during cell cycle regulation in mouse PMID: 12121977
- may contribute to the molecular processes during contextual memory reconsolidation PMID: 12882314
- transgenic mice that expressed JunB under the control of the ubiquitin C promoter were partially protected from the transforming potential of the Abelson oncogene. However, transformed B cells eventually escaped from the inhibitory effect of JunB. PMID: 12907453
- JunB plays a crucial role in endochondral ossification by regulating proliferation and function of chondrocytes and osteoblasts PMID: 14576352
- These data reveal a novel function of JunB as a positive regulator controlling primarily osteoblast as well as osteoclast activity. PMID: 14769860
- Vasoactive intestinal peptide binding to VPAC(2) on CD4 T cells specifically induces an up-regulation of the Th2-type transcription factors c-Maf and JunB, which consequently enhances IL-4 and IL-5 production, leading to a Th2-type phenotype. PMID: 15187104
- phosphorylation of JunB at Ser-79 is essential for its interaction with p300 PMID: 15308641
- Has a stem cell-specific role, deficiency can result in myeloproliferative disorders. PMID: 15507213
- JunB mRNA is significantly increased in mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinsae deficient cells. PMID: 15558021
- PTHrP upregulates JunB and reduces cyclin D1 expression while inducing G1 cell cycle arrest in differentiated osteoblasts PMID: 15883646
- JunB may be a key mediator of PTHrP actions in cementoblasts. PMID: 16418780
- Enhanced MMP-2 transcription and translation following I/R injury are mediated by induction, via oxidant stress, of discrete AP-1 transcription factor components, JunB and FosB. PMID: 16699069
- JunB contribute to the development of PU.1 knockdown-induced AML by blocking differentiation and increasing self-renewal. PMID: 17041602
- NF-kappaB-induced JunB plays a critical role in VEGF regulation and tumor angiogenesis. PMID: 17255940
- In the absence of JunB, transformed leukemic cells acquire an enhanced proliferative capacity, which presages a more malignant disease. PMID: 17297445
- JunB is required for the induction of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) by hypoglycemia. PMID: 17341624
- JunB is a critical regulator of intrinsic mast cell functions including cross-talk with endothelial cells. PMID: 17982078
- G-CSF is a direct transcriptional target of JunB and mutant epidermis releases large amounts of G-CSF that reach high systemic levels and cause skin ulcerations, myeloproliferative disease and low bone mass. PMID: 18641637
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:BZIP family, Jun subfamily
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:16477
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000064680
UniGene: Mm.1167
Most popular with customers
-
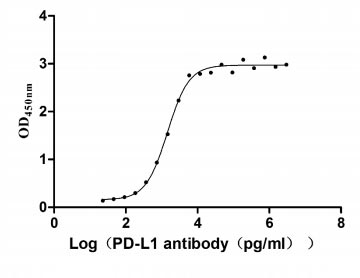
Recombinant Human Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (CD274), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
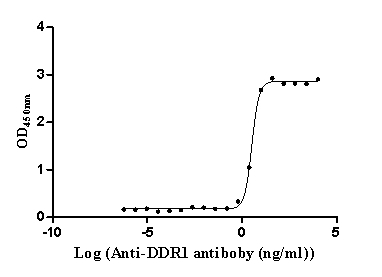
Recombinant Human Epithelial discoidin domain-containing receptor 1 (DDR1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
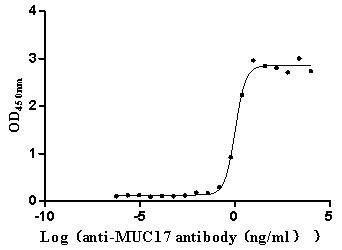
Recombinant Human Mucin-17 (MUC17), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
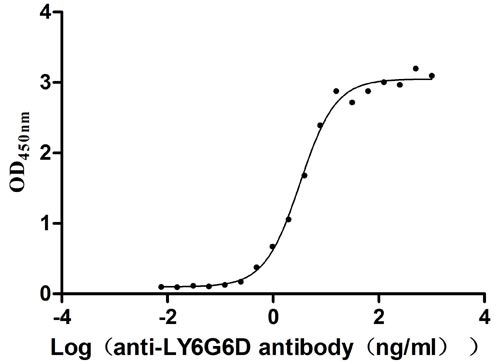
Recombinant Human Lymphocyte antigen 6 complex locus protein G6d (LY6G6D) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Membrane spanning 4-domains A1 (MS4A1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
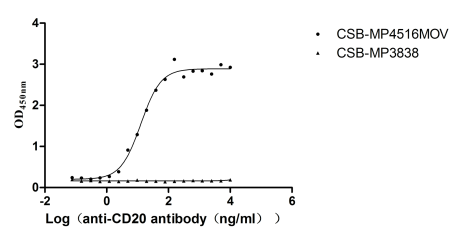
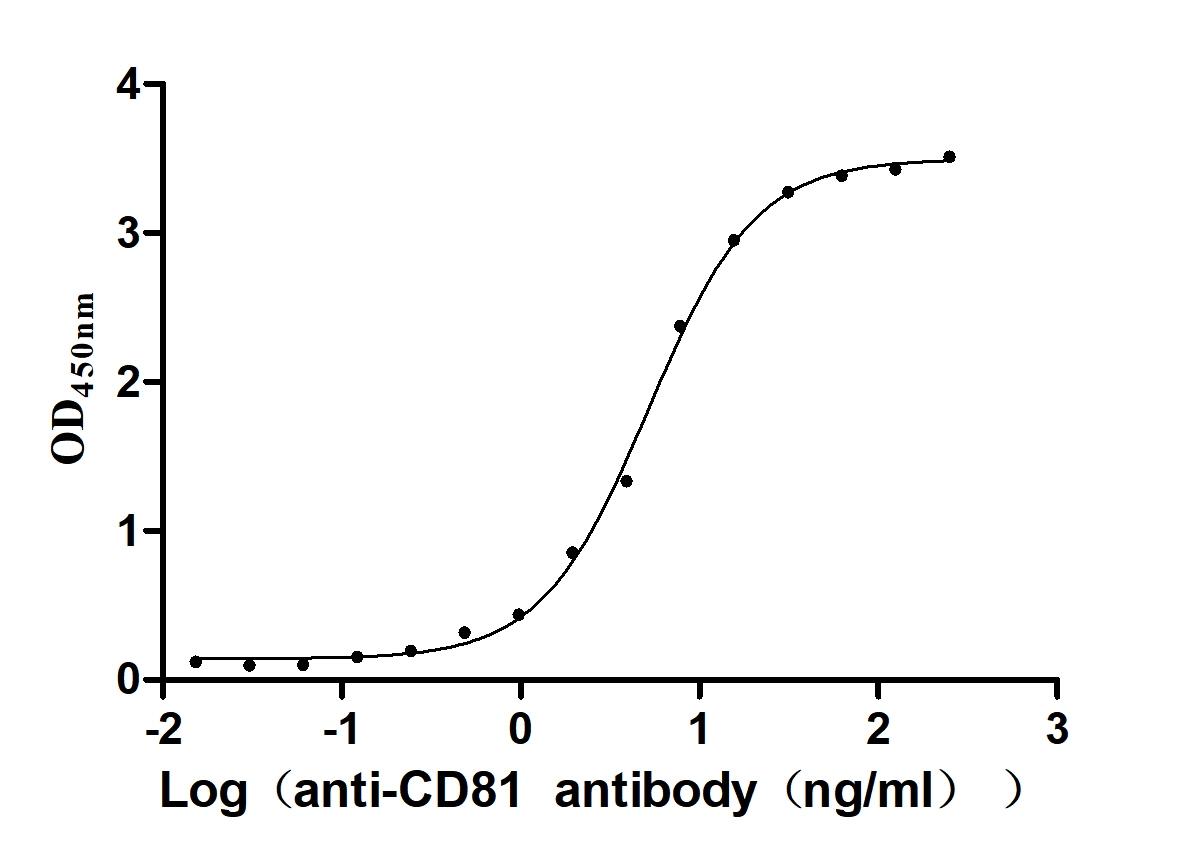
Recombinant Human CD81 antigen (CD81), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
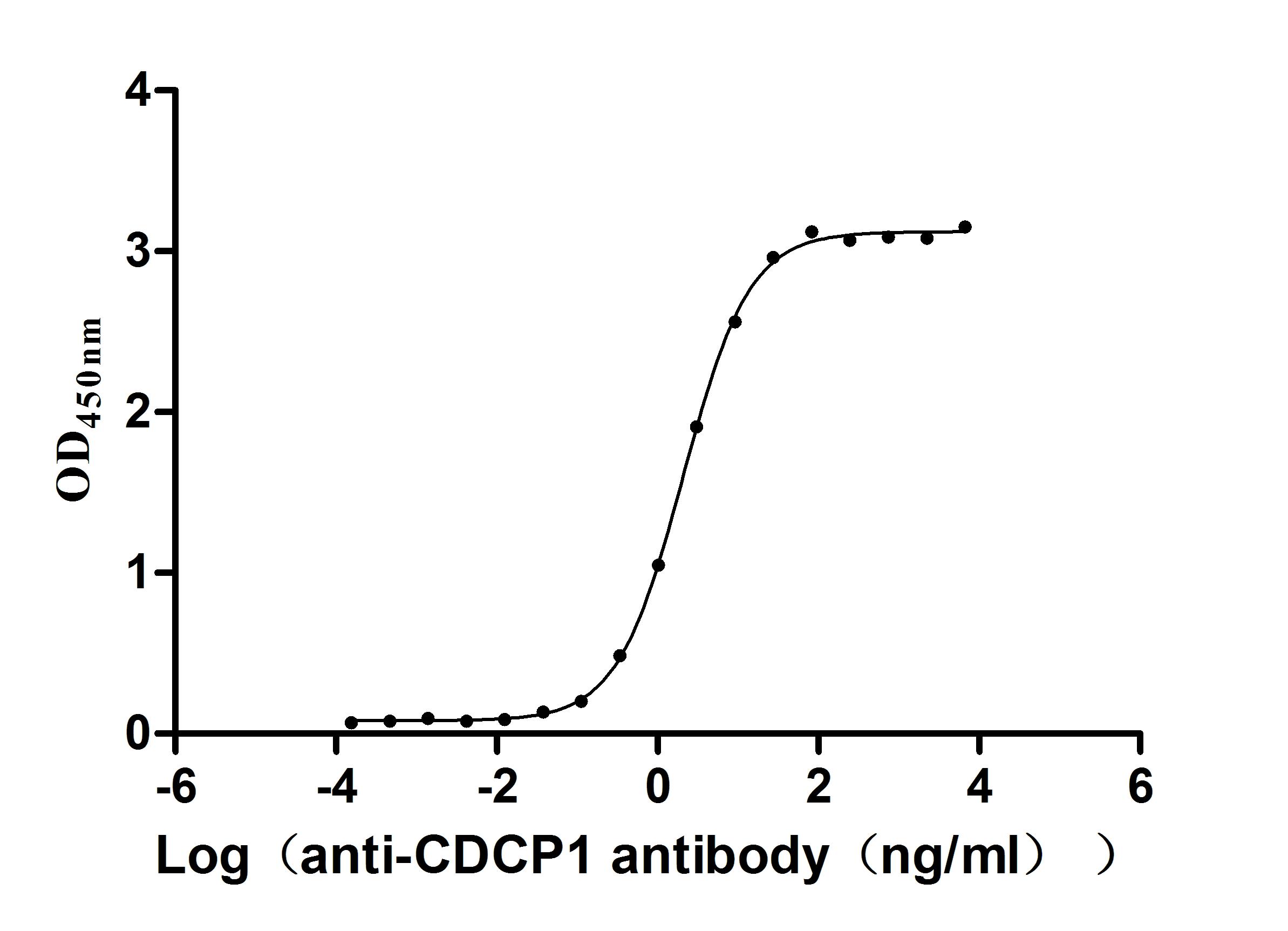
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis CUB domain containing protein 1 (CDCP1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
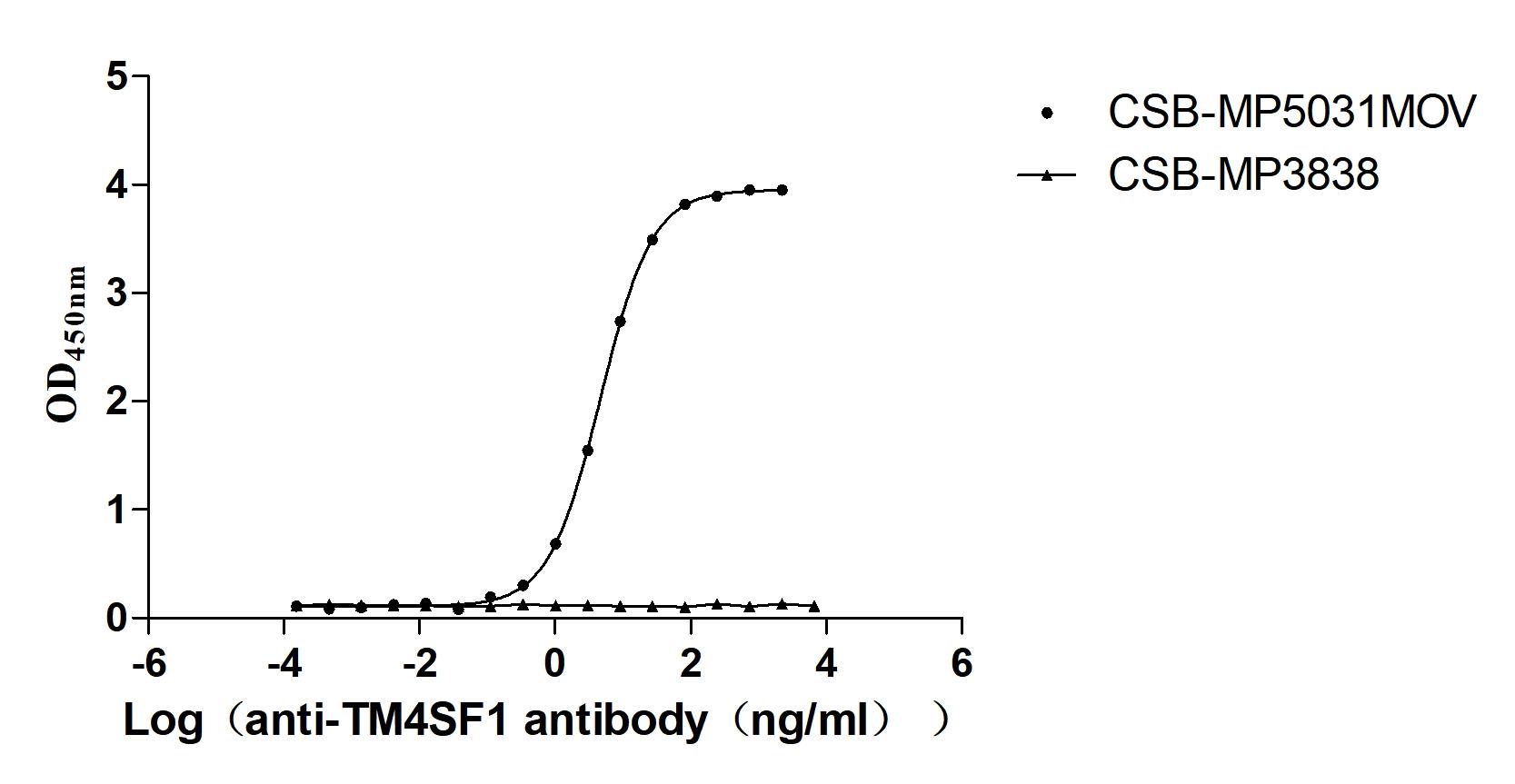
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Transmembrane 4 L6 family member 1 (TM4SF1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)