Recombinant Mouse Vitamin D3 receptor (Vdr)
-
中文名称:小鼠Vdr重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP025832MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Vdr重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP025832MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Vdr重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP025832MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Vdr重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP025832MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Vdr重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP025832MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Vdr
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Vdr; Nr1i1; Vitamin D3 receptor; VDR; 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor; Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group I member 1
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Full length protein
-
表达区域:1-422
-
氨基酸序列MEAMAASTSL PDPGDFDRNV PRICGVCGDR ATGFHFNAMT CEGCKGFFRR SMKRKALFTC PFNGDCRITK DNRRHCQACR LKRCVDIGMM KEFILTDEEV QRKREMIMKR KEEEALKDSL RPKLSEEQQH IIAILLDAHH KTYDPTYADF RDFRPPIRAD VSTGSYSPRP TLSFSGDSSS NSDLYTPSLD MMEPASFSTM DLNEEGSDDP SVTLDLSPLS MLPHLADLVS YSIQKVIGFA KMIPGFRDLT SDDQIVLLKS SAIEVIMLRS NQSFTLDDMS WDCGSQDYKY DITDVSRAGH TLELIEPLIK FQVGLKKLNL HEEEHVLLMA ICIVSPDRPG VQDAKLVEAI QDRLSNTLQT YIRCRHPPPG SHQLYAKMIQ KLADLRSLNE EHSKQYRSLS FQPENSMKLT PLVLEVFGNE IS
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Nuclear receptor for calcitriol, the active form of vitamin D3 which mediates the action of this vitamin on cells. Enters the nucleus upon vitamin D3 binding where it forms heterodimers with the retinoid X receptor/RXR. The VDR-RXR heterodimers bind to specific response elements on DNA and activate the transcription of vitamin D3-responsive target genes. Plays a central role in calcium homeostasis.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Data suggest that Smad-specific E3 ubiquitin ligase 2 (SMURF2)-mediated SMAD3 protein (SMAD3) monoubiquitination interferes with the formation of a SMAD3-vitamin D receptor (VDR) complex. PMID: 28216630
- Vitamin D inhibits lymphangiogenesis through VDR-dependent mechanisms. PMID: 28303937
- Data suggests that exposure to vitamin D deficiency during perinatal period directly affects expression of genes involved in development of adipose tissue in non-obese offspring; expression levels of Pparg (peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma) and Vdr (vitamin D receptor) are up-regulated in adipose tissue of male offspring. PMID: 28004271
- The elevated levels of miR-351 promoted hepatic fibrosis by targeting the vitamin D receptor (VDR), which is an antagonist of SMAD signaling. PMID: 29255036
- the crucial role of VDR in anti-inflammatory effects in lungs PMID: 28803336
- In murine blood cells 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D, but not all-trans-retinoic acid, upregulates the expression of VDR. PMID: 28635660
- These findings suggest that the vitamin D treatment-induced increase in bone mass is mediated by suppressing bone resorption through VDR in osteoblast-lineage cells. PMID: 28177161
- Gut epithelial VDR signaling controls mucosal inflammation by suppressing epithelial cell apoptosis. PMID: 29228157
- Expression of VDR exclusively in the distal intestine can prevent abnormalities in calcium homeostasis and bone mineralization associated with systemic VDR deficiency. PMID: 28938396
- Data suggest that the absence of VDR inhibits atherosclerotic plaque calcification in hypercholesterolemic Apoe(-/-) mice, providing additional insight into the role of vitamin D in atherosclerotic plaque calcification. PMID: 27567005
- Activated RAS signaling reduced Vitamin D Receptor (VDR) level in intestinal epithelial cells. PMID: 28104492
- Loss of the vitamin D receptor in macrophages and granulocytes mildly affected colitis-associated symptoms but greatly increased proinflammatory cytokine expression in the inflamed colon, suggesting a prominent role for innate immune cell vitamin D signaling in controlling gut inflammation. PMID: 28472309
- Unique protective roles for vitamin D signaling during colitis in the colon epithelium as well as nonepithelial cells in the colon microenvironment (i.e., modulation of M biology). PMID: 28368514
- Vdr and Casr are required for beta-catenin-regulated cell proliferation and Adherens junction formation essential for re-epithelialization after wounding. Vitamin D and calcium signaling in keratinocytes are required for a normal regenerative response of the skin to wounding. PMID: 28368538
- Absence of VDR-mediated PPARgamma suppression underlies alopecia in VDR-/- mice. PMID: 27932380
- Through the VDR, vitamin D is an environmental factor that helps to maintain low serum IgE responses. PMID: 28003380
- VDR is important for the maintenance of physiological level of Axin1 PMID: 27601169
- The data support the hypothesis that Vdr in mature adipocytes alters the metabolic response to high-fat diets and exerts anti-proliferative effects on the mammary epithelium. PMID: 26429395
- The data demonstrate that deficiency in the vitamin D signaling via VDR knockout enhances the pathological phenotype in this experimental cardiomyopathy and suggest an important role for vitamin D in modulating disease severity in common cardiovascular disorders. PMID: 26429397
- Absence of VDR or presence of an unliganded VDR does not affect the profile and function of ex vivo generated bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. PMID: 26343449
- JNK1 physically and functionally interacted with VDR and positively regulated VDR expression at transcriptional and translational levels, which influenced calcitriol-mediated inhibition of cancer cell proliferation. PMID: 27174721
- Vitamin D receptor activation reduces dissecting abdominal aortic aneurysm formation induced by Ang-II in apoE(-/-) mice PMID: 27283745
- VDR may function as a selective suppressor/de-repressor of gene expression in the absence of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. PMID: 26323657
- In the presence of normocalcemia, absence of VDR or its ligand-activated transcription of genes has no direct regulatory effect on murine glucose homeostasis or gene expression in islets of Langerhans. PMID: 26877201
- The Vdr-/- mouse model displays sex- and site-specific differences in skeletal structures with long-term feeding of a rescue diet. PMID: 26690785
- The endothelial cell VDR plays a tonic inhibitory role in regulating glucose disposal and could prove to be a factor in controlling glucose homeostasis in the intact organism. PMID: 26369613
- Cyp27b1(-/-) mice exhibited hypocalcemia, growth defects, and skeletogenesis dysfunction, similar to Vdr(-/-) mice, but do not display alopecia PMID: 28025137
- expression in macrophages is essential for the normal expansion of tissue-resident macrophages in response to cutaneous wounding PMID: 27526034
- Collectively, we identify a novel regulatory pathway in which 1, 25(OH)2D3 induces VDR expression and promotes VDR interaction with p50 subunit of NF-kappaB, which in turn attenuates the association of KLF5 with p50 subunit of NF-kappaB and thus exerts anti-inflammatory and anti-proliferative effects on macrophages. PMID: 27856242
- there was a positive correlation between VDR status and the expression of Suppressor of fused gene (SuFu), a hedgehog pathway inhibitor. miR-214 on the other hand suppressed SuFu protein expression. PMID: 27693451
- Vitamin D and its receptor might be involved in the progression of diabetic nephropathy by regulating transforming growth factor-beta, angiotensinogen expression and apoptosis of podocytes. PMID: 27180929
- The major finding of this study is that large intestine VDR significantly contributes to whole-body Ca metabolism but that duodenal compensation may prevent the consequences of VDR deletion from large intestine and kidney in growing mice. PMID: 26211511
- The present study investigated whether the vitamin D/vitamin D receptor (VDR) pathway may ameliorate lipopolysaccharide (LPS)induced ALI through maintaining the integrity of the alveolar epithelial barrier. PMID: 26675943
- Data, including data from studies in knockout mice, suggest that VDR regulates expression of ezrin in enterocytes; however, VDR appears not to be involved in morphology of tight junctions and absorption of large molecules in enterocytes. PMID: 26606857
- These data indicate a synergistic crosstalk between 1alpha,25(OH)2D3 and BMP2 toward osteogenesis and mineral deposition, involving both VDR and Pdia3. PMID: 23784946
- study is the first to report an in vivo association between vitamin D, myostatin, and the regulation of muscle mass PMID: 26340892
- The current study reveals an important and novel mechanism for VDR by regulation of epithelial barriers. PMID: 26212084
- VitD3 reinforced physical interaction between placental VDR and NF-kappaB p65 subunit. PMID: 26065916
- 1,25D3 modulates CD8+ T cell phenotype via recruitment of the VDR transcription factor to the promoter region of Cyp11a1 leading to prevention of lung allergic responses. PMID: 26750596
- Data (including data from studies in knockout mice) suggest signal transduction via calcitriol/calcitriol receptor regulates expression of Elovl3 (fatty acid elongase 3) and alters fatty acid composition in subcutaneous (not visceral) adipose tissue. PMID: 26488808
- Absent immune cell VDR expression does not impact the strength/phenotype/linetics of heart transplant rejection in mice and does not impact the graft-prolonging effects of costimulatory blockade including that induced by clinically used CTLA4Ig. PMID: 25719262
- these studies delineate a protective role for vitamin D receptor signaling in Ron-induced mammary tumorigenesis through disruption of beta-catenin activation. PMID: 26008979
- These studies define mechanisms associated with hormonal regulation of the Vdr and hint at the differential nature of VDR binding activity at the Vdr gene in different primary target tissues in vivo. PMID: 26504088
- VDR expression is lost in the majority of the colon tumor cells. PMID: 25873367
- cross-talk between the maternal decidua and the placenta, as well as maternal vitamin D status, may be more important in determining pregnancy outcome than conceptus expression of VDR. PMID: 26121239
- Dysbiosis caused by vitamin D receptor deficiency confers colonization resistance to Citrobacter rodentium through modulation of innate lymphoid cells. PMID: 25315967
- Our findings show a direct, VDR-mediated, protective effect of 1,25(OH) )2D3 against ischemic injury-induced blood-brain barrier dysfunction in cerebral endothelial cells PMID: 25815722
- PPARgamma was also decreased upon treatment with VDR siRNA. The above results demonstrate that active vitamin D promoted M1 phenotype switching to M2 via the VDR-PPARg pathway. PMID: 25961000
- Myeloid VDR deletion enables M2 monocytes to transport cholesterol into atherosclerotic plaques. PMID: 25801026
- VDR is a novel endogenous self-defensive and cardioprotective receptor against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury, via mechanisms (at least in part) reducing oxidative stress, and inhibiting apoptosis and autophagy. PMID: 25365634
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus. Cytoplasm.
-
蛋白家族:Nuclear hormone receptor family, NR1 subfamily
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:22337
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000023119
UniGene: Mm.245084
Most popular with customers
-
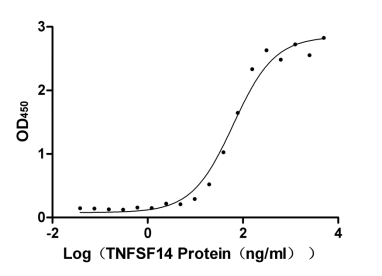
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 14 (TNFRSF14), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
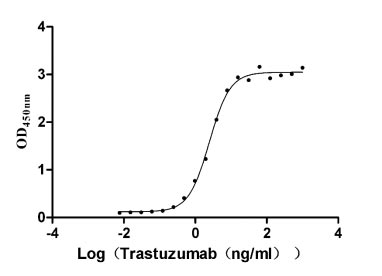
Recombinant Human Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 (ERBB2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human R-spondin-1 (RSPO1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Rat Microtubule-associated protein tau (Mapt) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
Recombinant Human Microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
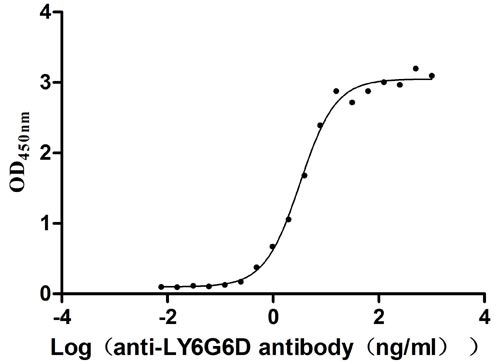
Recombinant Human Lymphocyte antigen 6 complex locus protein G6d (LY6G6D) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
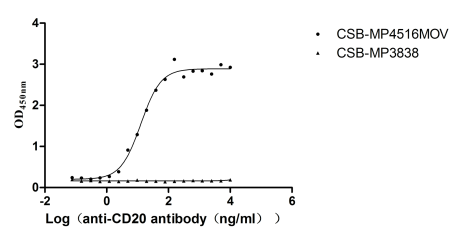
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Membrane spanning 4-domains A1 (MS4A1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)



-AC1.jpg)