Recombinant Mouse cGMP-dependent protein kinase 1 (Prkg1)
-
中文名称:小鼠Prkg1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP018715MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Prkg1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP018715MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Prkg1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP018715MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Prkg1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP018715MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Prkg1; Prkg1b; Prkgr1a; Prkgr1bcGMP-dependent protein kinase 1; cGK 1; cGK1; EC 2.7.11.12; cGMP-dependent protein kinase I; cGKI
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length of Mature Protein
-
表达区域:2-671
-
氨基酸序列SELEEDFAK ILMLKEERIK ELEKRLSEKE EEIQELKRKL HKCQSVLPVP STHIGPRTTR AQGISAEPQT YRSFHDLRQA FRKFTKSERS KDLIKEAILD NDFMKNLELS QIQEIVDCMY PVEYGKDSCI IKEGDVGSLV YVMEDGKVEV TKEGVKLCTM GPGKVFGELA ILYNCTRTAT VKTLVNVKLW AIDRQCFQTI MMRTGLIKHT EYMEFLKSVP TFQSLPDEIL SKLADVLEET HYENGEYIIR QGARGDTFFI ISKGQVNVTR EDSPSEDPVF LRTLGKGDWF GEKALQGEDV RTANVIAAEA VTCLVIDRDS FKHLIGGLDD VSNKAYEDAE AKAKYEAEAA FFANLKLSDF NIIDTLGVGG FGRVELVQLK SEESKTFAMK ILKKRHIVDT RQQEHIRSEK QIMQGAHSDF IVRLYRTFKD SKYLYMLMEA CLGGELWTIL RDRGSFEDST TRFYTACVVE AFAYLHSKGI IYRDLKPENL ILDHRGYAKL VDFGFAKKIG FGKKTWTFCG TPEYVAPEII LNKGHDISAD YWSLGILMYE LLTGSPPFSG PDPMKTYNII LRGIDMIEFP KKIAKNAANL IKKLCRDNPS ERLGNLKNGV KDIQKHKWFE GFNWEGLRKG TLTPPIIPSV ASPTDTSNFD SFPEDSDEPP PDDNSGWDID F
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Serine/threonine protein kinase that acts as key mediator of the nitric oxide (NO)/cGMP signaling pathway. GMP binding activates PRKG1, which phosphorylates serines and threonines on many cellular proteins. Numerous protein targets for PRKG1 phosphorylation are implicated in modulating cellular calcium, but the contribution of each of these targets may vary substantially among cell types. Proteins that are phosphorylated by PRKG1 regulate platelet activation and adhesion, smooth muscle contraction, cardiac function, gene expression, feedback of the NO-signaling pathway, and other processes involved in several aspects of the CNS like axon guidance, hippocampal and cerebellar learning, circadian rhythm and nociception. Smooth muscle relaxation is mediated through lowering of intracellular free calcium, by desensitization of contractile proteins to calcium, and by decrease in the contractile state of smooth muscle or in platelet activation. Regulates intracellular calcium levels via several pathways: phosphorylates IRAG1 and inhibits IP3-induced Ca(2+) release from intracellular stores, phosphorylation of KCNMA1 (BKCa) channels decreases intracellular Ca(2+) levels, which leads to increased opening of this channel. PRKG1 phosphorylates the canonical transient receptor potential channel (TRPC) family which inactivates the associated inward calcium current. Another mode of action of NO/cGMP/PKGI signaling involves PKGI-mediated inactivation of the Ras homolog gene family member A (RhoA). Phosphorylation of RHOA by PRKG1 blocks the action of this protein in myriad processes: regulation of RHOA translocation; decreasing contraction; controlling vesicle trafficking, reduction of myosin light chain phosphorylation resulting in vasorelaxation. Activation of PRKG1 by NO signaling alters also gene expression in a number of tissues. In smooth muscle cells, increased cGMP and PRKG1 activity influence expression of smooth muscle-specific contractile proteins, levels of proteins in the NO/cGMP signaling pathway, down-regulation of the matrix proteins osteopontin and thrombospondin-1 to limit smooth muscle cell migration and phenotype. Regulates vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) functions in platelets and smooth muscle.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- These data thus demonstrate the existence of two differently distributed cGKI isoforms in the dorsal root ganglion, and may provide insight into the cellular and molecular mechanisms of pain. PMID: 30152261
- This study demonstrates that H- ras deletion protects against AngII-induced cardiac remodeling, possibly via a mechanism in which PKG-Ibeta overexpression could play a partial role, and points to H-Ras and/or downstream proteins as potential therapeutic targets in cardiovascular disease. PMID: 29054855
- that PKG-I expressed in nociceptors is not only a key determinant of dorsal root ganglion hyperexcitability and spinal synaptic plasticity but also an important modulator of cortical neuronal activity in pathological pain states PMID: 28326941
- analysis of the role of binding interface with protein kinase G-Ialpha leucine zipper in vascular function PMID: 28280239
- Brown adipose tissue, via Nox4-derived hydrogen peroxide, induces cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase G type-1alpha activation, resulting in reduced vascular contractility. PMID: 28062507
- disulfide formation at Cys(43) does not directly activate PKGIalpha, and the C43S-mutant PKGIalpha has a higher Ka for cGMP. Results highlight that mutant enzymes should be carefully biochemically characterized before making in vivo inferences. PMID: 28360102
- PKG Ialpha disulfide formation triggers cardiac injury, and this initiation of maladaptive signaling can be blocked by pharmacological therapies that elevate cGMP, which binds kinase to limit its oxidation. PMID: 27342776
- Cyclic GMP kinase deletion causes iron deficiency anemia, duodenal ulcers, and bleeding in the knockout mice. PMID: 26830212
- Protein kinase G has a role in regulating production of H2S, which governs oxygen sensing PMID: 25900831
- these results demonstrate that myocardial PKG1alpha oxidation prevents a beneficial response to pathological stress, may explain variable responses to PKG1alpha pathway stimulation in heart disease PMID: 25938783
- Data show that cGMP-dependent kinase (cGK-Ialpha) knockdown partially rescued TNF-alpha-induced decrease in 42-kDa cGMP-dependent protein kinase-anchoring protein (GKAP42) and impairment of insulin signals. PMID: 25586176
- miR-20a expression is up-regulated in response to hypoxia in both mouse and human pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells PMID: 25447536
- These findings characterize PKG as a novel regulator of AR-mediated transcription by enhancing AR cofactor p44/WDR77's function. PMID: 23755100
- A functional leucine zipper domain in PKG-1alpha is essential for maintenance of a low pulmonary vascular tone in normoxia. PMID: 25128522
- For the initial phase of angiotenin II-induced cardiac hypertrophy, lack of cardiomyocyte cGKI activity does not worsen hypertrophic growth. PMID: 25139994
- the key role of PKG-I in transforming growth factor beta1 induction by like weak inducer of apoptosis in kidney cells PMID: 24872318
- Results indicate that cGMP, acting primarily through cGKIalpha, is an important suppressor of kidney fibrosis. PMID: 23760283
- cGKI and Trpc1,3,6 channels are not functionally coupled in vascular smooth cell. PMID: 23832809
- Increasing PKG activity ameliorates renal fibrosis in part through regulation of macrophage and tubular cell function, leading to reduced TGF-beta-induced fibrosis. PMID: 24573388
- cGMP, through activation of PKGI, inhibits c-Abl, leading to increased key antioxidant enzymes and resistance to lung endothelial oxidant injury. PMID: 24401847
- In dystrophic hearts, excess contractility and arrhythmia are coupled to TRPC6 and are ameliorated by its targeted suppression or PKG activation. PMID: 24449818
- PKG-1alpha dimerization is a major contributing factor to the vasodilator actions of DHEA. PMID: 24375799
- mutation of the PKGIalpha LZ domain produces a clinically relevant model for hypertensive heart disease of aging. PMID: 23657971
- ANP attenuates the inflammatory actions of histamine via endothelial GC-A/cGMP/cGKI signaling and inhibitory phosphorylation of TRPC6 channels. PMID: 23814119
- PKG positively regulates proteasome activities and proteasome-mediated degradation of misfolded proteins, likely through posttranslational modifications to proteasome subunits. PMID: 23770744
- Data indicate that oxidative activation of PKG Ialpha is a key mediator of hypotension and consequential organ injury during sepsis. PMID: 23716652
- RhoA is a PKGIalpha target and direct binding of activated PKGIalpha to RhoA is central to cGMP-mediated inhibition of the VSMC Rho kinase contractile pathway PMID: 23066013
- Data indicate that the 2 mechanisms (cGMP binding and the disulfide homodimer) of activating PKG1alpha are intricately linked with the binding of cGMP preventing oxidation to the disulfide state. PMID: 23006734
- PKG-I deficiency induces pulmonary hypertension through Rho A/Rho kinase activation-mediated vasoconstriction and pulmonary vascular remodeling. PMID: 22632818
- PKG-I-mediated presynaptic facilitation and synaptic long-term potentiation in spinal projection neurons is functionally involved in activity-dependent centrally mediated nociceptive hypersensitivity. PMID: 22427743
- these findings suggest that cGK-Ialpha interacts with and phosphorylates rhotekin, thereby contributing to neurite outgrowth regulation. PMID: 22503686
- Data show that protection of the duodenum from acid injury requires neuronal cGMP kinase I. PMID: 22253479
- Sodium depletion enhances renal expression of (pro)renin receptor via cyclic GMP-protein kinase G signaling pathway. PMID: 22203739
- role in noise-induced hearing loss and endogenous signaling pathway and activation of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase PMID: 22270721
- different signaling pathways exist for each cGKI isoform in vivo in fundus muscles PMID: 21914444
- There are sex differences in the effects of PKG-I activation on the regulation of adipose tissue function and diet-induced obesity. PMID: 20930715
- Genetic deletion of cGKI in non-neuronal cells results in a complex metabolic phenotype, including liver inflammation and fasting hyperglycemia. PMID: 21464444
- protein kinase G type-I is essential for promoting proliferation and cell survival of mouse bone marrow stromal cells PMID: 21328456
- Basal/moderately elevated PKG activity protects against high/pathological-level nitric oxide-induced apoptosis and promotes DNA synthesis/proliferation in vascular smooth muscle cells. PMID: 20060325
- cGKI modulates glucagon release by suppression of calcium in alpha cells in mice. PMID: 20978093
- Ang II suppression by ANP was abolished in cardiomyocytes of mice deficient in GC-A, in cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase I (PKG I) or in the regulator of G protein signalling (RGS) 2, a target of PKG I PMID: 20352235
- cGMP/cGKI signaling differentially inhibits contraction: in jejunum, inhibition is performed without changing [Ca(2+)](i) and is dependent on phosphatase activity, whereas in colon, inhibition is mediated by inhibition of [Ca(2+)](i) signals. PMID: 19628652
- Cyclis GMP, through PKGI, attenuated H(2)O(2)-induced cytotoxicity in lung microvascular endothelial cells by increasing catalase and Gpx-1 expression through an unknown posttranscriptional effect. PMID: 20453163
- evidence for PKGIalpha-dependent phosphorylation and activation of neuronal AAAD in vitro, and introduce AAAD as a putative PKGIalpha substrate. PMID: 20456015
- These data establish that glucose-mediated downregulation of PKG levels stimulates TSP1 expression and enhances TGF-beta activity and matrix protein expression, which can contribute to vascular remodeling in diabetes. PMID: 20164378
- Activation and inhibition of protein kinase G (PKG) respectively upregulates and downregulates recombinant potassium channel subfamily K (TASK1) channels heterologously expressed in PKG-loaded human embryonic kidney cells in vitro. PMID: 20410120
- cardiac myocyte cGKI does not affect the development of heart hypertrophy induced by pressure overload or chronic isoproterenol infusion PMID: 20212138
- (D)-Amino acid analogues of DT-2 as highly selective and superior inhibitors of cGMP-dependent protein kinase Ialpha. PMID: 20018259
- PKGI links NO and cGMP signaling with the RhoA-ROCK and the insulin pathways, thereby controlling induction of adipogenic and thermogenic programs during brown fat cell differentiation PMID: 19952371
- Cytosolic cGKI can support fear memory consolidation and LTP in neurons of the lateral amygdala via activation of CREB and CRE-dependent transcription. PMID: 20171263
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm.
-
蛋白家族:Protein kinase superfamily, AGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family, cGMP subfamily
-
组织特异性:Detected in cerebellum, hippocampus, dorsomedial hypothalamus, medulla, subcommissural organ, cerebral cortex, amygdala, habenulae, various hypothalamic regions, olfactory bulb, pituitary gland, and retina. Isoform alpha is prominent in the cerebellum and
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:19091
UniGene: Mm.381170
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human papillomavirus type 16 Protein E7 (E7) (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: Human papillomavirus type 16
-
Recombinant Human Cytokine receptor common subunit beta (CSF2RB), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Retinol-binding protein 4 (Rbp4) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Rat Microtubule-associated protein tau (Mapt) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
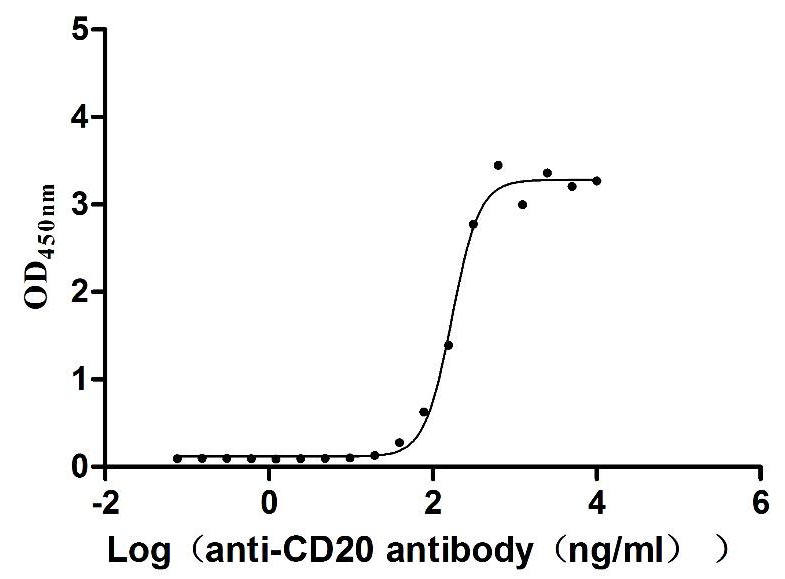
Recombinant Dog B-lymphocyte antigen CD20 (MS4A1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris)
-
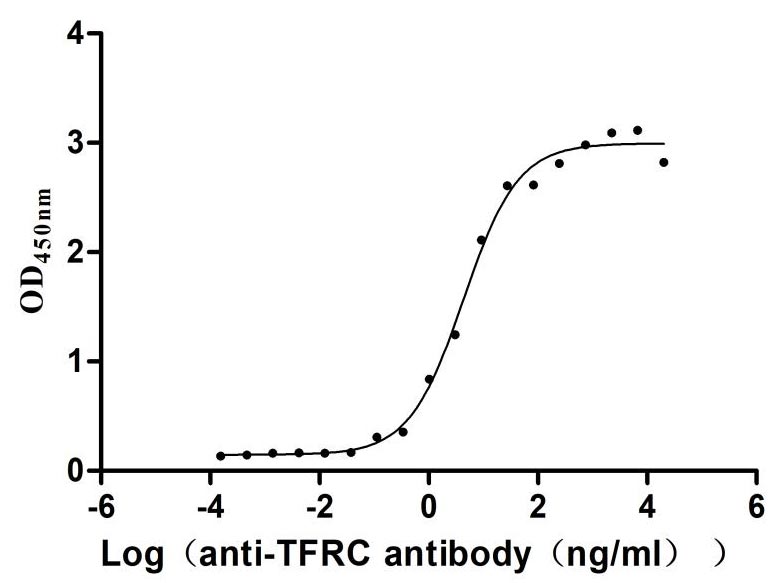
Recombinant Human Transferrin receptor protein 1 (TFRC), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
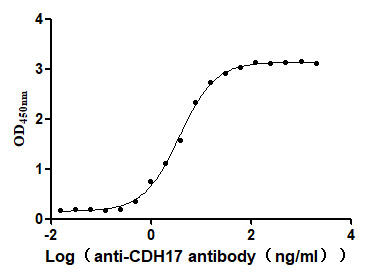
Recombinant Human Cadherin-17 (CDH17), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
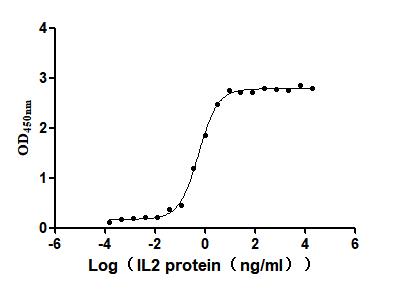
Recombinant Human Interleukin-2 (IL2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)