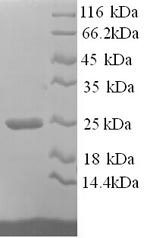
Recombinant Rat Collagen alpha-1 (I) chain, partial
-
货号:CSB-YP005727RA
-
规格:¥1836
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:Greater than 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Col1a1Collagen alpha-1(I) chain; Alpha-1 type I collagen
-
种属:Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
来源:Yeast
-
分子量:25.4kDa
-
表达区域:955-1207aa
-
氨基酸序列QRGERGFPGLPGPSGEPGKQGPSGASGERGPPGPMGPPGLAGPPGESGREGSPGAEGSPGRDGAPGAKGDRGETGPAGPPGAPGAPGAPGPVGPAGKNGDRGETGPAGPAGPIGPAGARGPAGPQGPRGDKGETGEQGDRGIKGHRGFSGLQGPPGSPGSPGEQGPSGASGPAGPRGPPGSAGSPGKDGLNGLPGPIGPPGPRGRTGDSGPAGPPGPPGPPGPPGPPSGGYDFSFLPQPPQEKSQDGGRYYRA
Note: The complete sequence including tag sequence, target protein sequence and linker sequence could be provided upon request. -
蛋白标签:N-terminal 6xHis-tagged
-
产品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:Tris-based buffer,50% glycerol
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Type I collagen is a member of group I collagen (fibrillar forming collagen).
-
基因功能参考文献:
- the activation of Pin1 promoted cardiac extracellular matrix deposition and oxidative stress damage by regulating the phosphorylation of the MEK1/2ERK1/2 signaling pathway and the expression of alphaSMA. PMID: 29286102
- In vitro analysis using LX2 HSC cells indicated that ATII can augment TGFbeta1 and collagen type I alpha1 mRNA expression via periostin expression, suggesting that the interaction between ATII and periostin may serve a role in liver fibrosis development. In conclusion, blockade of ATIIinduced periostin may suppress the progression of liver fibrosis development. PMID: 28849131
- miR21 regulates expression of alphaSMA and collagen I in activated rat hepatic stellate cells by directly targeting Smad7. PMID: 28731181
- Taken together, the lentiviral RNAi vector targeting the TGF beta-1 gene of rats was successfully constructed, which effectively silenced the TGF beta-1 gene of the HSCT6 cells and inhibited the expression of Col1a1. PMID: 28713909
- the diagnostic value of urinary collagen degradation products in a proteinuria-driven fibrosis rat model, was investigated. PMID: 28320405
- Brefeldin A induced a significant up-regulation of Col1a1 mRNA levels in CFSC-2G hepatic stellate cells that was time-dependent. The UPR correlated with enhanced mRNA and protein levels of collagen type I in these cells. Analysis of the 3 branches of UPR revealed the activation of IRE1alpha, PERK and ATF6 in response to BFA. An IRE1alpha-p38 MAPK-Smad pathway may be responsible for the fibrogenic action of BFA on HSC. PMID: 27155082
- treatment with LG ameliorated STZ-induced DN via the inhibition of oxidonitrosative stress as well as downregulation of KIM-1, NGAL, TGF-beta1, and collagen-1 mRNA expressions. PMID: 27756197
- In a liver fibrosis cellular model, tenascin-C promotes migration of hepatic stellate cells and production of type I collagen via TGF-beta1 and alpha9beta1 integrin pathway. PMID: 27031437
- Liganded vitamin D receptor through its interacting repressor inhibits the expression of Col1a1. PMID: 27351590
- In a pure VO model, chymase produced in adult cardiac fibroblasts leads to autophagic degradation of newly synthesized intracellular procollagen I, suggesting a new role of chymase in extracellular matrix degradation PMID: 26807691
- signaling through Na/K-ATPase regulates miRNAs and specifically, miR-29b-3p expression both in vivo and in vitro. PMID: 26702050
- A reciprocal regulatory relationship between DDR2 and collagen, involving cross-talk between the GPCR and RTK pathways, is central to Angiotensin II-induced increase in collagen expression in cardiac fibroblasts. PMID: 26674152
- Preferential sites for intramolecular glucosepane cross-link formation in type I collagen has been described. PMID: 26049074
- The present findings suggest that prolyl 3-hydroxylation incrementally regulates collagen fibril diameter in tendon. PMID: 26567337
- Flouride affected collagen I arrangement and produced ultrastructural changes in bone tissue. Meanwhile, the mRNA expression of COL1A1 and COL1A2 were reduced and the COL I protein levels decreased in the fluorosis group. PMID: 25655816
- High Collagen Type I expression is associated with renal fibrosis in experimental kidney diseases. PMID: 25784725
- Increased expression of Acan and Col2a1 along with decreased expression of Col1a1 and Mmp13 indicated formation of hyaline cartilage in this group. PMID: 25128628
- These data support the hypotheses that, in dentin, the interaction between COL1 and PP may initiate crystal nucleation and that additional interactions between PP and the growing crystals may modulate the crystal growth pattern and crystal size. PMID: 15609627
- Fetal and adult human skin fibroblasts retain their differential proliferative response to TGF-beta when cultured in the presence of fibronectin and unpolymerized or polymerized collagen. PMID: 24735795
- Regional differences in cell proliferation and fibronectin structure were dependent on both soluble fibronectin concentration and fibronectin-collagen type I interactions. PMID: 24116223
- This study suggests that laminin and type I collagen support the function of folliculostellate cells by increasing fibromodulin protein expression in the anterior pituitary. PMID: 23959432
- The naive effector cells of collagen type I during acute experimental pancreatitis are acinar cells and not pancreatic stellate cells PMID: 24036265
- Data suggest that miR-711-SP1-collagen-I pathway may be strategies for miRNA-based anti-fibrotic drug research. PMID: 23633075
- The DNMT-mediated DNA methylation is an important mechanism in regulating the TGF-beta1-induced COL1A1 gene expression. PMID: 23560091
- Hypothesized that reducing collagen I accumulation in glomerulosclerosis would lower Hic-5 expression,reducing apoptosis, and maintain glomerular integrity. NTU281 treatment reduced glomerular col I accumulation, Hic-5 and alpha-SMA expression, and apoptosis. PMID: 23508044
- These findings suggest that amide I nonlinear optical chiral effects in type I collagen assemblies arise predominantly from the chiral organization of amide chromophores within individual collagen molecules, rather than from supramolecular structures. PMID: 23200051
- Hypoxia alone can upregulate DNA synthesis and expression of collagen type I and III mRNA in adult rat cardiac fibroblasts. PMID: 21166192
- Crystal structures of Hsp47 in its free form and in complex with homotrimeric synthetic collagen model peptides, are presented. PMID: 22847422
- Curcumin could suppress bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting the synthesis and deposition of type I collagen and reducing expression of TGF-beta1. PMID: 18727865
- These data demonstrate a relationship between miR-133a and Col1A1, suggesting that myocardial fibrosis occurring in Ang II-dependent hypertension is regulated by the down-regulation of miR-133a and miR-29b through the modulation of Col1A1 expression. PMID: 21769867
- S-adenosyl-L-methionine inhibits Col1A1 processing leading to increased ubiquitination and decreased secretion. PMID: 21645221
- The regulatory effect of melatonin (MLT)cannot be explained by its effect on procollagen gene expression, since neither MLT nor pinealectomy is shown to have an influence on alpha1 (I) and alpha1 (III) procollagen mRNA content in the scar. PMID: 20388018
- High fat diet reduces the levels of type I tropocollagen and adiponectin and these effects are deleterious for skin function. PMID: 20397200
- Bushen Rougan Recipe can decrease the expressions of collagen type I and CTGF mRNAs in rats with hepatic fibrosis. PMID: 18782537
- Craniofacial growth and type I collagen gene expresion in the rat occur mainly between days 10 and 21. PMID: 20149607
- AT2 receptor is involved in collagen metabolism in cardiac fibroblasts by regulating the levels of Col I and TIMP-1 mRNA. PMID: 18095594
- Data support that post-translational glycosylation of collagen I has a role in the induction in endothelial cells in vitro of molecules conductive to self-organization in vessels-like structures. PMID: 20006603
- Deducted interpretations from our experimental approach suggest that Ang II stimulates indirectly (via SNS) and inhibits directly (via AT1 receptors) the collagen type I at transcriptional and protein levels. PMID: 19679517
- Type I collagen gene expression is affected by mechanical loading. PMID: 11924646
- Gene expression of TGF-beta1, type I collagen, and connective tissue growth factor using primary cultured pancreatic stellate cells. PMID: 12199527
- p38 MAPK mediates the regulation of alpha1(I) procollagen mRNA levels by TNF-alpha and TGF-beta in a cell line of rat hepatic stellate cells PMID: 12297293
- hypoxic enhancement of the posttranscriptional step of collagen synthesis contributed to the accelerated deposition of collagen fibrils PMID: 12408871
- dental pulp contains competent progenitor cells capable of differentiating into new generations of odontoblast-like cells which express high levels of Col1a1-2.3-GFP PMID: 12755333
- TRAM2, as a part of the translocon, is required for the biosynthesis of type I collagen by coupling the activity of SERCA2b with the activity of the translocon PMID: 14749390
- both p38 MAPK and Smad signaling independently and additively regulate alpha1(I) collagen gene expression by transcriptional activation PMID: 15647278
- Results show that 70-kDa ribosomal S6 kinase plays a crucial role in hepatic stellate cell proliferation, collagen type I expression, and cell cycle control, thus representing a potential therapeutic target for liver fibrosis. PMID: 15677443
- Results conclude that residues 19-46 of bone sialoprotein represent a novel collagen-binding site. PMID: 15703183
- Endo180 binds to the C-terminal region of type I collagen, and this interaction appears to play an important role in cell-matrix adhesion PMID: 15817460
- Our results demonstrate that inhibition of alphaI(I)-collagen gene expression by curcumin in activated HSCs results from suppression of CTGF gene expression through increasing cellular GSH contents and interruption of TGF-beta signaling. PMID: 16306131
- Data present a crystallographic determination of the collagen type I supermolecular structure. PMID: 16751282
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Secreted, extracellular space, extracellular matrix.
-
蛋白家族:Fibrillar collagen family
-
组织特异性:Forms the fibrils of tendon, ligaments and bones. In bones the fibrils are mineralized with calcium hydroxyapatite.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: rno:29393
STRING: 10116.ENSRNOP00000005311
UniGene: Rn.2953
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Early activation antigen CD69 (CD69), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Interleukin-2 receptor subunit alpha (IL2RA), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Zinc transporter ZIP6 isoform X1(SLC39A6),partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human Interleukin-12 receptor subunit beta-1(IL12RB1),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)