Recombinant Rat Excitatory amino acid transporter 2 (Slc1a2), partial
-
中文名称:大鼠Slc1a2重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP021433RA
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:大鼠Slc1a2重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP021433RA
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:大鼠Slc1a2重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP021433RA-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:大鼠Slc1a2重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP021433RA
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:大鼠Slc1a2重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP021433RA
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Slc1a2; Eaat2; Glt1Excitatory amino acid transporter 2; GLT-1; Sodium-dependent glutamate/aspartate transporter 2; GLUT-R; Solute carrier family 1 member 2
-
种属:Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Sodium-dependent, high-affinity amino acid transporter that mediates the uptake of L-glutamate and also L-aspartate and D-aspartate. Functions as a symporter that transports one amino acid molecule together with two or three Na(+) ions and one proton, in parallel with the counter-transport of one K(+) ion. Mediates Cl(-) flux that is not coupled to amino acid transport; this avoids the accumulation of negative charges due to aspartate and Na(+) symport. Essential for the rapid removal of released glutamate from the synaptic cleft, and for terminating the postsynaptic action of glutamate.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Expression of glutamate transporter-1 (GLT-1) in the supplementary motor area is reduced after strenuous exercise, resulting in an increased extracellular glutamate concentration and decreased extracellular lactate level that may be responsible for the development of fatigue. GLT-1-mediated uptake of glutamate ameliorates exercise-induced fatigue in rat models. PMID: 29603414
- Chronic voluntary wheel running results in increased gene expression of GLT-1 (and VGLUT3) in the frontal cortex without changes in other glutamate transporter subtypes. PMID: 29375045
- These data shed new light on the important role astrocytic EAAT2 plays on buffering nucleus tractus solitarii excitation and overall cardiorespiratory function. PMID: 28677303
- GLT-1 is up-regulated during the induction of brain ischemic tolerance after cerebral ischemic preconditioning. PMID: 26732590
- The data of this study reveal that astrocytic GLT-1 surface mobility,via its transport activity, is modulated during neuronal firing, which may be a key process for shaping glutamate clearance and glutamatergic synaptic transmission. PMID: 27189737
- Study suggests that mature astrocytes have low expression levels of xCT and that they do not depend on its function to survive. In contrast, oligodendrocytes, which express high levels of xCT, are the most vulnerable cell type of CNS to glutathione depletion upon chronic blockage of xCT or under oxidative glutamate toxicity. PMID: 27247047
- infection of co-cultures with shRNA directed against recombination signal binding protein for immunoglobulin kappa J, a Notch effector, also reduces endothelia-dependent increases in enhanced green fluorescent protein and GLT-1 PMID: 28771710
- his study showed an increased expression of glial (GLAST and GLT-1) after paraoxon exposure. PMID: 27769869
- the expression of GLT-1 on astrocytes decreased, but pretreatment with CEF seemed to prevent this downregulation. In addition, every intervention used in this study seemed to reduce xCT expression on astrocytes and neurons. The results of this study indicate that modulation of Glu transporter expression may restore Glu homeostasis PMID: 29045497
- Spinal glial glutamate transporters GLAST and GLT-1 have protective function by reducing and preventing selectively non-evoked pain behavior after incision. This is a result of increased GLAST expression regulated by the MAPK p38 after incision PMID: 26920805
- Ceftriaxone significantly increased glutamate transporter 1 expression in the prefrontal cortex and the nucleus accumbens of the nicotine (NIC) and NIC-EtOH rats as compared to NIC and NIC-EtOH saline-treated rats. These findings provide further support for GLT-1-associated mechanisms in EtOH and/or NIC abuse. PMID: 27060486
- GAT1 inhibitor administration also hindered Wnt3-induced neurogenesis. PMID: 27226528
- The effects of RNA interference-mediated GLT1 gene silencing on cell viability, JNK activation, NMDAR (NR1 and NR2B) activation, cell apoptosis and Akt activation in the hippocampal neuronal cells were slightly reversed by propofol treatment. PMID: 27430327
- Results suggest that, via astrocytes, IL-17A could promote glutamate excitotoxicity in multiple terms: by decreasing the astrocyte ability to uptake extracellular glutamate, due to a reduced gene expression of glutamate transporters (GLAST and GLT-1); by decreasing intracellular glutamate conversion into non-toxic glutamine; by potentiating glutamate exocytosis in a Ca2+ dependent manner PMID: 28104249
- The results of this study suggest that the regulation of GLT-1 and xc- plays a role in the development of cerebral tolerance to ischemia and that this regulation may be a novel approach in the therapy of brain ischemia. PMID: 26861954
- Maternal separation increased total GLT1 in hippocampi of SHR, WKY, and SD, and reduced GLT1b in SHR hippocampus PMID: 26464063
- Hypoxic exposure significantly increased SLC1A5 expression in neurovascular unit cells in vitro, but suppressed EAAT2 expression. PMID: 26459476
- Chronic postnatal stress led to decreased Glt1 expression in hippocampus and frontal cortex. PMID: 26037264
- only in the absence of chloride, GLT-1 GTS remains constant at all glutamate concentrations. Possible explanations for why apparent GTS might vary in the presence of chloride are discussed PMID: 26301411
- Study demonstrated that for the first time p-CX43 in the hippocampal astrocytes is important for the regulation of GLT-1 expession via activation of P2X7 receptors, which contributes to neuronic autophagy following traumatic brain injury PMID: 26031379
- Ceftriaxone significantly attenuated relapse-like ethanol intake partly through upregulation of the levels of GLT-1a and GLT-1b isoforms and xCT in the prefrontal cortex and the nucleus accumbens PMID: 24687412
- Results indicated that pre-ischemic exercise could exert neuroprotection against ischemic injury by promoting GLT-1 to promote the uptake of glutamate and inhibiting the mRNA expression level of NR2B and mGluR5 to reduce the excitotoxicity of glutamate PMID: 24907601
- Results suggest the role of glutamate excitotoxicity in neuronal death in the midline thalamic region following kainic acid-induced status epilepticus due to astrocytic EAAT2 downregulation. PMID: 25059512
- TNF-alpha substantially increased the expression of GLT-1a and GLT-1b in astrocyte cultures. PMID: 24836816
- GSK3beta stimulated the activity of GLT-1 and reduced that of GLAST PMID: 25454285
- studies further support the notion that GLT-1 is an attractive candidate molecule associated with the fundamental processes of MDD and may be a potential, and novel pharmacological target for the treatment of MDD. PMID: 25480579
- sumoylated EAAT2 localizes to intracellular compartments, whereas non-sumoylated EAAT2 resides on the plasma membrane PMID: 24753081
- A potential up-regulation of GLT-1 via ceftriaxone administration has detrimental effects on spatial learning and memory. PMID: 24650590
- Taken together, our results demonstrated that acute gastric mucosa injury induced by aspirin is related to reduction of glutamate-cystine/glutamate transporter system activity. PMID: 24866234
- Dopamine depletion from the prefrontal cortex increases membrane expression of GLT-1 protein, positively correlating with the extent of high-affinity dopamine depletion. PMID: 24611756
- Neuron-glial interactions contribute to mechanisms of psychostimulant addiction, particularly via expression and function of the GLT-1 astroglial glutamate transporter. PMID: 23985782
- Astrocytes exposed to thiamine deficient conditions resulted in a progressive decrease in glutamate uptake over 24 h. Immunoblotting and flow cytometry measurements indicated this was accompanied by a 20-40% loss of GLT-1b. PMID: 24735535
- This study demonistrated that Up-regulation of neuronal and astrocytic GLT-1 mRNA in the hippocampal CA1 subfield during the induction of brain ischemic tolerance in rat. PMID: 24442982
- findings suggest important roles for up-regulated EAAT2 in chronic brain ischemia especially in the regulation of high-affinity of extracellular glutamate and minimization of white matter damage PMID: 23602887
- YY1, with HDACs as corepressors, is a critical negative transcriptional regulator of EAAT2 and mediates Mn-induced EAAT2 repression. PMID: 24469401
- a role for neuronal transporters in glutamate accumulation observed in the retina following an ischemic event PMID: 23936321
- results demonstrate that glutamate transporters are differentially expressed in nervous structures of wild-type and transgenic animals although the total GLT-1 activity was constantly decreased during the disease progression PMID: 23665075
- Results show importance of EAAT2 and EAAT3 in the regulation of rat Llocus coeruleus by glutamate. Neuronal EAAT3 is responsible for terminating action of synaptically released glutamate, whereas glial EAAT2 regulates tonic glutamate concentrations. PMID: 23638698
- During the chronic period of this model of temporal lobe epilepsy, EAAT2 mRNA expression is decreased in the hippocampus. PMID: 23392471
- Data indicate that the scaffolding protein PICK1 (protein interacting with C kinase 1) interacts specifically with the glutamate transporter GLT1b. PMID: 23697999
- results shed light on the complex influence of the pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-alpha on GLT-1a mRNA and protein expression and on necessity to consider the GLT-1 isoforms with appropriate tools in studies addressing the regulation of glutamate transporters PMID: 21371514
- Downregulation of the cystine/glutamate antiporter system was accompanied by the progression of osteoarthritis. PMID: 23020698
- Reactive oxygen species and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 mediated reduction of GLT-1 expression may be involved in chemical hypoxia-induced neural injury. PMID: 22895544
- our study highlights the impact of an epigenetically adaptive DNA element of the GLT-1 promoter being decisive for brain region-specific activity and reactivity. PMID: 22593010
- GLT-1 protein up-regulation was observed in the traumatic brain injury group treated with ceftriaxon. PMID: 22710775
- data demonstrate that activation of GPR30 increases GLT-1 expression via multiple pathways, suggesting that GPR30 is worthwhile as a potential target to be explored for developing therapeutics of excitotoxic neuronal injury PMID: 22645130
- Subcellular distribution and dynamic remodeling of predominant GLT-1 into discrete clusters is examined in developing hippocampal astrocytes. PMID: 22052455
- Pigment epithelium-derived factor acts as an antioxidative agent against the decrease in GLAST expression in retinal Muller cells in diabetic conditions. PMID: 22266516
- higher expression of GLT-1 in the CA3 and DG contributes to their inherent resistance to ischemia PMID: 21925558
- Exon-4 skipping GLT 1 is abundantly expressed in the brain and may represent either a functional glutamate transporter or a modulator of glutamate transporter function. PMID: 21964391
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:Dicarboxylate/amino acid:cation symporter (DAACS) (TC 2.A.23) family, SLC1A2 subfamily
-
组织特异性:Localized in brain and is highly enriched in the Purkinje cell layer in cerebellum.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: rno:29482
STRING: 10116.ENSRNOP00000007604
UniGene: Rn.10240
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Lymphotoxin-alpha (LTA) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
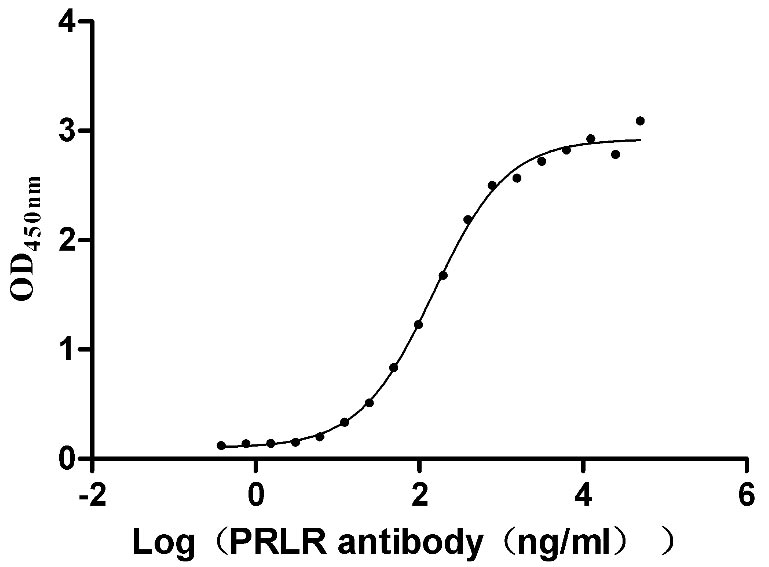
Recombinant Human Prolactin receptor (PRLR), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis CD44 antigen (CD44), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human Microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
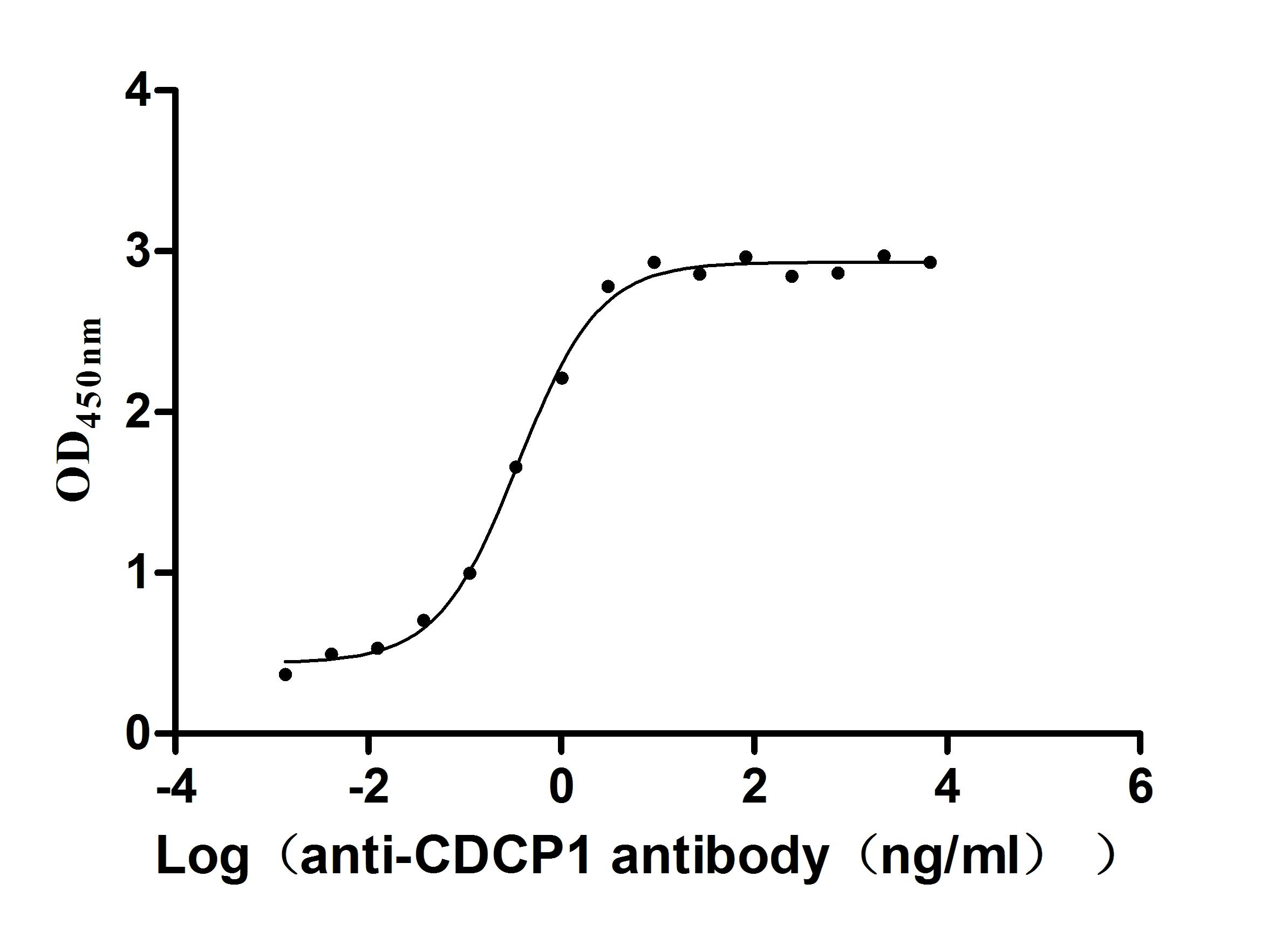
Recombinant Human CUB domain-containing protein 1 (CDCP1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator(BTLA), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Urokinase-type plasminogen activator(PLAU) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)