Recombinant Rat Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 11 (Tnfsf11), partial
-
货号:CSB-YP880653RA
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP880653RA
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP880653RA-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP880653RA
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP880653RA
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Tnfsf11; Opgl; Rankl; Trance; Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 11; Osteoclast differentiation factor; ODF; Osteoprotegerin ligand; OPGL; Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand; RANKL; TNF-related activation-induced cytokine; TRANCE; CD antigen CD254) [Cleaved into: Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 11; membrane form; Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 11; soluble form]
-
种属:Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Cytokine that binds to TNFRSF11B/OPG and to TNFRSF11A/RANK. Osteoclast differentiation and activation factor. Augments the ability of dendritic cells to stimulate naive T-cell proliferation. May be an important regulator of interactions between T-cells and dendritic cells and may play a role in the regulation of the T-cell-dependent immune response. May also play an important role in enhanced bone-resorption in humoral hypercalcemia of malignancy. Induces osteoclastogenesis by activating multiple signaling pathways in osteoclast precursor cells, chief among which is induction of long lasting oscillations in the intracellular concentration of Ca (2+) resulting in the activation of NFATC1, which translocates to the nucleus and induces osteoclast-specific gene transcription to allow differentiation of osteoclasts. During osteoclast differentiation, in a TMEM64 and ATP2A2-dependent manner induces activation of CREB1 and mitochondrial ROS generation necessary for proper osteoclast generation.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- results of this study concluded that the RANK, RANK-L and OPG system participates in bone remodeling after RME PMID: 29297549
- in this animal model the increase of RANK/RANKL and HGF markers is related to a specific immune response, and probably contributed to the evolution of periodontal disease PMID: 29211121
- In the supplemented and nonsupplemented rats groups, RANKL was upregulated compared with the control group. PMID: 28473060
- the canonical Wnt pathway inhibitor DKK1 blocked the osteogenesis effect and rescued the ratio of RANKL/OPG in periodontal ligament stem cells under force treatment for 1h PMID: 27154288
- study identified a number of differentially expressed bone-related mRNAs of potential significance and confirmed the osteoprotegerin/receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B (RANK)/RANK ligand (RANKL) pathway PMID: 25406873
- High-dose diosgenin treatment down-regulated expression of RANKL significantly in tibia from OVX rats compared to control. PMID: 25257532
- Data indicate that after loading jump (JL) for 6 weeks, the expressions of of interleukin 6 (IL-6), and ligand of receptor activator of NF-kappaB (RANKL) genes were markedly elevated in tibia. PMID: 25200151
- mechanical stimulation inhibits the activity of RANKL in rats PMID: 23553492
- Our findings indicate that the expression of RANKL in the occlusal portion of the bony crypt is unrelated to osteoclast recruitment and differentiation but is crucial to their activation during the creation of the eruption pathway. PMID: 23636419
- RANK and RANKL were expressed by T lymphocytes and macrophages in acute cellular kidney rejection after transplantation in rats PMID: 23769040
- In rheumatoid arthritis methotrexate/leflunomide combination therapy would relive the synovium hypertrophy through depressing cell viability and osteoclasia through decreasing RANKL and Il-17. PMID: 23334376
- There was no change in OPN expression after orthodontic retention and bone remodeling. PMID: 22353912
- the increase in RANK-RANKL expression is a response to podocyte injury, and RANK-RANKL may be a novel receptor-ligand complex for the survival response during podocyte injury. PMID: 22848465
- Insulin could promote osteoblastic differentiation of calcifying vascular smooth muscle cells by increased RANKL expression through ERK1/2 activation, but not PI3K/Akt activation. PMID: 22194983
- TRANCE/RANKL is constituively expressed by rat plasmacytoid dendritic cells. PMID: 22428075
- Pressure-overloaded myocardium generates RANKL, which induces inflammation mediators and myocardial inflammation. PMID: 22298642
- Bone loss and recovery in a receptor activator for nuclear factor kappa B ligand (RANKL)-administered rat model was assessed PMID: 20480144
- RANKL/OPG are key factors linking bone formation to resorption during bone remodeling. PMID: 21771583
- Vitamin C deficiency increased osteoclastogenesis by increasing RANK expression. PMID: 20444587
- These results suggest that antibody to RANKL can inhibit A. actinomycetemcomitans-specific T cell-induced periodontal bone resorption by blockade and reduction of tissue sRANKL. PMID: 21078845
- RANKL contributes to vascular calcification by regulating bone morphogenetic protein-2 and calcification inhibitor matrix Gla protein (MGP) expression, as well as bone-related proteins, and is counteracted by estrogen in a receptor-dependent manner. PMID: 20595654
- the toothless (tl) osteopetrotic rat mutation is not in the TNFSF11 locus PMID: 11804028
- accelerates nuclear translocation of nuclear factor kappa B in osteoclasts by elevaing cytosolic Ca2+ PMID: 12496256
- Effects of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate on osteoclastogenesis and its role in RANKL-induced signaling. PMID: 14672351
- RANK ligand is strongly up-regulated during acute heart allograft rejection; its blockade prolongs rat heart allograft survival. PMID: 14734743
- Detection of RANKL mRNA and protein in bone cells. PMID: 15704000
- Results suggest that the RANKL expressed in thymic epithelial cells plays a role in the development of T cells during thymic regeneration. PMID: 15844004
- Portasystemic shunting caused low turnover osteoporosis that was RANKL independent. PMID: 16874862
- Prolactin decreased RANKL mrna in cultured osteoblasts. PMID: 18432284
- These data indicate that serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels are a major determinant of osteoclastogenesis and bone mineral volume. PMID: 18597628
- Recombinant RANKL (rRANKL) mutants within the TNF-like core domain exhibited diminished osteoclastogenic potential as compared with wild-type rRANKL1 encoding the full TNF-like core domain [amino acids (aa) 160-318]. PMID: 19008464
- Orchiectomy increases the concentration of free sRANKL in bone marrow of aged rats. PMID: 19501680
- Bony spur formation can thus be considered a process that occurs independent of TNFalpha and RANKL and is triggered by destructive arthritis. PMID: 19714640
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Single-pass type II membrane protein.; [Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 11, soluble form]: Secreted.
-
蛋白家族:Tumor necrosis factor family
-
组织特异性:Highly expressed in thymus and bone tissues.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: rno:117516
STRING: 10116.ENSRNOP00000013210
UniGene: Rn.217570
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human CD226 antigen (CD226), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-3 (ERBB3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Transthyretin (Ttr) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Claudin (CLDN18)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human Complement component C1q receptor (CD93), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
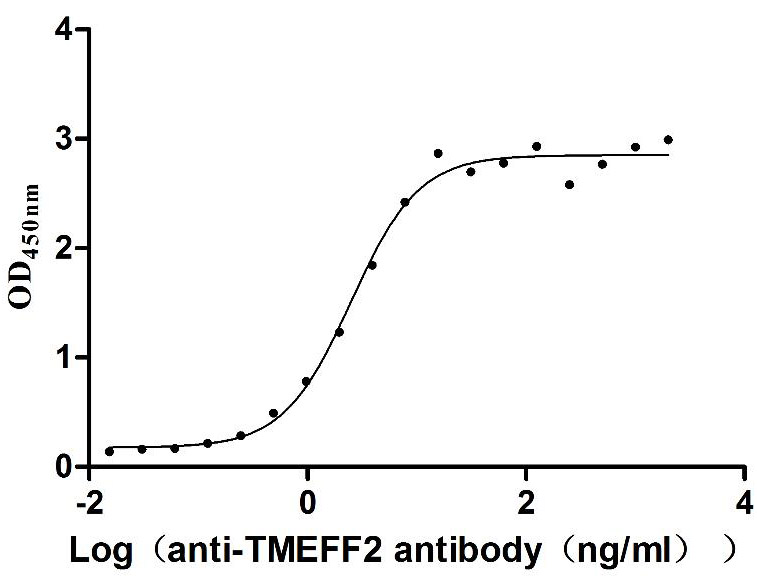
Recombinant Human Tomoregulin-2 (TMEFF2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
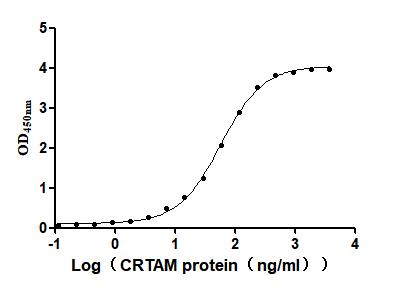
Recombinant Mouse Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (Crtam), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
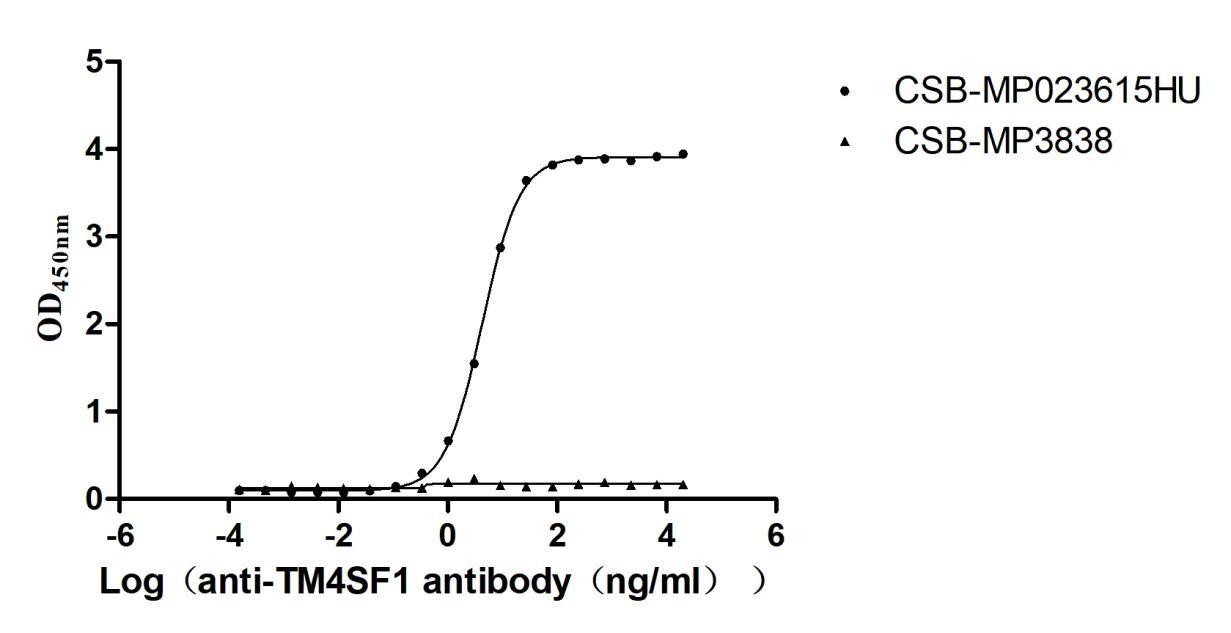
Recombinant Human Transmembrane 4 L6 family member 1(TM4SF1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)