Recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae Pheromone alpha factor receptor (STE2), partial
-
中文名称:酿酒酵母STE2重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP517141SVG1
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:酿酒酵母STE2重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP517141SVG1
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:酿酒酵母STE2重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP517141SVG1-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:酿酒酵母STE2重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP517141SVG1
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:酿酒酵母STE2重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP517141SVG1
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:STE2
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:STE2; YFL026W; Pheromone alpha factor receptor
-
种属:Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Receptor for the peptide pheromone alpha factor, the mating factor of yeast.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Interaction between Ste2p and Gpa1p takes palce before ligand binding via the Ste2p C-terminal domain and the Gpa1p N-terminal domain. PMID: 28958779
- yeast pheromone receptor Ste2 forms predominantly tetramers at average expression levels of 2 to 25 molecules per pixel and a mixture of tetramers and octamers at expression levels of 25-100 molecules per pixel. Ste2 is a class D GPCR found in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae of the mating type a, and binds the pheromone a-factor secreted secreted by cells of the mating type a PMID: 27993568
- The main difference between the Ste2 and Ste3 receptor observed in this work was that while hyperactive mutations were found for Ste3, no gain-of-function mutant for the Ste2 receptor was found. this fi nding is an outcome of the different strategies the two genes have adopted for their expression. PMID: 27150158
- Results suggest that the G-protein-coupled receptor, Ste2 binds the inhibitory G-protein signaling, Sst2 forming a complex with antagonistic functions. PMID: 28034910
- Variable Dependence of Signaling Output on Agonist Occupancy of Ste2p, a G Protein-coupled Receptor in Yeast PMID: 27646004
- results extend previous observations and quantify the contributions of Ste2p variants to mediating cell cycle arrest versus downstream mating functionalities. PMID: 26232403
- we propose that the N-terminus of Ste2p plays multiple regulatory roles in controlling receptor function. PMID: 26707753
- A strategy for the identification of stabilized variants of the yeast alpha-factor receptor Ste2p. PMID: 25647246
- Results show that Ste2 is downregulated by endocytosis, both constitutive and ligand induced and its internalization requires its phosphorylation and ubiquitinylation through the action of alpha arrestins. PMID: 24820415
- C-terminally trancated forms of Ste2p exert dominant-negative effects. PMID: 22923047
- structure determination of transmembrane segments of Y4 and the yeast Ste2p G-protein-coupled receptors PMID: 22947943
- the identification of disulfide bonds that stabilize the active state of the yeast alpha-mating pheromone receptor Ste2p PMID: 22387470
- C-terminus contains multiple functional domains with differential and interdependent roles in regulating Ste2p function. PMID: 22100461
- a cryptic polyadenylation site is present inside the coding region of the a-specific STE2 gene, encoding the receptor for the alpha-factor PMID: 21969566
- study provides new information about role of specific residues of STE2, a GPCR, in signal transduction and how peptide ligand binding activates the receptor PMID: 21728340
- These results suggest that receptor--agonist interactions, such as those involving Ste2p, involve at least two sites, of which only one is specific for the activated conformation of the receptor. PMID: 21477594
- Kinetic analysis suggests that alpha-factor associates with its receptor STE2 via a two-stage process consisting of an initial binding event followed by a rearrangement of the ligand-receptor complex. PMID: 15491163
- Thirty-five different STE2 suppressor mutations were identified by isolating second-site suppressor mutations that restored function to defective receptors carrying either an F204S or Y266C substitution. PMID: 15667221
- NMR analysis; findings suggest helical subdomains existed in both the transmembrane and cytosolic tail; as the tail participates in down-regulation of Ste2p, helical regions in the tail may play a role in protein-protein interactions in endocytosis PMID: 16128581
- there is an interaction between specific residues in an active state, but not the resting state, of Ste2p PMID: 16314417
- that G protein signaling and homologous desensitization are independent cellular processes PMID: 16325780
- TEDS site phosphorylation of the yeast myosins I is required for ligand-induced but not for constitutive endocytosis of Ste2p PMID: 16478726
- signal transduction by oligomeric Ste2p receptors appears to be a cooperative process requiring an interaction between functional monomers PMID: 16709573
- Amiono acid residues of Ste2 that are accessible to the cytoplasmic G-protein are defined and provide an important structural framework for the interpretation of the role of Ste2 residues that function in G-protein activation. PMID: 17176053
- an interaction between Ste2p and Ste3p has roles in yeast cellular mating PMID: 17369365
- presence of an alpha-helix in the segment encompassing residues 10-30, which is perturbed around the internal Pro-24 residue PMID: 17449670
- set the stage for the determination of the 3D structure of these large domains of a G protein-coupled receptor in micelles using high-resolution NMR PMID: 18260136
- alpha-Factor induced stabilization of the dimeric form and higher order oligomeric forms of the Ste2p receptor. PMID: 18996443
- Study is the first to report DOPA cross-linking of a peptide hormone to a GPCR and the first to identify a residue-to-residue cross-link between Ste2p and alpha-factor, thereby defining a specific contact point between the bound ligand and its receptor. PMID: 19152328
- high-resolution NMR study on an 80-residue fragment of Ste2p; data support stable fold for the TM parts of TM1-TM2; NMR structure is consistent with biochemical experiments that identified the ligand-binding site within this region of the receptor PMID: 19383463
- Results support the conclusion that G protein-coupled receptors, including Ste2, form oligomers and not just dimers, since TM1 and TM4 are too far apart in the class A GPCRs to form contacts in the same dimer moiety. PMID: 19588927
- The effect of ligand (alpha-factor) on dimer formation of STE2 suggests that dimers are formed in the resting state and the activated state of the receptor by different transmembrane interactions. PMID: 19839649
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:G-protein coupled receptor 4 family
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: sce:YFL026W
STRING: 4932.YFL026W
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human HLA class II histocompatibility antigen gamma chain (CD74), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
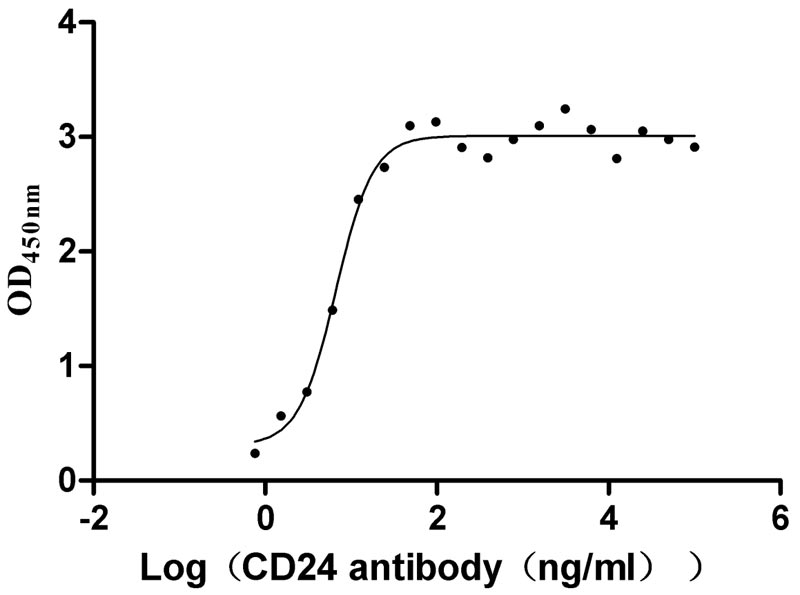
Recombinant Human Signal transducer CD24 (CD24)-Nanoparticle (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 8 (CCR8)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
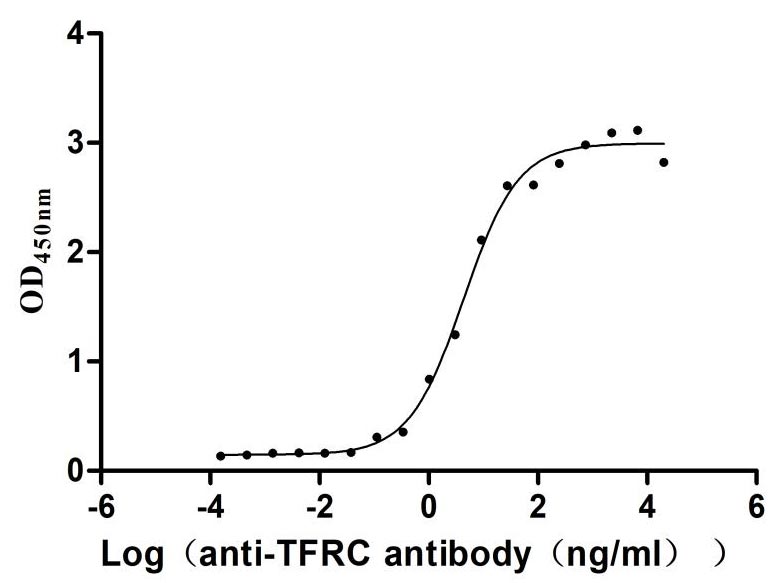
Recombinant Human Transferrin receptor protein 1 (TFRC), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
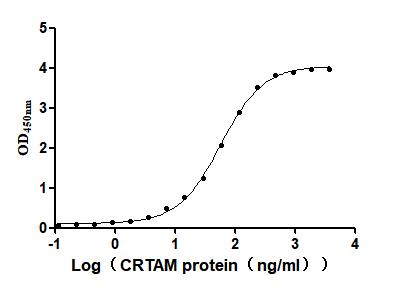
Recombinant Mouse Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (Crtam), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human CD70 antigen (CD70), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Kidney-associated antigen 1(KAAG1) (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Mucin-13(MUC13),partial (Active)
Express system: yeast
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)