Recombinant Human Intermediate conductance calcium-activated potassium channel protein 4 (KCNN4)
-
货号:CSB-CF012086HU
-
规格:¥9720
-
图片:
-
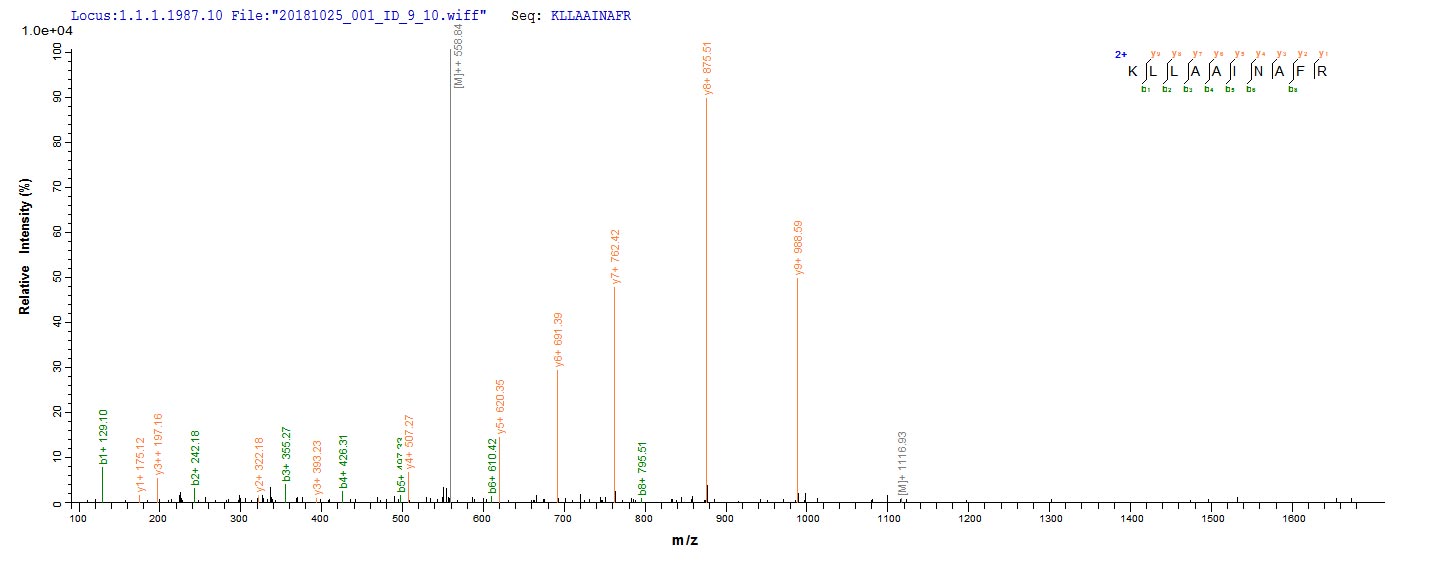
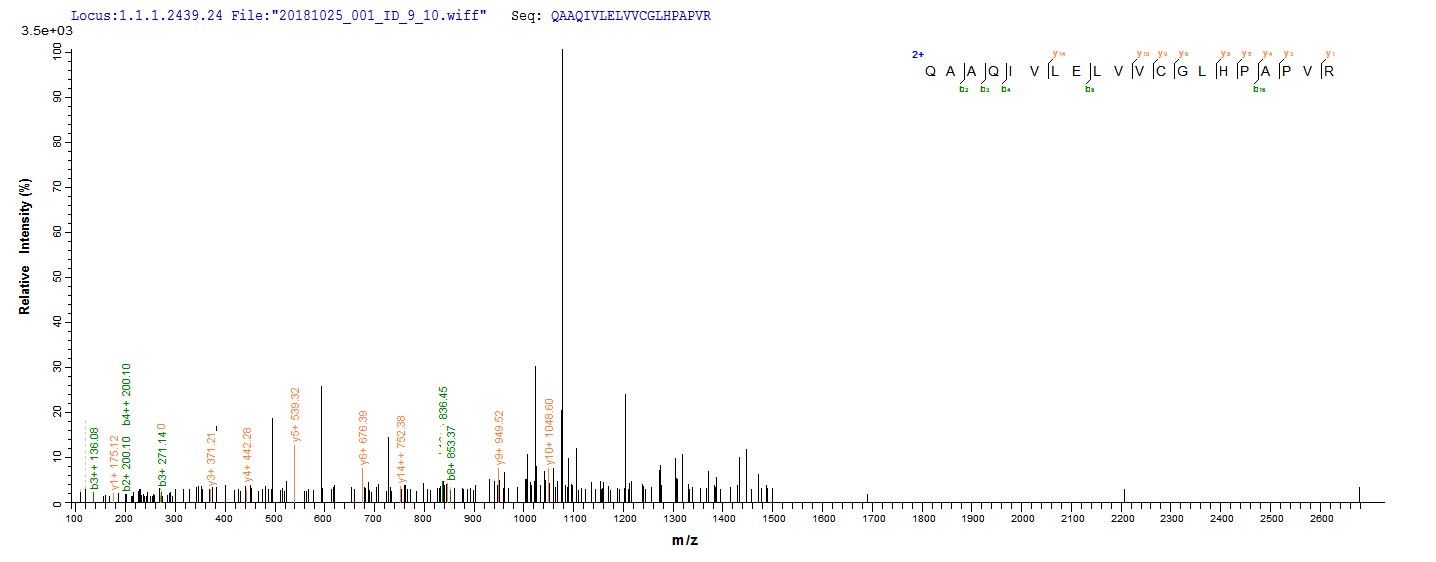
Based on the SEQUEST from database of E.coli host and target protein, the LC-MS/MS Analysis result of CSB-CF012086HU could indicate that this peptide derived from E.coli-expressed Homo sapiens (Human) KCNN4.
-
Based on the SEQUEST from database of E.coli host and target protein, the LC-MS/MS Analysis result of CSB-CF012086HU could indicate that this peptide derived from E.coli-expressed Homo sapiens (Human) KCNN4.
-
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:Greater than 85% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:KCNN4; IK1; IKCA1; KCA4; SK4; Intermediate conductance calcium-activated potassium channel protein 4; SKCa 4; SKCa4; IKCa1; KCa3.1; KCa4; Putative Gardos channel
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length
-
来源:in vitro E.coli expression system
-
分子量:59.1 kDa
-
表达区域:1-427 aa
-
氨基酸序列MGGDLVLGLGALRRRKRLLEQEKSLAGWALVLAGTGIGLMVLHAEMLWFGGCSWALYLFLVKCTISISTFLLLCLIVAFHAKEVQLFMTDNGLRDWRVALTGRQAAQIVLELVVCGLHPAPVRGPPCVQDLGAPLTSPQPWPGFLGQGEALLSLAMLLRLYLVPRAVLLRSGVLLNASYRSIGALNQVRFRHWFVAKLYMNTHPGRLLLGLTLGLWLTTAWVLSVAERQAVNATGHLSDTLWLIPITFLTIGYGDVVPGTMWGKIVCLCTGVMGVCCTALLVAVVARKLEFNKAEKHVHNFMMDIQYTKEMKESAARVLQEAWMFYKHTRRKESHAARRHQRKLLAAINAFRQVRLKHRKLREQVNSMVDISKMHMILYDLQQNLSSSHRALEKQIDTLAGKLDALTELLSTALGPRQLPEPSQQSK
Note: The complete sequence including tag sequence, target protein sequence and linker sequence could be provided upon request. -
蛋白标签:N-terminal 10xHis-tagged
-
产品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:Lyophilized from Tris/PBS-based buffer, 6% Trehalose
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
产品描述:
This recombinant HumanKCNN4 protein is an in vitro E.coli (cell-free) expressed Full Length protein. Its purity is 85%+ determined by SDS-PAGE. Cell-free protein expression is the in vitro synthesis of a protein using translation-compatible extracts of whole cells. In principle, whole-cell extracts contain all the macromolecules and components needed for transcription, translation, and even post-translational modification. These components include RNA polymerase, regulatory protein factors, transcription factors, ribosomes, and tRNA. When supplemented with cofactors, nucleotides, and the specific gene template, these extracts can synthesize proteins of interest in a few hours.
The KCNN4 is the encoding gene for the KCa3.1/SK4, which plays a critical role in calcium-activated anion secretion in mice and humans. It is abundantly expressed in non-excitable cells such as erythrocytes, lymphocytes, and placenta cells. The KCa3.1 has been found to participate in the pacemaker activity of cardiomyocytes sourcing from human embryonic stem cells (hESC-CMs). It is involved in cancer progression, including cell proliferation, apoptosis, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and metastasis. -
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Forms a voltage-independent potassium channel that is activated by intracellular calcium. Activation is followed by membrane hyperpolarization which promotes calcium influx. Required for maximal calcium influx and proliferation during the reactivation of naive T-cells. Plays a role in the late stages of EGF-induced macropinocytosis.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- These results suggest that His358, the inhibitory histidine in KCa3.1, might coordinate a copper ion through a similar binding mode. PMID: 29953543
- present study was designed to evaluate in hereditary xerocytosis the functional link between mutated Piezo1 and KCNN4 PMID: 28619848
- this study reports cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of a human SK4-CaM channel complex in closed and activated states at 3.4- and 3.5-angstrom resolution, respectively. PMID: 29724949
- Expression of intermediate-conductance calmodulin/calcium-activated K+ channels 3.1 (KCa3.1) mRNA and protein was detected in all three layers of the human cornea. PMID: 29554088
- KCa3.1 channels are important modulators in hepatocellular homeostasis. PMID: 27354175
- Tumor suppressor miR-497-5p down-regulates KCa3.1 expression and contributes to the inhibition of angiosarcoma malignancy development. PMID: 27531900
- We identified a two-gene signature including KCNN4 and S100A14 which was related to recurrence in optimally debulked serous ovarian carcinoma patients PMID: 27270322
- Human arrhythmogenic calmodulin mutations impede the activation of SK2 channels in human embryonic kidney 293 cells. PMID: 27165696
- This study found a very substantial functional expression of KCa3.1 channels in microglia from adult epilepsy patients. PMID: 27470924
- Data show that RNAi-mediated knockdown of KCa3.1 and/or TRPC1 leads to a significant decrease in cell proliferation due to cell cycle arrest in the G1 phase. PMID: 27183905
- Higher epithelial KCNN4 expression was closely correlated with advanced TNM stages and predicted a poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. PMID: 29050937
- Here, the s demonstrate that phosphorylation of His358 activates KCa3.1 by antagonizing copper-mediated inhibition of the channel. PMID: 27542194
- This work demonstrates the critical role of SK4 Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channels in adult pacemaker function. PMID: 28219898
- Blocking KCa3.1 suppresses plaque instability in advanced stages of atherosclerosis by inhibiting macrophage polarization toward an M1 phenotype. PMID: 28062499
- IKCa1 is overexpressed in cervical cancer tissues, and IKCa1 upregulation in cervical cancer cell linea enhances cell proliferation, partly by reducing the proportion of apoptotic cells. PMID: 28280257
- Findings suggest that SK4 channels are expressed in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells and are involved in the proliferation, apoptosis, migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition processes of TNBC cells. PMID: 27124117
- KCa3.1 blockade protects against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury through the attenuation of apoptosis by interference with intrinsic apoptotic and endoplasmic reticulum stress-related mediators. PMID: 26438401
- KCa3.1 in human immature dendritic cells play a major role in their migration and constitute an attractive target for the cell therapy optimization PMID: 27020659
- The results suggest that KCa3.1 activation contributes to dysfunctional tubular autophagy in diabetic nephropathy through PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways. PMID: 27029904
- that KCa3.1 channels are key actors in the migration capacity of neutrophils, and its inhibition did not affect other relevant cellular functions PMID: 26138196
- KCa3.1 and CFTR colocalize at the plasma membrane. PMID: 27092946
- KCNN4 inhibition differentially regulates migration of intestinal epithelial cells in inflamed vs. non-inflamed conditions in a PI3K/Akt-mediated manner. PMID: 26824610
- KCa3.1 protein expression was increased in asthmatic compared to healthy airway epithelium in situ, and KCa3.1 currents were larger in asthmatic compared to healthy HBECs cultured in vitro PMID: 26689552
- Data show that calcium-dependent potassium channel KCa3.1 operates as a positive feedback mechanism for intracellular Ca2+ increase. PMID: 26418693
- high KCa3.1-mRNA expression levels were indicative of low disease specific survival of ccRCC patients, short progression-free survival, and a high metastatic potential. Therefore, KCa3.1 is of prognostic value in ccRCC PMID: 25848765
- KCa3.1 activation in human lung mast cells is highly dependent on Ca(2+) influx through Orai1 channels, mediated via a close spatiotemporal interaction between the two channels. PMID: 26177720
- Novel Gardos channel mutations linked to dehydrated hereditary stomatocytosis (xerocytosis). PMID: 26178367
- describes patients from 2 well-phenotyped hereditary xerocytosis (HX) kindreds, including from one of the first HX kindreds described, who lack predicted heterozygous PIEZO1-linked variants PMID: 26198474
- identification of a dominantly inherited missense mutation in the Gardos channel in 2 unrelated families and its association with chronic hemolysis and dehydrated cells, also referred to as hereditary xerocytosis PMID: 26148990
- Inhibition of K(Ca)3.1 by EETs (14,15-EET), 20-HETE, and omega3 critically depended on the presence of electron double bonds and hydrophobicity within the 10 carbons preceding the carboxyl-head of the molecules. PMID: 25372486
- Ca2+- and KCa3.1-dependent processes facilitate "constitutive" alpha smooth muscle actin expression and Smad2/3 signalling in IPF-derived fibroblasts, and thus promote fibroblast to myofibroblast differentiation. PMID: 25476248
- The role and mechanisms of KCa3.1 in progressive diabetic chronic kidney disease are reviewed. PMID: 25415613
- The present study shows that KCNN4 is expressed at the mRNA and protein level in RA-SFs, is functionally active, and has a regulatory impact on cell proliferation and secretion of pro-inflammatory and pro-destructive mediators. PMID: 25545021
- Overexpression of CCL20 in human proximal tubular cells is inhibited by blockade of KCa3.1 under diabetic conditions through inhibition of the NF-kappaB pathway. PMID: 24733189
- Blood brain barrier endothelial cells exhibit KCa3.1 protein and activity. PMID: 25477223
- These data suggest that NO activates KCNN4 channels through the PKG but not the PKA pathways. PMID: 24826782
- Mg(2+) inhibits KCa3.1 via a rapid, voltage-dependent mechanism that leads to a reduction of the channel's unitary current and by reducing the open probability of the channel PMID: 24193405
- Tumor-associated macrophages participate in the metastasis of CRC induced by PRL-3 through secretion of IL-6 and IL-8 in a KCNN4 dependent manner. PMID: 24885636
- KCa3.1 confers an invasive phenotype that significantly worsens a patient's outlook with malignant glioma. PMID: 24585442
- These findings highlight a novel role for the KCa3.1 channel in human BSM cell phenotypic modulation. PMID: 24055799
- blockade of KCa3.1 attenuates diabetic renal interstitial fibrogenesis through inhibiting activation of fibroblasts PMID: 24166472
- The channel gating process for KCa3.1 and the S5 transmembrane segment is controlled by aromatic-aromatic interactions involving the pore helix. PMID: 24470490
- KCa3.1 has a role in diabetic nephropathy. (review) PMID: 24963668
- Our findings suggest that KCa3.1 channels play an important role in the pathogenesis of chronic AV and constitute an attractive target for the prevention of arteriopathy. PMID: 24312257
- Our results suggested that IKCa1 may play a role in the proliferation of human HCC, and IKCa1 blockers may represent a potential therapeutic strategy for HCC. PMID: 23392713
- KCa3.1 pharmacological blockade attenuated human myofibroblast proliferation, wound healing, collagen secretion and contractility in vitro, and this was associated with inhibition of TGFbeta1-dependent increases in intracellular free Ca2+. PMID: 24392001
- blocking KCa3.1 increases the degranulation and cytotoxicity of adherent Natural killer cells, but not of non-adherent-Natural killer cells. PMID: 24146918
- This study provides insight into the key molecular determinants for the high-affinity binding of peptide toxins to KCa3.1. PMID: 24138859
- KCa3.1 activity has an important role in glioblastoma invasiveness. PMID: 23949222
- Globotriaosylceramide accelerates the endocytosis and lysosomal degradation of endothelial KCa3.1 via a clathrin-dependent process, leading to endothelial dysfunction in Fabry disease. PMID: 24158513
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Dehydrated hereditary stomatocytosis 2 (DHS2)
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:Potassium channel KCNN family, KCa3.1/KCNN4 subfamily
-
组织特异性:Widely expressed in non-excitable tissues.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 6293
OMIM: 602754
KEGG: hsa:3783
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000262888
UniGene: Hs.10082
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Pro-neuregulin-1, membrane-bound isoform (NRG1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Glucagon receptor (GCGR), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Angiopoietin-2 (ANGPT2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
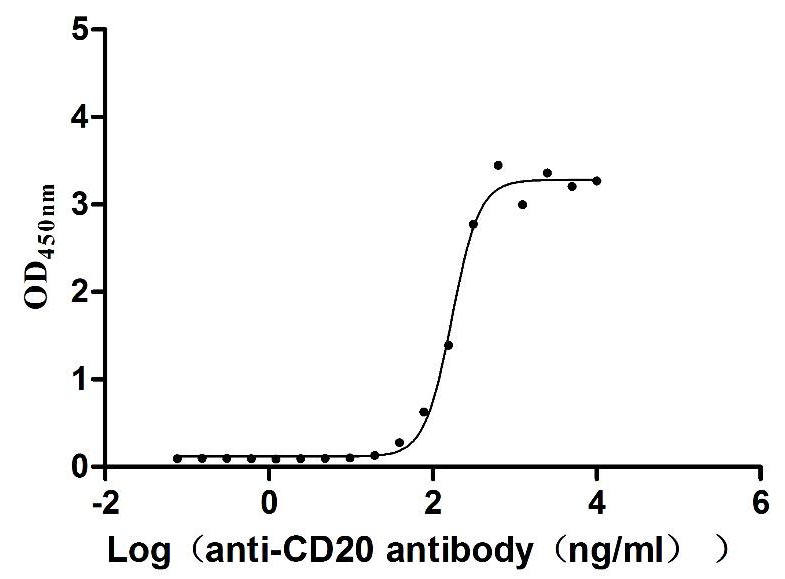
Recombinant Dog B-lymphocyte antigen CD20 (MS4A1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris)
-
Recombinant Human Claudin-6 (CLDN6)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Dickkopf-related protein 1 (DKK1) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
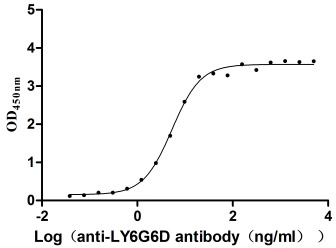
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis lymphocyte antigen 6 family member G6D (LY6G6D) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)


-AC1.jpg)

-AC1.jpg)

-AC1.jpg)
-AC1.jpg)