Recombinant Mouse ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 11 (Kcnj11)
-
中文名称:小鼠Kcnj11重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-CF730752MO
-
规格:
-
来源:in vitro E.coli expression system
-
其他:
产品详情
-
基因名:Kcnj11
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Kcnj11; ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 11; Inward rectifier K(+ channel Kir6.2; Potassium channel, inwardly rectifying subfamily J member 11
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:full length protein
-
表达区域:1-390
-
氨基酸序列MLSRKGIIPEEYVLTRLAEDPAEPRYRTRERRARFVSKKGNCNVAHKNIREQGRFLQDVF TTLVDLKWPHTLLIFTMSFLCSWLLFAMVWWLIAFAHGDLAPGEGTNVPCVTSIHSFSSA FLFSIEVQVTIGFGGRMVTEECPLAILILIVQNIVGLMINAIMLGCIFMKTAQAHRRAET LIFSKHAVITLRHGRLCFMLRVGDLRKSMIISATIHMQVVRKTTSPEGEVVPLHQVDIPM ENGVGGNGIFLVAPLIIYHVIDSNSPLYDLAPSDLHHHQDLEIIVILEGVVETTGITTQA RTSYLADEILWGQRFVPIVAEEDGRYSVDYSKFGNTIKVPTPLCTARQLDEDRSLLDALT LASSRGPLRKRSVAVAKAKPKFSISPDSLS
Note: The complete sequence including tag sequence, target protein sequence and linker sequence could be provided upon request. -
蛋白标签:N-terminal 10xHis-tagged
-
产品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:Lyophilized from Tris/PBS-based buffer, 6% Trehalose, pH 8.0
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:This receptor is controlled by G proteins. Inward rectifier potassium channels are characterized by a greater tendency to allow potassium to flow into the cell rather than out of it. Their voltage dependence is regulated by the concentration of extracellular potassium; as external potassium is raised, the voltage range of the channel opening shifts to more positive voltages. The inward rectification is mainly due to the blockage of outward current by internal magnesium. Can be blocked by extracellular barium. Can form cardiac and smooth muscle-type KATP channels with ABCC9. KCNJ11 forms the channel pore while ABCC9 is required for activation and regulation.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- lack of Kir6.2 promoted neuronal differentiation via inhibiting the downregulation of glia cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), which negatively related to the level of microRNA-133b. PMID: 29564810
- reduced age-dependent weight gain of WNK1 TG mice seems to be related with the decreased Kir6.2 expression via WNK1- and WNK4-regulated protein stability of Kir6.2. PMID: 29392534
- both Kir6.1(V65M) and Kir6.2(V64M) mutations essentially abolish high-affinity sensitivity to the KATP blocker glibenclamide in both intact cells and excised patches. This raises the possibility that, at least for some CS mutations, sulfonylurea therapy may not prove to be successful and highlights the need for detailed pharmacogenomic analyses of CS mutations. PMID: 28842488
- data demonstrate that increased Kir6.2 is seen in reactive astrocytes in old 3xTg-Alzheimer's disease (AD) mice and human AD tissue PMID: 27586053
- ATP-sensitive K(+) Kir6.2 channels may play a novel role in regulating myocardial energy metabolism. PMID: 28667052
- Cardiac ischemia causes a loss of the sarcolemmal KATP channel density by internalization through a pathway mediated by dynamin-dependent endocytosis and CaMKII-mediated signaling. Ischemic preconditioning counteracts thiscloss and restores the density of the sarcolemmal KATP channels. PMID: 27037371
- Lack of kcnj11 expression increases peroxynitrite-mediated modification of the key calcium-handling protein sarcoendoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPase after myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury, contributing to impaired diastolic function. PMID: 28209764
- K(ATP) channels seem to play an essential role in murine myometrial motility via activation of SUR2B and Kir6.2 PMID: 27086859
- A Conserved Residue Cluster That Governs Kinetics of ATP-dependent Gating of Kir6.2 Potassium Channels. PMID: 25934393
- ATP-sensitive potassium currents from channels formed by Kir6 and a modified cardiac mitochondrial SUR2 variant PMID: 24037327
- The Kir6.2-containing K-ATP channel is required for cardioprotection of resveratrol. PMID: 24498880
- Report mechanical dyssynchrony as an early marker of cardiomyopathic disease in ATP-sensitive K channel-deficient dilated cardiomyopathy. PMID: 24308936
- a role of K(ATP)-channel-dependent neuronal excitability in catecholaminergic neurons in maintaining thermogenic BAT sympathetic tone and energy homeostasis. PMID: 24011078
- Data indicate that betaIV-Spectrin-targeted CaMKII directly phosphorylates the inwardly-rectifying potassium channel, Kir6.2. PMID: 24101510
- Kir6.2 subunits are critical in resistance to endotoxemia-induced cardiac dysfunction through reducing myocardial damage by inhibition of apoptosis and inflammation. PMID: 23659427
- These findings reveal unrecognized slide helix elements that are required for functional channel expression and control of Kir6.2 gating by intracellular ATP. PMID: 23798684
- We found that perfused hearts from Kir6.2(-/-) mice exhibited a normal baseline response to ischemia-reperfusion injury, were not protected by ischemic preconditioning PMID: 23585131
- Data from Kir6.2 knockout mice suggest that KATP channel-independent mechanism mediated by vagus nerve plays critical role in insulin secretion by pancreatic beta cells in response to eating of dietary carbohydrates. PMID: 23608222
- CaMKII phosphorylation of Kir6.2 promotes endocytosis of cardiac ATP-sensitive potassium channels. PMID: 23223335
- The mutation Kir6.2-V59M decreases ATP block of cardiac K(ATP) channels but did not affect heart function, suggesting that metabolic changes fail to open the mutated channel to an extent that affects function (at least in the absence of ischaemia). PMID: 22252471
- Kir6.2/SUR2B complex can be inhibited by protein kinase C in a Ca(2+)-dependent manner and that this inhibition is likely to be as a result of internalization. PMID: 22207763
- Report unique properties of the ATP-sensitive potassium channel in the mouse ventricular cardiac conduction system. PMID: 21984445
- Kir6.2-containing K(ATP) channels play an important role in maintaining myocardial oxygenation balance under acute stress conditions and in post-stress recovery. PMID: 20202704
- The novel cGMP/PKG/ROS/calmodulin/CaMKII signaling pathway may regulate cardiomyocyte excitability by opening K(ATP) channels and contribute to cardiac protection against ischemia-reperfusion injury. PMID: 21479273
- Homozygous male and female adult Kcnj11 ( Y12STOP ) mice exhibited impaired glucose tolerance and a defect in insulin secretion as measured in vivo and in vitro. PMID: 20694718
- Ankyrin-B regulates Kir6.2 membrane expression and function in heart. PMID: 20610380
- Sequestration of Kir6.2 in rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) of Sur1 ( -/- ) islet cells is associated with an increase in rough endoplasmic reticulum length and mild oxidative stress without activation of the classical ER stress response. PMID: 20383647
- the glycine at 156 is not essential for K(ATP) channel gating and the Kir6.2 gating defect caused by the G156R mutation could be rescued by manipulating chemical interactions between pore residues PMID: 20032456
- Kir6.2 potaasium channel govern muscle energy economy, and their downregulation in a tissue-specific manner could present an antiobesity strategy by rendering muscle increasingly thermogenic at rest and less fuel efficient during exercise. PMID: 20074528
- the SUR1 TMD0-Kir6.2 interface is mobile and that the gating modes of Kir6.2 correlate with distinct positions of TMD0 PMID: 19933268
- Kir6.2 channels figure prominently in modulating ischemia/reperfusion injury in the mouse PMID: 11854323
- interaction of H+ with ATP in regulating a cloned K(ATP) channel, i.e. Kir6.2 expressed with and without the SUR1 subunit. PMID: 12205184
- Kir6.2 has a role in maintaining homeostasis and adapting to stress PMID: 12271142
- Ba(2+) was used to determine the location of the ligand-sensitive gate in Kir6.2. Internal Ba(2+) could still access its binding site when the channel was shut. The ligand-sensitive gate lies within or above the selectivity filter. PMID: 12524524
- intact K(ATP) channels are integral in ischemic preconditioning-induced protection of cellular energetic dynamics and associated cardiac performance PMID: 12598229
- four mutations associated with congenital hyperinsulinism disrupted K(ATP) channel activity by different mechanisms PMID: 12627323
- Results identify two amino acids in the ATP-sensitive potassium channel Kir6.2 that appear to interact directly with ATP and may contribute to the ATP binding site. PMID: 12805206
- Using Kir6.2 tandem dimer constructs, evidence is provided that the ion pair likely forms by residues from two adjacent Kir6.2 subunits and that the E229/R314 intersubunit ion pairs may contribute to a structural framework. PMID: 12885877
- The transgenic overexpression of Kir6.2 in forebrain significantly protects mice from hypoxic-ischemic injury and neuronal damage seen in stroke. PMID: 15080888
- GIP is the major insulinotropic factor in the secretion of insulin in response to glucose load in K(ATP) channel-deficient mice. PMID: 15362972
- Arcuate nucleus neurons have the ability to sense higher glucose concentrations than 5 mmol/l through a new K(ATP) channel-independent mechanism. PMID: 15504956
- Deficit in repolarization reserve, demonstrated in Kir6.2-knockout hearts, translated into a high risk for induction of triggered activity and ventricular dysrhythmia. PMID: 15561906
- As seen in knockout mice, Kir6.2-containing K(ATP) channel activity is required for attainment of the physiologic benefits of exercise training without injury. PMID: 15561907
- Kir6.2 null and Kir6.1 null mice reveal that KATP channels are critical metabolic sensors in acute metabolic changes, including hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia, ischemia, and hypoxia. (review) PMID: 15561908
- Although Kir6.2 is expressed in multiple tissues, its primary functional consequence in both transgenic and knockout mice is enhanced beta-cell electrical activity. PMID: 15561946
- the present study using Kir6.2 knockout hearts provides evidence that the activation of K(ATP) channels contributes to the shortening of APD, whereas it is not the primary cause of extracellular K(+) accumulation during early myocardial ischemia PMID: 15598870
- use homology modelling and ligand docking to construct a model of the Kir6.2 tetramer and identify the ATP-binding site. Ligand binding occurs at the interface between two subunits PMID: 15650751
- Conformational dynamics of the ligand-binding domain of Kir6.2 PMID: 15749783
- the epoxyeicosatrienoic acid-Kir6.2 interaction may allosterically change the ATP binding site on Kir6.2, reducing the channel sensitivity to ATP PMID: 15760904
- glucose-sensing cells in the pancreas and hypothalamus employ a similar set of stimulus-response elements PMID: 15782099
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:Inward rectifier-type potassium channel (TC 1.A.2.1) family, KCNJ11 subfamily
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:16514
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000136002
UniGene: Mm.333863
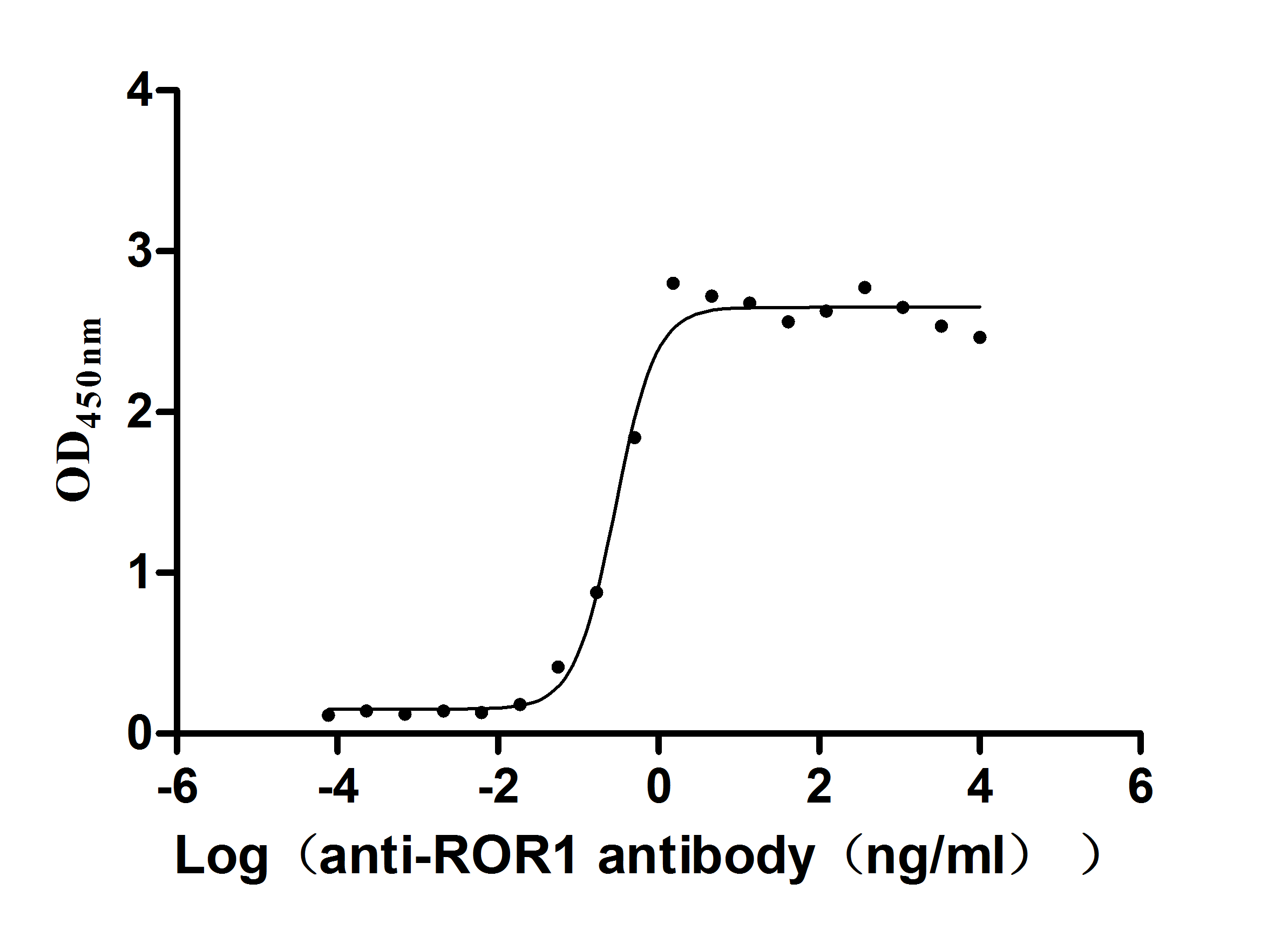
Most popular with customers
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
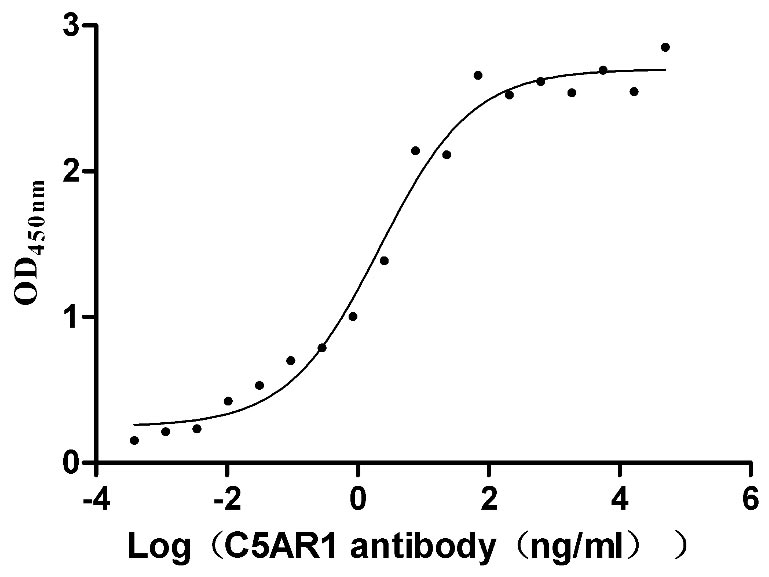
Recombinant Human C5a anaphylatoxin chemotactic receptor 1 (C5AR1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
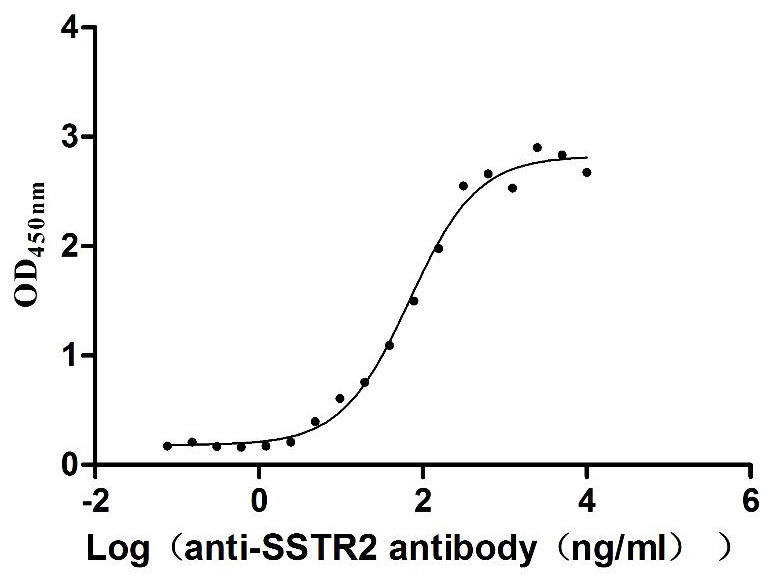
-
Recombinant Human Somatostatin receptor type 2 (SSTR2)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
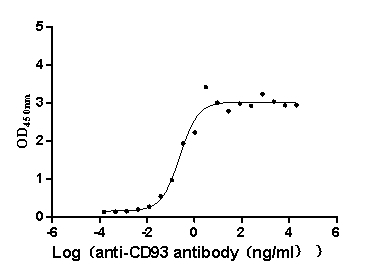
-
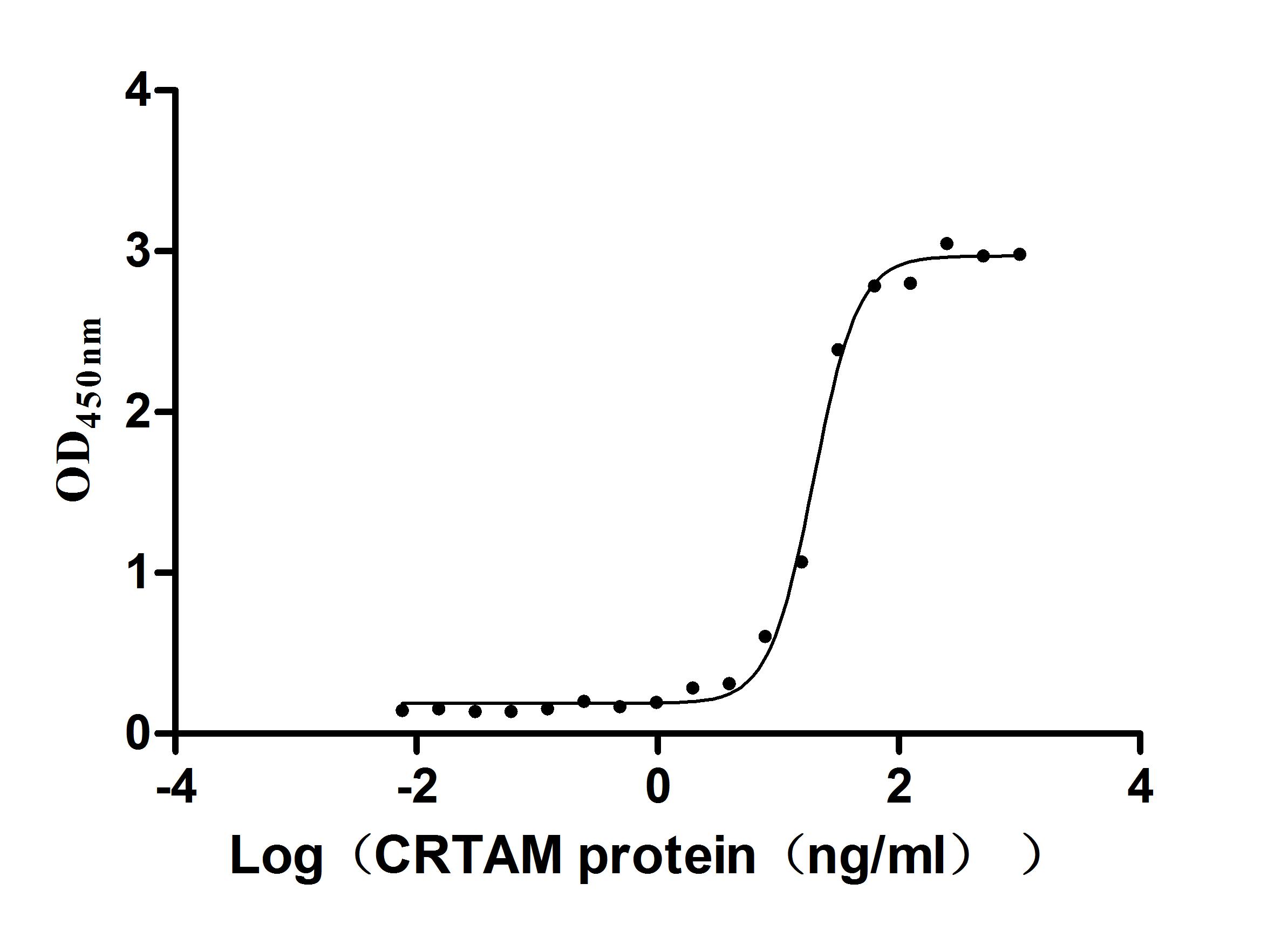
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis CD93 molecule (CD93), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
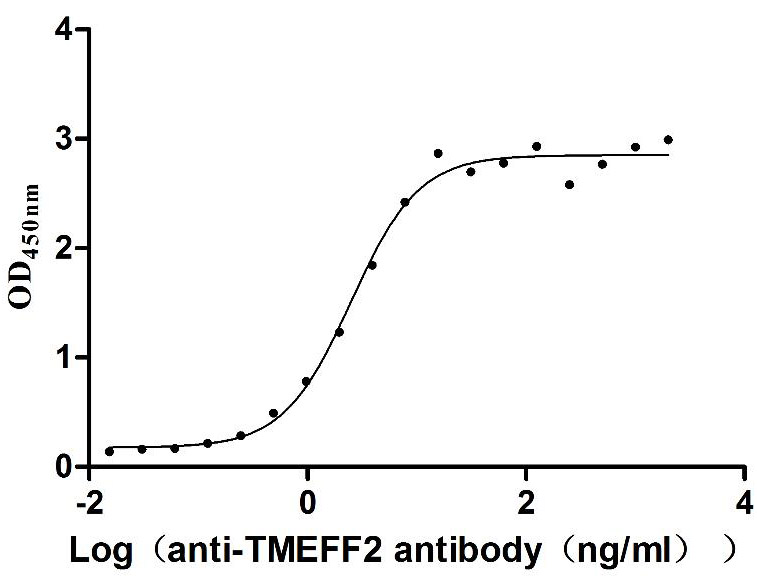
Recombinant Human Tomoregulin-2 (TMEFF2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Cell adhesion molecule 1 (CADM1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
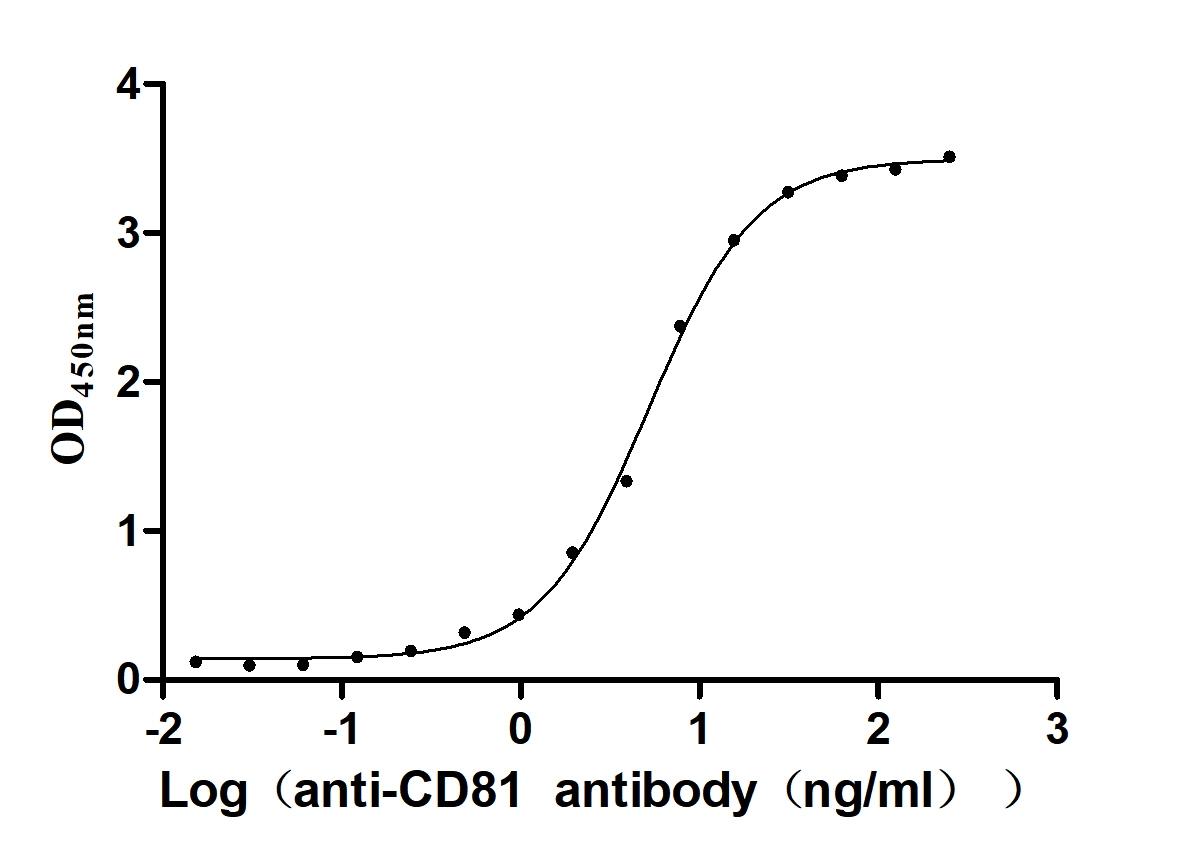
Recombinant Human CD81 antigen (CD81), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)