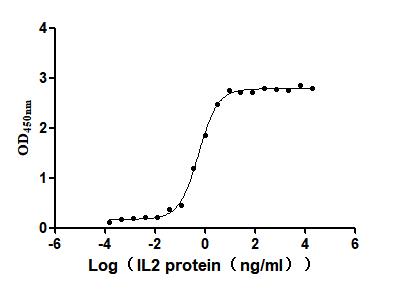
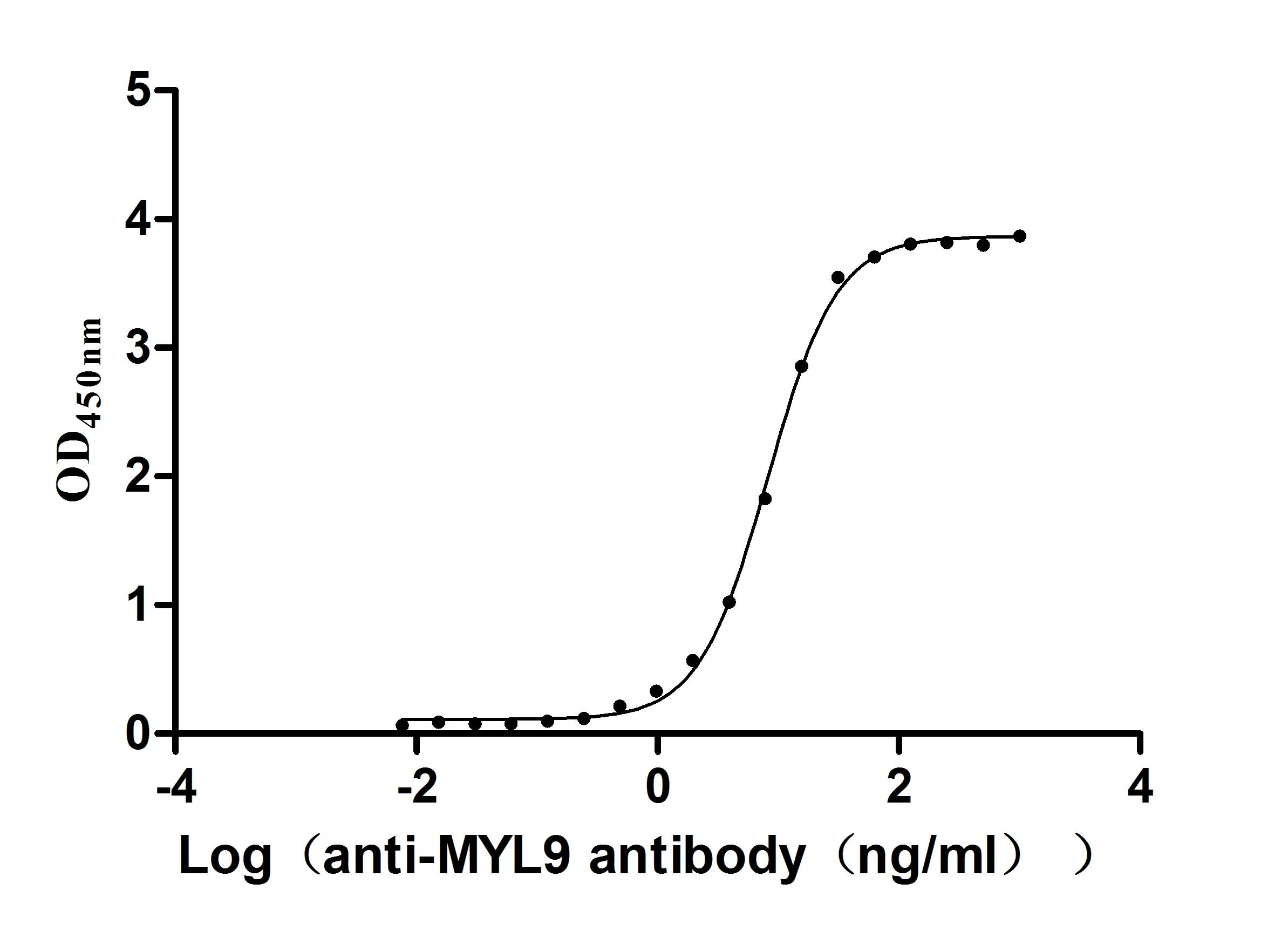
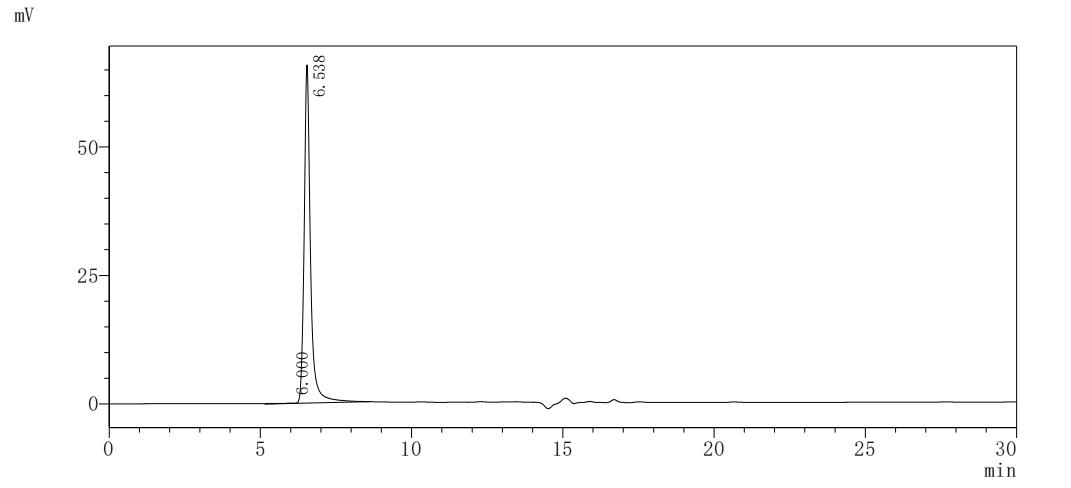
Recombinant Mouse Early activation antigen CD69 (Cd69)
-
货号:CSB-CF004952MO
-
规格:
-
来源:in vitro E.coli expression system
-
其他:
产品详情
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Cd69; Early activation antigen CD69; CD antigen CD69
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:full length protein
-
表达区域:1-199
-
氨基酸序列MDSENCSITENSSSHLERGQKDHGTSIHFEKHHEGSIQVSIPWAVLIVVLITSLIIALIALNVGKYNCPGLYEKLESSDHHVATCKNEWISYKRTCYFFSTTTKSWALAQRSCSEDAATLAVIDSEKDMTFLKRYSGELEHWIGLKNEANQTWKWANGKEFNSWFNLTGSGRCVSVNHKNVTAVDCEANFHWVCSKPSR
Note: The complete sequence including tag sequence, target protein sequence and linker sequence could be provided upon request. -
蛋白标签:N-terminal 10xHis-tagged
-
产品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:Lyophilized from Tris/PBS-based buffer, 6% Trehalose, pH 8.0
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Involved in lymphocyte proliferation and functions as a signal transmitting receptor in lymphocytes, natural killer (NK) cells, and platelets.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- These studies showed that VCAM1 contributes not only to the initiation of myelination but also to its regulation through controlling the abundance of CD69, demonstrating that an intercellular molecule whose primary role is in the immune system can also play an unexpected role in the CNS. PMID: 27876794
- AIM plays an orchestrating role in the resolution process of inflammation by altering the profile of pulmonary lipid mediators PMID: 29070674
- Data show that a subset of inflammation-induced CD69(+) Kupffer cells which can feedback inhibit CD4 T cell response via cell surface TGF-beta1 at the late stage of immune response against infection. PMID: 27933593
- Specific niches for lung-resident memory CD8+ T cells at the site of tissue regeneration enable CD69-independent maintenance. PMID: 27815325
- this study shows that CD69 serves as a key mediator of the pathogenesis of psoriasis by controlling LAT1-CD98-mediated metabolic cues PMID: 27376471
- Loss of CD69 is associated with enhanced protection against vaccinia virus infection. PMID: 27147744
- The data highlight the contribution of CD69 as a nonredundant key regulator of BIC/miR-155-dependent regulatory T cell development and homeostasis. PMID: 28167605
- Data show that after tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced protein 8 like-2 (TIPE2) gene was down-regulated, the expression of the CD69 antigen was increased, and the proliferation of T lymphocytes and the secretion of cytokines IL-2 and IFN-gamma were enhanced. PMID: 27363266
- The generation of cancer-specific CD8(+) CD69(+)-expressing lymphocytes that inhibit colon cancer growth has been described. PMID: 26314763
- Maintenance of immune tolerance by Foxp3+ regulatory T cells requires CD69 expression. PMID: 24934597
- AIM(-/-) mice were highly susceptible to steatosis-associated HCC development, whereas no AIM(+/+) mouse developed the disease despite comparable liver inflammation and fibrosis in response to a long-term high-fat diet. PMID: 25284781
- our findings reveal potent strategies to safely increase AIM levels, which could form the basis for developing novel therapies for obesity PMID: 24804991
- CD69 interference with S1P1 function regulates peripheral T cell retention. PMID: 25624457
- The NKG2A expression was increased in hepatic CD69-NK cells. PMID: 23904369
- Report role of ZAP-70 kinase mutation/deletion on thymocyte-positive selection via CD69 signaling. PMID: 24266404
- The early activation marker CD69 regulates the expression of chemokines and CD4 T cell accumulation in intestine. PMID: 23776480
- Data indicate that CD69 is upregulated on endogenous dendritic cells (DC) upon activation. PMID: 23119065
- Intron I acts as an important regulatory element of CD69 expression. PMID: 22456278
- Data show that CD69 is critical for the generation and maintenance of professional memory T-helper (Th) lymphocytes, which can efficiently help humoral immunity in the late phase. PMID: 22474373
- CD69 plays an important role in the progression of bleomycin-induced experimental lung inflammation and fibrosis. PMID: 21970554
- data presented indicated that the activation Ag CD69 plays a role in regulating mucosal immune responses in the intestine PMID: 22250092
- These results suggest that CD69 on macrophages is involved in cigarette smoke-induced acute pulmonary inflammation. PMID: 22070386
- CD69 regulates S1P-induced skin dendritic cell migration by modulating S1P(1) function. PMID: 21412255
- Studies provide a mechanistic link between CD69 and the regulation of T(H)17 responses. PMID: 21427408
- Defective early and adaptive immune response in CD69-/- mice but augmented immune response in CD69-/- RAG2-/- mice implicate CD69 in the well fitting of innate components and lymphocytes. PMID: 20440294
- the CD69 cytoplasmic tail associates with the Jak3/Stat5 signaling pathway, which regulates the transcription of RORgammat and, consequently, differentiation toward the Th17 lineage PMID: 20696842
- CD69 acts as a brake on the progression and severity of autoimmune myocarditis and the development of dilated cardiomyopathy. PMID: 20855659
- the early activation receptor CD69 is an intrinsic modulator of immune allergic processes through the negative regulation of allergen-induced T-cell effector responses. PMID: 20621339
- These findings identify an integral membrane interaction between CD69 and S1P(1) and suggest that CD69 induces an S1P(1) conformation that shares some properties of the ligand-bound state, thereby facilitating S1P(1) internalization and degradation. PMID: 20463015
- Functionally, CD69-positive naive CD4-positive T cells exhibit faster and greater cytokine production than do CD69-negative naive CD4-positive T cells. PMID: 20304829
- CD69 plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of allergen-induced eosinophilic airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness. PMID: 19923457
- The generation of mature, single-positive thymocytes is dysregulated by CD69 blockade or overexpression PMID: 11751950
- potential role for CD69 in controlling thymocyte export PMID: 12039905
- deficiency results in enhanced antitumor immunity PMID: 12732655
- a critical role for CD69 antigen in neutrophil function in arthritis induction during the effector phase. PMID: 12882836
- Results show that CD69 is a negative modulator of autoimmune reactivity and inflammation through the synthesis of TGF-beta1. PMID: 12975472
- CD69 forms a complex with and negatively regulates S1P1 and that it functions downstream of IFN-alpha/beta, and possibly other activating stimuli, to promote lymphocyte retention in lymphoid organs PMID: 16525420
- Chitosan and alginate biopolymers up-regulate CD69 expression by B-cells and CD4+ T-cells. PMID: 17317051
- There is no significant role for CD69 against atherosclerosis in apoE(-/-) mice, an experimental disease model featuring a local inflammatory response triggered and sustained by alterations in lipid homeostasis. PMID: 18703531
- CD69 engagement activates extracellular signal-regulated MAP kinase (ERK) in CD69positiveCD4positiveCD25negative T cells of the tumor-bearing host, leading to maintenance of highly expressed, membrane-bound transforming growth factor-beta1. PMID: 19109141
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Membrane; Single-pass type II membrane protein.
-
组织特异性:Expressed on the surface of activated T-cells, B-cells, natural killer cells, neutrophils and platelets.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:12515
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000032259
UniGene: Mm.74745
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Pro-neuregulin-1, membrane-bound isoform (NRG1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
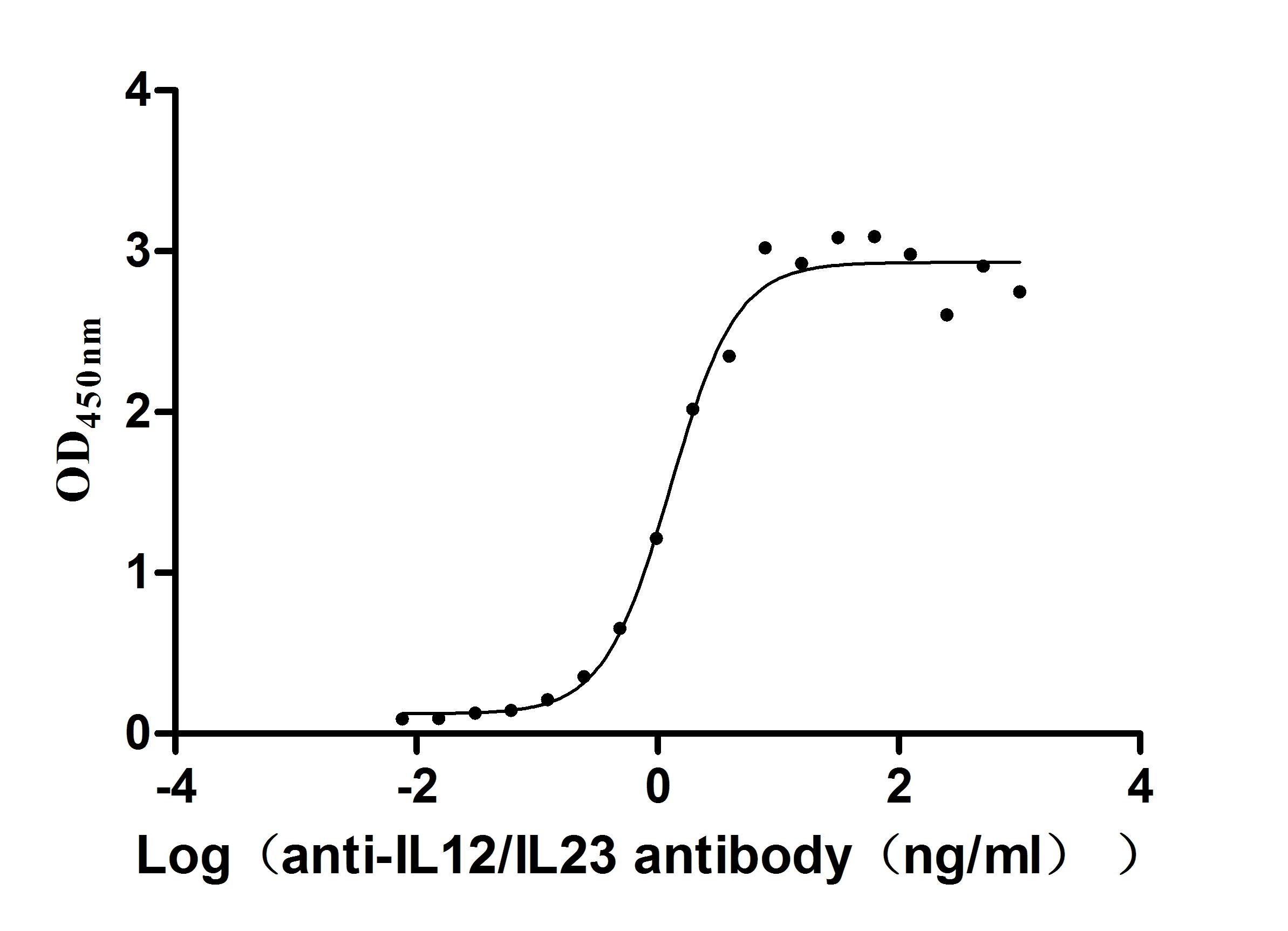
Recombinant Human IL12B&IL12A Heterodimer Protein (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
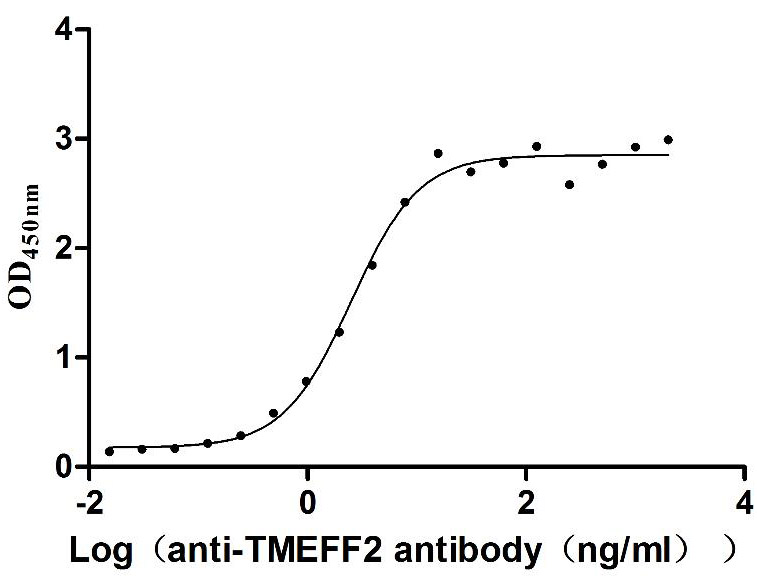
Recombinant Human Tomoregulin-2 (TMEFF2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
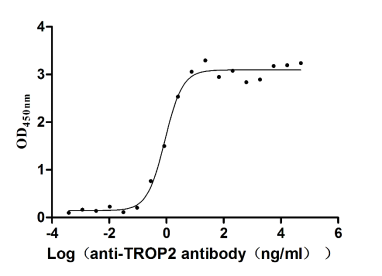
Recombinant Human Tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 (TACSTD2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
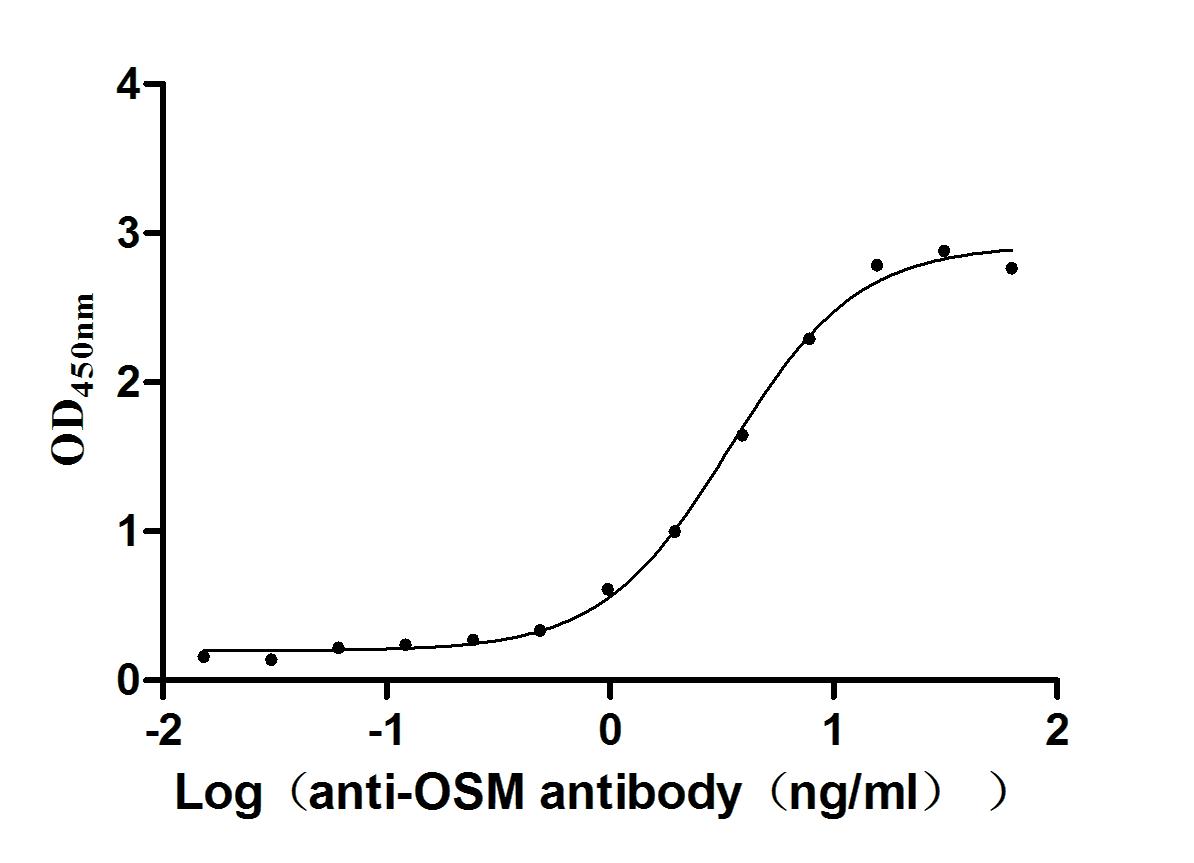
Recombinant Human Oncostatin-M (OSM), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Interleukin-2 (IL2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Myosin regulatory light chain 12B(MYL12B) (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 9 (CCR9)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)