GLP-1R:GPCR糖稳态和能量代谢分子,2型糖尿病药物研发有效靶点!
日期:2023-08-02 13:47:52
GLP-1R属于G蛋白偶联受体(GPCR)B族成员。GPCR是近年来药物开发研宄的热门家族靶点,其中,GLP-1R的药物研发已取得显著成功!GLP-1R被认为是2型糖尿病(T2DM)最为有效的治疗靶点之一。多年的基础研究和临床研究表明GLP-1与受体GLP-1R相互作用,有效调节机体的糖稳态和能量代谢。大量研究已证实,GLP-1R在糖尿病和肥胖症中扮演着重要的调控作用,具有降糖和减重的功能。因此,越来越多的研究者对能够同时抵抗肥胖和降低血糖的GLP-1R表现出了重视和兴趣!未来,GLP-1R靶点在T2DM临床药物研发上将占据重要地位!
1. 什么是GLP-1R?
1.1 GLP-1R的结构
胰高血糖素样肽-1受体(Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor,GLP-1R),是一种膜上的G蛋白偶联受体(GPCR)。人的GLP-1受体(hGLP-1R)基因位于人染色体6p21。结构上,典型特征是具有一个相对比较大的胞外域(ECD)和有α-螺旋束构成的7次跨膜核心域(TMD)(图1)[1]。该受体的N端胞外段长116个氨基酸残基,含有3对二硫键,在配体特异性识别中起重要作用。跨膜域由117-381位氨基酸残基组成,包括TM1-TM7及其之间的连接序列,这个结构域具有配体N端的结合位点,介导受体的激活。GLP-1R的C端胞内序列长59个氨基酸残基,是招募下游G蛋白的主要结构域 [1-3]。

图1. GLP-1R跨膜区的氨基酸残基以α螺旋形式排列 [1]
1.2 GLP-1R的表达和功能
GLP-1R在机体中广泛分布于被检测的胰岛、胃、小肠、心脏、肾脏、肺及大脑等组织中。在胃肠道中,GLP-1R可延迟胃排空,增加饱食感,控制食物摄取来减轻体重。在神经组织中,GLP-1R保护神经细胞和增强学习记忆能力。在心血管方面,GLP-1R调控心率、心室舒张压,并抑制心肌细胞的凋亡 [4-8]。GLP-1R在胰岛β细胞中发挥主要作用,GLP-1R的激活,促进胰岛素的释放,抑制胰高血糖素的释放,有助于调节血糖水平。因此,GLP-1R是糖尿病治疗的重要靶点 [4-8]。
2. GLP-1R的配体
GLP-1R的内源性配体为胰高血糖素样多肽-1(GLP-1)和胃泌酸调节素(oxyntomodulin,OXM)。胰高血糖素样多肽-1(GLP-1)和胃泌酸调节素(OXM)由肠道内的L细胞分泌,主要分布在消化系统的小肠和结肠的上皮层。当食物进入消化系统,尤其是通过小肠时,L细胞受到刺激并释放这两种肽类激素GLP-1和OXM [9-13]。
GLP-1是体内GLP-1R的主要激动剂,主要是通过“two-domain model”来激活受体。首先GLP-1 C端域(cGLP-1)同GLP-1R胞外域(ECD)形成的“affinity trap”结合,从而确保GLP-1 N端域(nGLP-1)与受体核心域(TMD)形成的“pocket”互交。这种相互作用能够有效激活PKA、PI3K、MAPK等多种下游信号通路,参与诸如胰岛素的释放,β-细胞增生,胰高血糖素释放减少,延迟胃排空等重要生理过程 [9-13]。
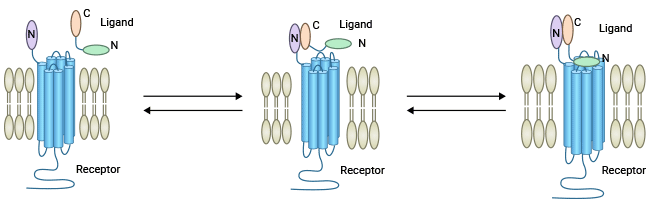
图2. G蛋白偶联受体与其配体结合的“two-domain model” [12]
3. GLP-1R调控的相关信号通路
GLP-1R是一种多效性偶联受体。当GLP-1R与其配体GLP-1结合时,G蛋白α亚基与β,γ亚基解离,从而引发受体变构,激活多种下游信号通路。这些信号通路包括多种G蛋白信号通路,如Gαs、Gαi、Gαo和Gαq/11,以及非G蛋白依赖的β-arrestin信号通路 [12, 14-16]。
在胰岛β细胞中,激活的GLP-1R通过偶联Gs蛋白,激活腺苷环化酶,增加cAMP含量,提高PKA和Epac2水平,导致离子通道活性改变。这一过程引起钾离子通道关闭,同时使电压依赖性钙离子通道(VDCCs)打开,促使钙离子内流,进而增加胰岛素原基因的转录和胰岛素分泌小泡释放。GLP-1通过cAMP-PKA途径提高葡萄糖感受性,刺激血糖依赖性胰岛素的分泌。GLP-1R通过G蛋白β、γ亚基激活PI3K和MAPK信号通路,诱导β细胞增值和分化 [12, 14-16]。
同时,cAMP还以PKA独立的方式与β细胞中cAMP调节的鸟苷酸交换因子(cAMP-GEFs)相互作用,激活Ras/MAPK信号通路,促进β细胞的生长和分化。GLP-1R还能通过调控cAMP反应元件结合蛋白(CREB)以及Bcl-2、Bcl-XL等蛋白复活因子来抑制细胞凋亡。近些年,也发现β-arrestin的募集也参与了GLP-1R功能 [12, 14-16]。例如,敲出β细胞中β-arrestin1会诱使cAMP的降低和胰岛素释放减少,敲出β-arrestin2的野生小鼠会产生餐后高血糖,糖耐性降低并会引起胰岛素抵抗等症状 [15]。
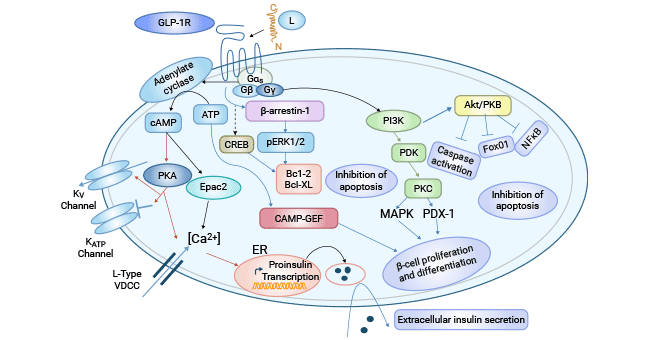
图3. 胰岛β细胞中GLP-1R调控的信号通路 [12]
4. GLP-1R在2型糖尿病等疾病中的作用
GLP-1R在2型糖尿病(T2DM)中已成为非常成功的药物靶点。同GLP-1的生理作用一样,不仅降糖效果显著,单独使用发生低血糖的风险小,还有减重、降压、改善血脂等作用。除糖尿病外,GLP-1R还在其他疾病中展现出潜力,如肥胖症、心血管疾病等,深入研究GLP-1R的功能,有望带来新的治疗方法和策略,为相关疾病带来积极影响。
4.1 GLP-1R和2型糖尿病
GLP-1R激动剂是一种新型抗2型糖尿病(T2DM)药物。目前大部分的降糖药会引起体重增加,如双胍类、噻唑烷二酮类TZDs、二肽基肽酶4(DPP-4)抑制剂。因此,T2DM患者迫切需要一种既可以降低血糖水平,并可以改善肥胖的药物治疗。在2型糖尿病治疗中,GLP-1R激动剂可以促进胰岛素释放、调节血糖水平,并改善胰岛素抵抗和β细胞功能 [17-20]。
也就是说,GLP-1R可同时降低血糖和改善肥胖症状。艾塞那肽(Exenatide)是第一款美国FDA批准用于治疗2型糖尿病的GLP-1R激动剂。近年来,已有多款GLP-1R靶向药研发成功,用于治疗2型糖尿病,如利司那肽(Lixisenatide)、聚乙二醇洛塞那肽(PEG-Loxenatide)、司美格鲁肽(Semaglutide)、贝那鲁肽(Beinaglutide)、艾塞那肽(Exenatide)、利拉鲁肽(Liraglutide)等 [17-22]。
4.2 GLP-1R和肥胖症
在某些病理状态下,肥胖患者可能会出现胰岛素抵抗,但他们的胰岛β细胞会增加胰岛素的分泌,以适应这种情况。但这种代偿性增加的胰岛β细胞在一段时间后可能会减退或衰竭,导致糖代谢紊乱,引发糖尿病。因此,糖尿病的高危因素与肥胖和超重等因素密切相关。大量研究揭示,糖尿病肥胖及糖尿病患者,其胰腺GLP-1R蛋白在胰腺的表达是逐渐下降的,这说明GLP-1R表达的下降是肥胖患者更易发展为糖尿病的重要病理机制之一 [23-26]。
4.3 GLP-1R和其它疾病
GLP-1R与糖尿病的多种并发症相关,尤其是动脉粥样硬化性心血管疾病。研究表明,GLP-1R激动剂(GLP-1RA)除了降血糖外,还能独立保护心血管系统。GLP-1R激动剂可通过调控巨噬细胞向M2型极化,在冠状动脉粥样硬化进程中发挥保护作用 [27-28]。
此外,在脊髓损伤研究中,GLP-1RA利拉鲁肽干预显示出促进运动功能恢复和保护脊髓组织的潜力 [29]。另外,在多囊卵巢综合症(PCOS)的研究中,GLP-1RA联合二甲双胍治疗可降低超重或肥胖PCOS患者的黄体生成素(LH)水平 [30]。进一步研究发现,GLP-1RA艾塞那肽通过调节下丘脑SIRT1和kisspeptin表达改善PCOS病情 [31-32]。
5. GLP-1R的临床在研药物
根据Pharmsnap的数据,目前有200多款基于GLP-1R靶点的药物正在进行临床研究。这些药物主要是GLP-1R激动剂,其中包括许多基于GLP-1R治疗糖尿病的小分子先导化合物。如前所述,多个GLP-1R药物已经上市,主要用于2型糖尿病治疗。近年来,也出现了基于GLP-1R的单抗、双抗等生物药,如GCGR x GLP-1R、GDF-15 x GIP-1R、FGF21 x GIP-1R双激动剂(表1)。这些基于GLP-1R的靶向药物有望更有效地管理血糖和调节血脂,同时延缓2型糖尿病患者的相关并发症,并改善患者的生活质量。这些探索对于下一代糖尿病药物的研发具有重要的临床应用意义!
| 药物 | 靶点 | 作用机制 | 在研适应症 | 药物最高研发状态(全球) | 药物类型 | 在研机构 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GMA102/105(重组抗人GLP-1受体人源化单克隆抗体) | GIP-1R | GIP-1R激动剂 | 2型糖尿病;肥胖;超重 | 临床3期 | 单克隆抗体 | 鸿运华宁(杭州)生物医药有限公司(Gmax Biopharm LLC) |
| Recombinant GLP-1 receptor agonists (Beijing Lepu)(重组GLP-1受体激动剂 | GIP-1R | GIP-1R激动剂 | 2型糖尿病;肥胖 | 临床3期 | 重组蛋白 | 北京乐普医药科技有限公司 |
| Ecnoglutide | GIP-1R | GIP-1R激动剂 | 肥胖;超重;非酒精性脂肪性肝炎;阿尔茨海默病 | 临床3期 | 重组蛋白 | 杭州先为达生物科技有限公司 (Hangzhou Sciwind Biosciences Co., Ltd.); Sciwind Biosciences APAC CO Pty. Ltd. |
| Efinopegdutide | GCGR+GIP-1R | GCGR激动剂; GIP-1R激动剂 |
非酒精性脂肪性肝炎;2型糖尿病 | 临床2期 | 重组蛋白 | Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC;韩美药品株式会社 (Hanmi Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.);Merck Gesellschaft mbH |
| GMA-106(重组人胰高糖素样肽1修饰抗人葡萄糖依赖性促胰岛素释放肽受体的人源化单克隆抗体) | GIPR+GIP-1R | GIPR拮抗剂; GIP-1R拮抗剂 |
2型糖尿病;非酒精性脂肪性肝炎;肺沉着症;超重;肥胖;非酒精性脂肪性肝炎;糖尿病 | 临床1期 | 双特异性抗体 | 鸿运华宁(杭州)生物医药有限公司 (Gmax Biopharm LLC);中国生物制药有限公司 (Sino Biopharmaceutical Ltd.) |
| IRDye800CW-exendin-4 | GIP-1R | GIP-1R激动剂;诊断染料分子 | 2型糖尿病 | 临床阶段不明 | 其他体内诊断药物;合成多肽 | Radboud University Nijmegen |
| ZT-007 | GDF-15+GIP-1R | GDF-15激动剂; GIP-1R激动剂 |
肥胖 | 临床前 | 重组蛋白 | 北京质肽生物医药科技有限公司 (Beijing QL Biopharmaceutical Co.,Ltd) |
| ZT-003 | FGF21+GIP-1R | FGF21激动剂; GIP-1R激动剂 |
肥胖;非酒精性脂肪性肝炎 | 临床前 | 重组蛋白 | 北京质肽生物医药科技有限公司 (Beijing QL Biopharmaceutical Co.,Ltd) |
| HTB-C041 | Collagen+GIP-1R | 胶原蛋白刺激剂;GIP-1R激动剂 | 2型糖尿病 | 临床前 | 重组蛋白 | 上海惠盾生物技术有限公司 (Shanghai Humantech Biotechnology Co.Ltd) |
| HDM-1005 | GIPR+GIP-1R | GIPR激动剂; GIP-1R激动剂 |
糖尿病;肥胖 | 临床前 | 双特异性抗体 | 华东医药股份有限公司 (Huadong Medicine Co., Ltd.) |
| P-017 | GIP-1R | GIP-1R拮抗剂 | / | 临床前 | 单克隆抗体 | 株式会社NB健康研究所 (NB Health Laboratory Co. Ltd.) |
| TB-01-3 | GIP-1R | GIP-1R拮抗剂 | 低血糖 | 临床前 | 单克隆抗体 | 扭轉生物科技有限公司 (Twist Bioscience Corp.) |
| P-11 | GIP-1R | GIP-1R激动剂 | 2型糖尿病 | 临床前 | 重组蛋白 | Protheragen, Inc. |
| GZR-18 | GIP-1R | GIP-1R激动剂 | 2型糖尿病;肥胖;超重 | 临床2期 | 生物药 | 甘李药业股份有限公司 (Gan & Lee Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd.) |
| HR-17031 | GIP-1R+INSR | GIP-1R激动剂;INSR激动剂 | 2型糖尿病 | 临床2期 | 生物药 | 江苏恒瑞医药股份有限公司 (Jiangsu Hengrui Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd.) |
| NPM-119 | GIP-1R | GIP-1R激动剂 | 2型糖尿病 | 临床2期 | 生物药 | 纳诺精密医疗有限公司 (Nano Precision Medical, Inc.);Vivani Medical, Inc. |
| NN-9277 | GCGR+GIP-1R | GCGR激动剂; GIP-1R激动剂 |
超重 | 临床1期 | 生物药 | 诺和诺德 (Novo Nordisk A/S) |
| XW-014 | GIP-1R | GIP-1R激动剂 | 2型糖尿病;非酒精性脂肪性肝炎;肥胖 | 临床1期 | 生物药 | 杭州先为达生物科技有限公司 (Hangzhou Sciwind Biosciences Co., Ltd.) |
| HL-08 | GIP-1R | GIP-1R调节剂 | 2型糖尿病 | 临床1期 | 生物药 | 华兰生物工程股份有限公司 (Hualan Biological Engineering, Inc.) |
| VTC-G15 | GIP-1R | GIP-1R激动剂 | 1型糖尿病 | 临床1期 | 生物药 | Mass General Brigham, Inc. |
| XW-015 | 胰淀素+GIP-1R | 胰淀素激动剂;GIP-1R激动剂 | 肥胖 | 临床前 | 生物药 | 杭州先为达生物科技有限公司 (Hangzhou Sciwind Biosciences Co., Ltd.) |
| LBT-6030 | GIPR+GIP-1R | GIPR激动剂;GIP-1R激动剂 | 糖尿病 | 临床前 | 生物药 | Longevity Biotech, Inc. |
| HYBR-011 | GIP-1R | GIP-1R激动剂 | 2型糖尿病 | 临床前 | 生物药 | 上海仁会生物制药股份有限公司 (Shanghai Benemae Pharmaceutical Corp.) |
| BEM-012 | GIP-1R | GIP-1R激动剂 | 2型糖尿病 | 药物发现 | 生物药 | 上海仁会生物制药股份有限公司 (Shanghai Benemae Pharmaceutical Corp.) |
表1:GLP-1R的临床在研药物(部分)
为鼎力协助科研和药企人员针对GLP-1R在糖尿病、肥胖症等疾病中的临床应用中的研究,CUSABIO推出GLP-1R活性蛋白(Code: CSB-MP009514HUb1)产品,助力您在GLP-1R机制方面的研究或其潜在临床价值的探索。(点击查看GLP-1R系列产品:GLP-1R蛋白;GLP-1R抗体;GLP-1R试剂盒)
GLP-1R蛋白
Recombinant Human Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor(GLP1R),partial (Active)(Code: CSB-MP009514HUb1)
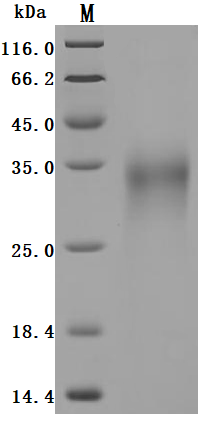
High purity was greater than 95% as determined by SDS-PAGE. SDS-PAGE (reduced) with 5% enrichment gel and 15% separation gel.
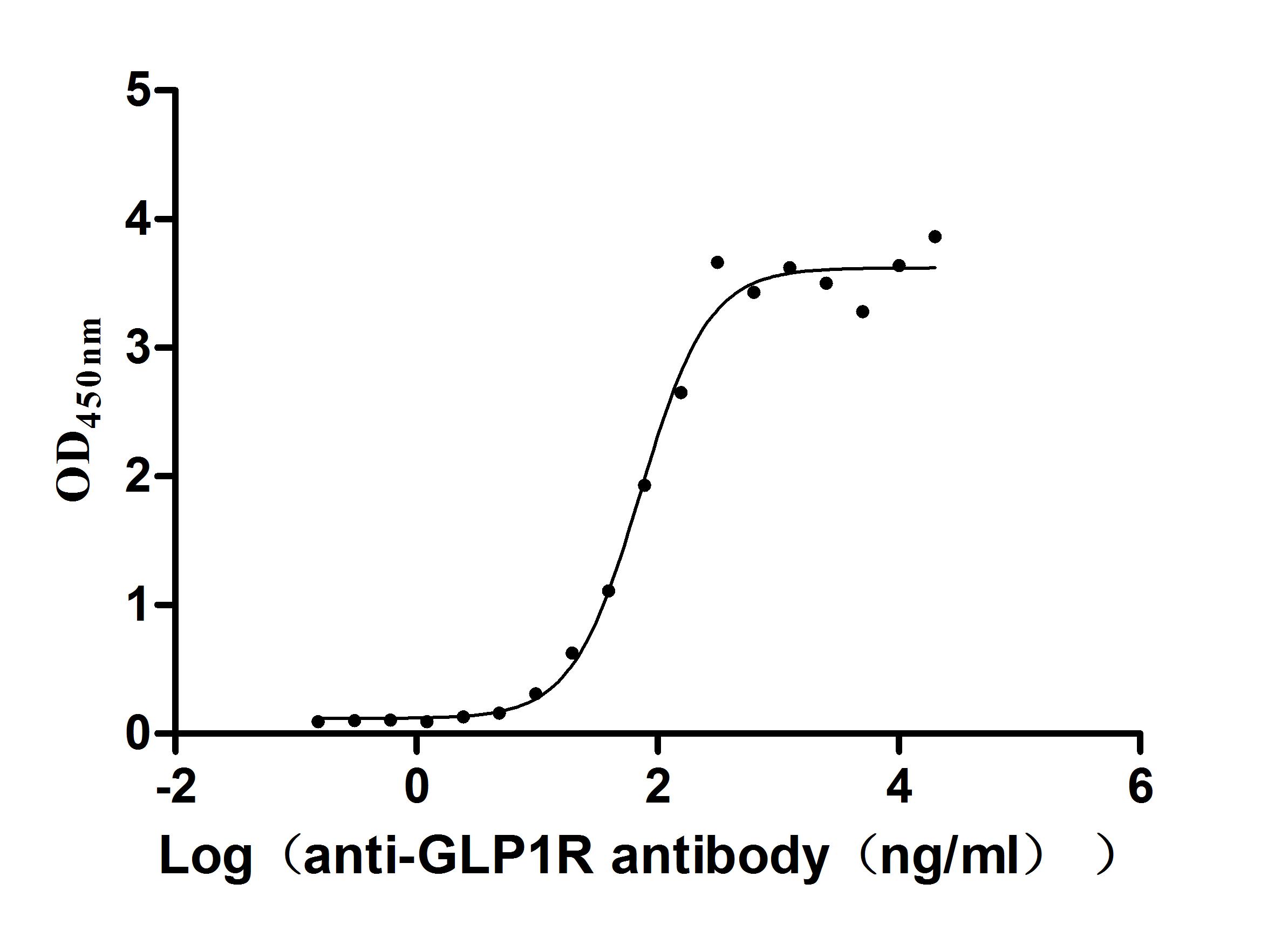
Immobilized Human GLP1R at 2 μg/mL can bind Anti-GLP1R recombinant antibody (CSB-RA009514MA1HU), the EC50 is 54.54-94.23 ng/mL.
GLP-1R抗体
GLP1R Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody (Active)(Code: CSB-RA009514MA1HU)
anti-GLP1R antibody
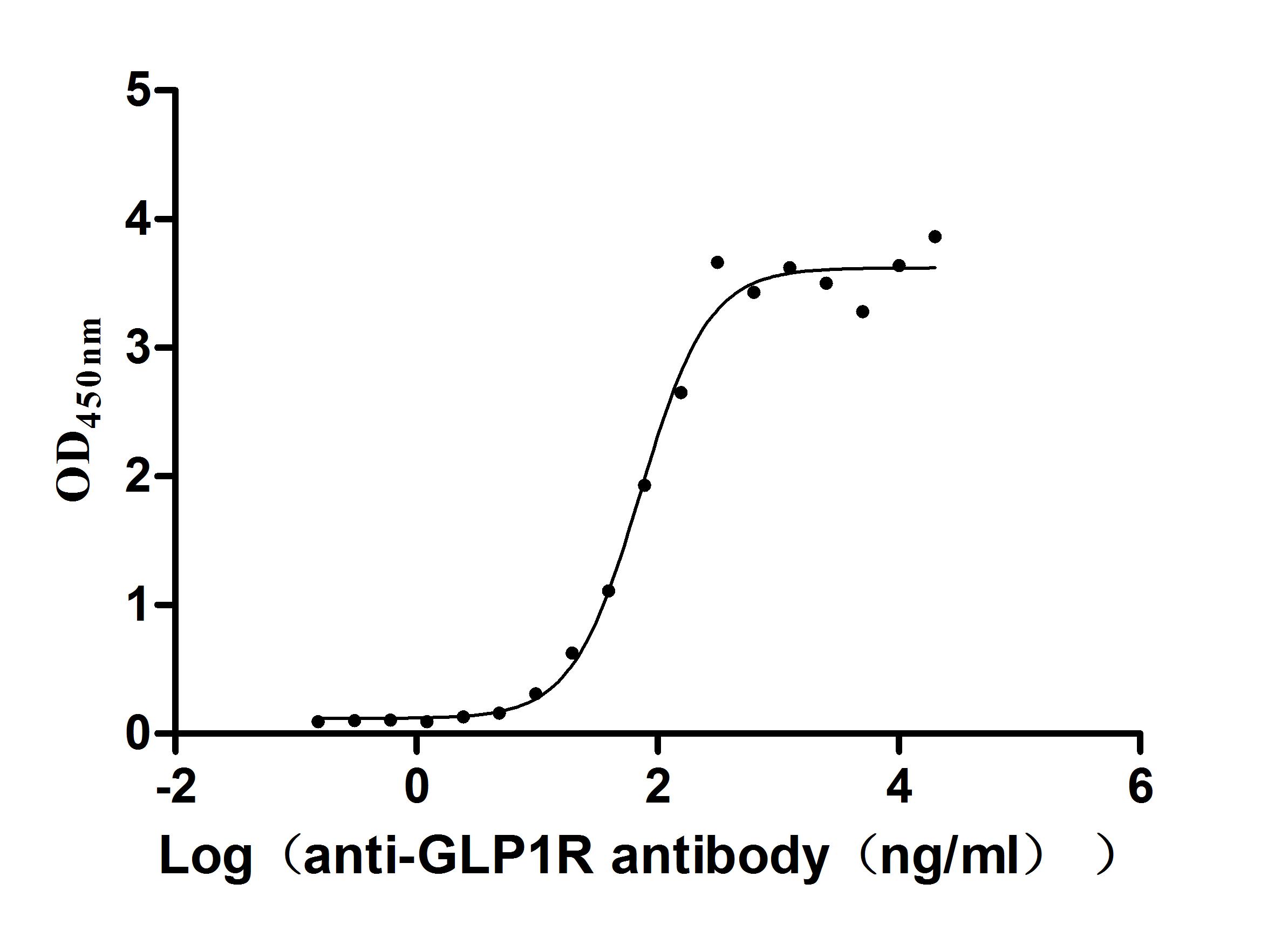
Activity: Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized Human GLP1R (CSB-MP009514HUb1) at 2 μg/mL can bind Anti-GLP1R recombinant antibody, the EC50 is 54.54-94.23 ng/mL.
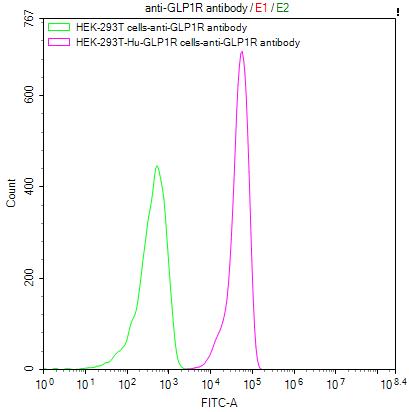
Untransfected HEK-293T cells surface (green line) and transfected Human GLP1R HEK-293T stable cells surface (red line) were stained with anti-GLP1R antibody (2µg/1*106 cells), washed and then followed by FITC-conjugated anti-Human IgG Fc antibody and analyzed with flow cytometry.
参考文献:
[1] Malm-Erjefält, Monika, et al. "Metabolism and excretion of the once-daily human glucagon-like peptide-1 analog liraglutide in healthy male subjects and its in vitro degradation by dipeptidyl peptidase IV and neutral endopeptidase."Drug Metabolism and Disposition 38.11 (2010): 1944-1953.
[2] Fujita, Hiroki, et al. "The protective roles of GLP-1R signaling in diabetic nephropathy: possible mechanism and therapeutic potential." Kidney international 85.3 (2014): 579-589.
[3] Pabreja, Kavita, et al. "Molecular mechanisms underlying physiological and receptor pleiotropic effects mediated by GLP‐1R activation." British Journal of Pharmacology 171.5 (2014): 1114-1128.
[4] Varin, Elodie M., et al. "Distinct neural sites of GLP-1R expression mediate physiological versus pharmacological control of incretin action." Cell reports 27.11 (2019): 3371-3384.
[5] Pyke, Charles, et al. "GLP-1 receptor localization in monkey and human tissue: novel distribution revealed with extensively validated monoclonal antibody." Endocrinology 155.4 (2014): 1280-1290.
[6] Zhou, Da, et al. "Sodium butyrate reduces high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis through upregulation of hepatic GLP-1R expression." Experimental & molecular medicine 50.12 (2018): 1-12.
[7] Morrow, Nadya M., Antonio A. Hanson, and Erin E. Mulvihill. "Distinct identity of GLP-1R, GLP-2R, and GIPR expressing cells and signaling circuits within the gastrointestinal tract." Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology 9 (2021): 703966.
[8] Ejarque, Miriam, et al. "Role of adipose tissue GLP-1R expression in metabolic improvement after bariatric surgery in patients with type 2 diabetes." Scientific reports 9.1 (2019): 6274.
[9] Zhang, Xiaolong, et al. "Discovery of novel OXM-based glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1)/glucagon receptor dual agonists." Peptides 161 (2023): 170948.
[10] Liu, Chunxia, Yuxing Zou, and Hai Qian. "GLP-1R agonists for the treatment of obesity: a patent review (2015-present)." Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Patents 30.10 (2020): 781-794.
[11] Cai, Xingguang, et al. "Novel glucagon-and OXM-based peptides acting through glucagon and GLP-1 receptors with body weight reduction and anti-diabetic properties." Bioorganic Chemistry 95 (2020): 103538.
[12] HU, Zhong-ping, et al. "Research Progress on Structure and Function of GLP-1R and Screening for Small Molecule Drugs." Biotechnology Bulletin 33.2 (2017): 30.
[13] Meurot, C., et al. "Targeting the GLP-1/GLP-1R axis to treat osteoarthritis: A new opportunity?." Journal of Orthopaedic Translation 32 (2022): 121-129.
[14] Liang, Yi-Lynn, et al. "Dominant negative G proteins enhance formation and purification of agonist-GPCR-G protein complexes for structure determination." ACS pharmacology & translational science 1.1 (2018): 12-20.
[15] Bitsi, Stavroula, et al. "Divergent acute versus prolonged pharmacological GLP-1R responses in adult β cell–specific β-arrestin 2 knockout mice." Science Advances 9.18 (2023): eadf7737.
[16] Challa, Tenagne Delessa, et al. "Regulation of adipocyte formation by GLP-1/GLP-1R signaling." Journal of Biological Chemistry 287.9 (2012): 6421-6430.
[17] Broide, E., et al. "Reduced GLP-1R expression in gastric glands of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus." The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 99.9 (2014): E1691-E1695.
[18] Simó, Rafael, and Cristina Hernández. "GLP-1R as a target for the treatment of diabetic retinopathy: friend or foe?." Diabetes 66.6 (2017): 1453-1460.
[19] Meier, Juris J. "GLP-1 receptor agonists for individualized treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus." Nature Reviews Endocrinology 8.12 (2012): 728-742.
[20] Bendotti, Giulia, et al. "The anti-inflammatory and immunological properties of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists." Pharmacological Research 182 (2022): 106320.
[21] Nevola, Riccardo, et al. "GLP-1 receptor agonists in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: current evidence and future perspectives." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24.2 (2023): 1703.
[22] Wharton, Sean, et al. "Daily Oral GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Orforglipron for Adults with Obesity." New England Journal of Medicine (2023).
[23] Jansen, Kirsten M., et al. "Impact of GLP-1 receptor agonist versus omega-3 fatty acids supplement on obesity-induced alterations of mitochondrial respiration." Frontiers in Endocrinology 14 (2023): 1098391.
[24] Mekhaimar, Menatalla, et al. "Glp-1 receptor agonists are associated with weight loss among lvad patients with diabetes and obesity." Journal of Cardiac Failure 29.4 (2023): 617.
[25] Cardoso, Luiz EM, et al. "Treatment with semaglutide, a GLP-1 receptor agonist, improves extracellular matrix remodeling in the pancreatic islet of diet-induced obese mice." Life Sciences 319 (2023): 121502.
[26] Palanca, Ana, et al. "Real-World Evaluation of GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Therapy Persistence, Adherence and Therapeutic Inertia Among Obese Adults with Type 2 Diabetes." Diabetes Therapy 14.4 (2023): 723-736.
[27] Luli, Alex, et al. "Barriers to Obtaining GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and SGLT2 Inhibitors in a Free Clinic Population With Type 2 Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease." Journal of Contemporary Pharmacy Practice 70.1 (2023): 9-13.
[28] Mahtta, Dhruv, et al. "Utilization rates of SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists and their facility-level variation among patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes: insights from the Department of Veterans Affairs." Diabetes Care 45.2 (2022): 372-380.
[29] Chen, Jian, et al. "Liraglutide activates autophagy via GLP-1R to improve functional recovery after spinal cord injury." Oncotarget 8.49 (2017): 85949.
[30] Han, Yi, Yingjie Li, and Bing He. "GLP-1 receptor agonists versus metformin in PCOS: a systematic review and meta-analysis." Reproductive biomedicine online 39.2 (2019): 332-342.
[31] Tao, Xin, et al. "Effects of metformin and Exenatide on insulin resistance and AMPKα-SIRT1 molecular pathway in PCOS rats." Journal of ovarian research 12.1 (2019): 1-8.
[32] Bednarz, Krzysztof, et al. "The role of glp-1 receptor agonists in insulin resistance with concomitant obesity treatment in polycystic ovary syndrome." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23.8 (2022): 4334.











