AQP5 Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA000915
-
规格:¥880
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
Uniprot No.:P55064
-
基因名:AQP5
-
别名:AQP 5 antibody; AQP-5 antibody; AQP5 antibody; AQP5_HUMAN antibody; Aquaporin 5 antibody; Aquaporin-5 antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human
-
免疫原:Synthesized peptide derived from the C-terminal region of Human AQP5.
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
标记方式:Non-conjugated
-
抗体亚型:IgG
-
纯化方式:The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存缓冲液:Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
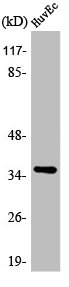
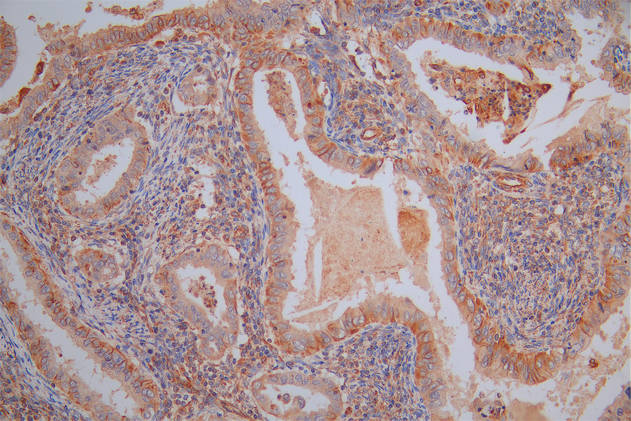
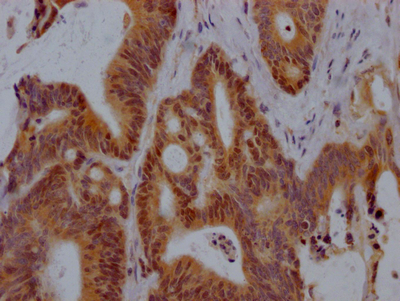
应用范围:WB, IHC, ELISA
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:500-1:2000 IHC 1:100-1:300 ELISA 1:40000 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Forms a water-specific channel. Plays an important role in fluid secretion in salivary glands. Required for TRPV4 activation by hypotonicity. Together with TRPV4, controls regulatory volume decrease in salivary epithelial cells. Seems to play a redundant role in water transport in the eye, lung and in sweat glands.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Results indicate that autophagy plays a crucial role in aquaporin 5 (AQP5) degradation in diabetic submandibular gland (SMG). PMID: 29951954
- these results suggest that AQP5 silencing enhances the sensitivity of colorectal cancer (CRC) cells to 5-FU, and the underlying mechanism is related to inhibition of the Wnt-beta-catenin pathway. AQP5 could be a useful therapeutic target for CRC treatment. PMID: 29390193
- Structural basis for mutations in human AQP5 associated with keratoderma has been described. PMID: 29799470
- The urea transporter subtypes, UT-A1 and UT-B1, were expressed in the skin basal cell layer and exocrine sweat glands. The abundance of UT-A1 and UT-B1 in uremic sweat glands was significantly increased in UP, while the expression of AQP5 was decreased. PMID: 29279852
- we demonstrated that AQP5 gene silencing could inhibit the proliferation, reduce the migration and promote the apoptosis of human glioma cells by suppressing EGFR/ERK/p38 MAPK signaling pathway PMID: 28404978
- Data suggest that urine AQP5/creatinine ratio is significantly higher in patients with diabetic nephropathy than in control subjects, subjects diabetes, or subjects with nephropathy of unknown etiology; urine AQP5/creatinine ratio increases with stage of diabetic nephropathy; this biomarker may improve clinical models in distinguishing diabetic nephropathy from normal controls and subjects with type 2 diabetic alone. PMID: 27103565
- We present the first Danish family diagnosed with autosomal dominant palmplantar ketratoderma of Bothnian type resulting from c.562C>T, p.Arg188Cys in the AQP5 gene. PMID: 27255181
- Findings show that overexpression of aquaporin 5 (AQP5) activated epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in colorectal cancer (CRC) cells. PMID: 28833571
- RAQP5 protein expression in breast cancer.Rac1 is a potential downstream signaling partner of AQP5 in breast cancer. PMID: 28958942
- The AQP5 genotype may influence survival following lipopolysaccharides by altering neutrophil cell migration. PMID: 27871297
- Mucins and AQP5 gene expression were significantly higher in patients with OME relative to controls. A 2-fold increase in AQP5 correlated with increased effusion viscosity (1.94 mL/mg; 95% CI, 0.08-3.80 mL/mg). PMID: 28594978
- The severity of preterm infants with acute respiratory distress syndrome was associated with the plasma level of AQP5; the more severe of the disease, the higher levels of plasma AQP5. PMID: 25877715
- AQP5 is up-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell line. AQP5 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis via NF-kappa B-regulated epithelial-mesenchymal transition. PMID: 28619511
- Double IF showed the co-localization of AQP5 and LC3B on BafA1-treated heated cells. In conclusion, we demonstrated that heat shock decreased AQP5 on cellular membranes and in the cytoplasm by activating autophagic degradation, and heat shock and AQP5 knockdown exerted similar anticancer effects, suggesting that heat shock exerts anticancer effects via the autophagic degradation of AQP5. PMID: 28358429
- we analyzed the urine excretion of AQP5 and AQP2 via exosomes, in 35 diabetic patients: 12 normoalbuminuric with normal renal function (DM), 11 with proteinuric nondiabetic nephropathy (NDN), and 12 with histological diagnosis and classification of DN. urinary AQP5 and AQP2 were significantly increased in DN patients. PMID: 28246612
- this study shows that S-allylmercapto-l-cysteine can suppress AQP5 secretion using the cell model of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease PMID: 27517516
- The current study suggests AQP5 rs1964676 as a new potential prognostic marker in patients with EBC involved in AQP5 expression PMID: 27978515
- Adjusting AQP5 protein levels could be considered a therapeutic strategy for the treatment of acute pulmonary edema induced by H2S and other hazardous gases PMID: 28088675
- nuclear matrix protein 4 overexpression increased Aquaporin 5 mRNA expression by 2.5-fold in HEK293 cells PMID: 27058007
- The findings presented here add further support to mutations in AQP5 being responsible for this particular subtype of NEPPK and also have implications for the optimal initial genetic screening of other British individuals with this clinical diagnosis. PMID: 26032342
- AQP5 plasma membrane abundance in transfected HEK293 cells is rapidly and reversibly regulated by at least three independent mechanisms involving phosphorylation at Ser156, protein kinase A activity and extracellular tonicity. PMID: 26569106
- AQP5 can be both overexpressed and lost in subgroups of prostate cancers PMID: 26614400
- AQP5 defined a subset of patients with Bcl-2-negative and p16-negative tumours with a poor clinical outcome. PMID: 26074259
- Histamine downregulates AQP5 production in human nasal epithelial cells by inhibiting cyclic adenosine monophosphate-responsive element binding protein (CREB) phosphorylation at serine 133. PMID: 25781725
- Aquaporin-5 is expressed in adipocytes with implications in adipose differentiation. PMID: 25631586
- These results indicate that NFAT5 plays important roles in proliferation and migration of human lung adenocarcinoma cells through regulating AQP5 expression, providing a new therapeutic option for lung adenocarcinoma therapy. PMID: 26299924
- The hyperosmotic induction of AQP5 and VEGF in retinal pigment epithelial cells was in part dependent on activation of NFAT5. PMID: 25878490
- AQP5 was strongly localized in the apical membrane and weakly localized in the cytoplasm of secretory epithelial cells. PMID: 25218052
- The AQP5 protein is up-regulated in prostate cancer and is closely related to advanced stage, lymph node metastasis, and poor prognosis. AQP5 expression was associated with cell proliferation and migration. PMID: 25217331
- In colorectal adenocarcinoma, 31.1% had high levels of expression of AQP5, 64.4% exhibited a moderate level of staining, and 4.4% had an absence of AQP5 staining. AQP5 was only occasionally detected in para-neoplastic (6.67%) and normal tissues (6.67%). PMID: 25109507
- Down-regulated aquaporin 5 inhibits proliferation and migration of human epithelial ovarian cancer 3AO cells. PMID: 25298246
- These findings indicate that AQP5-mediated regulation of microtubule dynamics modulates airway epithelial barrier properties and epithelial function. PMID: 22715407
- Survival of patients with a high AQP-5/PTEN coexpression was longer than that of patients with a low coexpression (p = 0.003). PMID: 24217644
- High AQP5 expression is associated with breast cancer. PMID: 24114055
- So these results indicate that AQP5 is associated with drug resistance of colon cancer, and that the AQP5-P38 MAPK pathway may represent a potential drug target to improve drug resistance of colon cancer cells. PMID: 24752576
- We described a Chinese family with palmoplantar keratoderma Bothnia type in which we identified a gain-of-function mutation in AQP5. PMID: 23867895
- By directing cellular localization of TRPC1 and AQP5 channels and by selectively regulating the functional assembly TRPC1-STIM1 channels, Cav1 is a crucial determinant of SG fluid secretion. PMID: 23203809
- AQP5-L51R does not exhibit the H2O or CO2 permeability of the wild-type protein. PMID: 23842530
- Mutations in AQP5 cause autosomal-dominant diffuse nonepidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma. PMID: 23830519
- The regulated AQP5 translocation may contribute to sweat secretion by increasing the water permeability of apical plasma membranes of sweat glands. PMID: 23473857
- AQP5 polymorphism A(-1364)C is associated with peritumoral brain edema in meningioma patients PMID: 23392848
- Our findings clearly indicate that binding of anti-M3R autoantibodies to the receptor, which was verified by immunoprecipitation, suppresses AQP5 trafficking to the membrane and contribute to impaired fluid secretion in SjS. PMID: 23382834
- Overexpression of AQP5 is associated with lymphatic Metastasis in gastric carcinoma. PMID: 23436048
- These observations suggest that AQP5 plays a key role in cervical cancer PMID: 22048942
- These observations suggest that sialadenosis is associated with a different AQP5 expression and distribution pattern in salivary acinar cells. PMID: 23160677
- A lipid, phosphatidylserine, is bound to AQP5 in the central pore, totally occluding it and inhibits the function of the central pore with an IC(50) in the micromolar range. PMID: 23176748
- The variant G allele of AQP5 polymorphism rs3736309 reduces the risk of Meniere's disease. PMID: 23352976
- AQP5 is a significant component of lens fiber cell membranes, representing the second most abundant water channel in these cells. PMID: 23313152
- The potential functions of AQP2 and AQP5 are in the resorption and secretion of endolymph. (Review) PMID: 22732097
- TNF-alpha inhibition of AQP5 expression in human salivary gland acinar cells is due to the epigenetic mechanism by suppression of acetylation of histone H4. PMID: 21973049
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Keratoderma, palmoplantar, Bothnian type (PPKB)
-
亚细胞定位:Apical cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cytoplasmic vesicle membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:MIP/aquaporin (TC 1.A.8) family
-
组织特异性:Detected in skin eccrine sweat glands, at the apical cell membrane and at intercellular canaliculi (at protein level).
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 638
OMIM: 600231
KEGG: hsa:362
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000293599
UniGene: Hs.298023
Most popular with customers
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-
-
-