CYP26A1 Antibody
-
货号:CSB-PA288324
-
规格:¥2024
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品名称:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) CYP26A1 Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:O43174
-
基因名:CYP26A1
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human,Mouse,Rat
-
免疫原:Synthesized peptide derived from internal of Human Cytochrome P450 26A1.
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
克隆类型:Polyclonal
-
纯化方式:The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
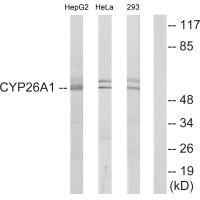
应用范围:ELISA,WB
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:500-1:3000 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:A cytochrome P450 monooxygenase involved in the metabolism of all-trans retinoic acid (atRA), a signaling molecule that binds to retinoic acid receptors and regulates gene transcription. Mechanistically, uses molecular oxygen inserting one oxygen atom into a substrate, and reducing the second into a water molecule, with two electrons provided by NADPH via cytochrome P450 reductase (CPR; NADPH-ferrihemoprotein reductase). Catalyzes the hydroxylation of carbon hydrogen bonds of atRA primarily at C-4 and C-18. Has no activity toward 9-cis and 13-cis retinoic acid stereoisomers. May play a role in the oxidative metabolism of xenobiotics such as tazarotenic acid.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Accumulating evidence suggest that cytochrome P450 (CYP26), the primary retinoid-inactivating enzyme, plays a critical role in the integration of two neoplastic molecular programs: the retinoid metabolism and Hedgehog pathways. (Review) PMID: 28754309
- CYP26A1 polymorphisms were associated with increased risk of malignant oral disorders in betel quid chewers. PMID: 25839051
- CYP26A1-mediated oncogenic characteristics may be partially responsible for the elevated expression of fascin. PMID: 26058854
- Molecular recognition of CYP26A1 binding pockets and structure-activity relationship studies for design of potent and selective retinoic acid metabolism blocking agents has been described. PMID: 25541526
- data suggested that CYP26A1 overexpression might contribute to the development and progression of cervical malignancies and squamous neoplasia of the head and neck PMID: 25294402
- HNF4alpha coordinates with retinoic acid receptors in a retinoic acid-dependent manner to strongly induce CYP26A1 gene expression in the liver, which may explain the high level of response to retinoic acid observed in vivo. PMID: 24819304
- In liver microsomes, CYP26A1 plays a role in clearing bioactive retinoids. PMID: 25492813
- CYP26 is able to inactivate retinoids in serum, preventing retinoic acid signaling and thus bone-marrow hematopoietic stem cell differentiation. PMID: 24043786
- The promoter region of CYP26A1 is significantly hypermethylated in allergic asthmatic subjects. PMID: 21975512
- Our observation suggests an involvement of enhanced CYP26A1 expression causing a functional vitamin A deficieny state in skin that can potentially lead to neoplastic transformation of keratinocytes in an early phase during skin carcinogenesis PMID: 22179182
- CYP26A1 and CYP26B1 are qualitatively similar retinoic acid hydroxylases with overlapping expression profiles; CYP26A1 has higher catalytic activity than CYP26B1. PMID: 22020119
- CYP26A1 and CYP26C1 play a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of nonsyndromic bilateral and unilateral optic nerve aplasia. PMID: 21850183
- Primary metabolites of all-trans-retinoic acid formed by CYP26A1 are identified and the ligand selectivity and ligand interactions of CYP26A1 are characterized. PMID: 21521770
- the functioning of multiple RAREs may account for the strong inducibility of CYP26A1 in liver, which, in turn, may be important physiologically for restoring retinoid homeostasis when the concentration of RA rises. PMID: 20682464
- CYP26A1 is expressed in human liver microsomes; its expression correlates with retinoic acid hydroxylation. PMID: 20513361
- The identification of a functional retinoic acid response element located 2.0 kb upstream of the Cyp26A1 transcriptional start site is reported. PMID: 16053444
- induction and regulation of CYP26A1 expression in human intestinal (Caco-2), liver (HepG2), endothelial (HUVEC), and APL (NB4) cell lines PMID: 16194896
- Variants in CYP26A1 are unlikely to be a major risk factor for caudal regression syndrome; further study with a larger number of genotyped subjects is required. PMID: 16463413
- Constitutive expression of CYP26AI in vivo and in organotypic culture was found to be restricted to basal epidermal keratinocytes, as well as eccrine sweat glands and sebaceous glands. PMID: 16778795
- g.3116delT mutation is of particular interest because it was identified in a patient with spina bifida and likely encodes a truncated protein with no enzymatic activity, as demonstrated by preliminary in vitro data. PMID: 16933217
- analysis of CYP26A1 active site architecture and ligand binding PMID: 17059167
- Low CYP26A1 expression may explain high risk of resistance installation, by increase retinoid pressure. PMID: 17218384
- Three new alleles termed as CYP26A1*2, CYP26A1*3, and CYP26A1*4, are potentially defective in all-trans retinoic acid metabolism. PMID: 17460545
- Overexpression of CYP26A1 causes intracellular retinoic acid depletion and drives the cell into a highly proliferative and invasive state with induction of other known oncogenes PMID: 18059332
- Results provide a biochemical framework for CYP26A1 function and offer insight into the role of CYP26A1 as a drug target as well as in fetal development and cell cycle regulation PMID: 18992717
- cytochrome P450 family 26 (CYP26) enzymes have a role in determining the cellular exposure to retinoic acid by inactivating retinoic acid in cells that do not need retinoic acid--REVIEW PMID: 19519282
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Endoplasmic reticulum membrane; Peripheral membrane protein. Microsome membrane; Peripheral membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:Cytochrome P450 family
-
组织特异性:Expressed in most fetal and adult tissues with highest levels in adult liver, heart, pituitary gland, adrenal gland, placenta and regions of the brain. Expressed at high levels in lung, pancreas, skin and uterus (at protein level). Lower expression level
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 2603
OMIM: 602239
KEGG: hsa:1592
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000224356
UniGene: Hs.150595
Most popular with customers
-
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-
-