EFHC1 Antibody
-
中文名称:EFHC1兔多克隆抗体
-
货号:CSB-PA708490ESR1HU
-
规格:¥440
-
促销:
-
图片:
-
Western blot
All lanes: EFHC1 antibody at 9.9 μg/ml
Lane 1: Mouse large intestine tissue
Lane 2: Mouse stomach tissue
Lane 3: Mouse brain tissue
Lane 4: Mouse kidney tissue
Lane 5: Mouse gonadal tissue
Lane 6: Hela whole cell lysate
Lane 7: 293T whole cell lysate
Secondary
Goat polyclonal to rabbit IgG at 1/10000 dilution
Predicted band size: 74, 32, 73 kDa
Observed band size: 74 kDa -
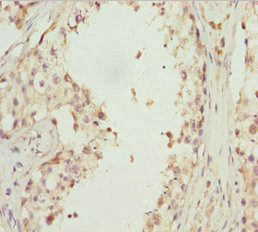
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human testis tissue using CSB-PA708490ESR1HU at dilution of 1:100
-
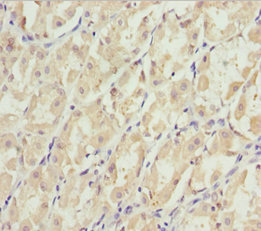
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human gastric cancer using CSB-PA708490ESR1HU at dilution of 1:100
-
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品名称:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) EFHC1 Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:Q5JVL4
-
基因名:EFHC1
-
别名:EF hand domain (C terminal) containing 1 antibody; EF hand domain containing protein 1 antibody; EF-hand domain-containing protein 1 antibody; Efhc1 antibody; EFHC1_HUMAN antibody; EJA1 antibody; EJM1 antibody; FLJ10466 antibody; FLJ37290 antibody; JAE antibody; Myoclonin 1 antibody; Myoclonin-1 antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反应种属:Human, Mouse
-
免疫原:Recombinant Human EF-hand domain-containing protein 1 protein (391-640AA)
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
标记方式:Non-conjugated
-
克隆类型:Polyclonal
-
抗体亚型:IgG
-
纯化方式:Antigen Affinity Purified
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存缓冲液:PBS with 0.02% sodium azide, 50% glycerol, pH7.3.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA, WB, IHC
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:1000-1:5000 IHC 1:20-1:200 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Microtubule-associated protein which regulates cell division and neuronal migration during cortical development. Necessary for mitotic spindle organization. Necessary for radial and tangential cell migration during brain development, possibly acting as a regulator of cell morphology and process formation during migration. May enhance calcium influx through CACNA1E and stimulate programmed cell death.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- EFHC1 mutations cause microtubule-associated defects in juvenile myoclonic epilepsy PMID: 28370826
- NHGRI gene-level evidence and variant-level evidence establish EFHC1 as the first non-ion channel microtubule-associated protein whose mutations disturb R-type VDCC and TRPM2 calcium currents in overgrown synapses and dendrites within abnormally migrated dislocated neurons, thus explaining CTC convulsions and "microdysgenesis" neuropathology of juvenile myoclonic epilepsy PMID: 27467453
- some EFHC1 mutations may be pathogenic only when introduced into specific genetic backgrounds to juvenile myoclonic epilepsy PMID: 25489633
- Myoclonin1/EFHC1 mutation was suggested releated to juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. PMID: 23756480
- These results show how Myoclonin1/EFHC1 mutations disrupt brain development and potentially produce structural brain abnormalities on which epileptogenesis is established. PMID: 22926142
- we conclude that mutations in the Myoclonin1/EFHC1 gene are an important cause of juvenile myoclonic epilepsy in Mexican patients. PMID: 22727576
- homozygous Phe229Leu mutation associated with primary intractable epilepsy in infancy PMID: 22690745
- The juvenile myoclonic epilepsy-related protein EFHC1 interacts with the redox-sensitive TRPM2 channel linked to cell death. PMID: 22226147
- Mutation analyses identified five missense mutations in EFHC1 that cosegregated with epilepsy or EEG polyspike wave in affected members of six unrelated families with JME and did not occur in 382 control individuals PMID: 15258581
- The combination of these polymorphisms could not be found in any control individuals, suggesting that they might be involved in genetic predisposition to migraine in this family. PMID: 16378686
- Deletion analyses revealed that the N-terminal region of EFHC1 is crucial for the association with the mitotic spindle and the midbody. Our results suggest that EFHC1 could play an important role during cell division. PMID: 16824517
- We found no evidence that EFHC1 is a major genetic risk factor for JME susceptibility in Dutch patients. PMID: 17054699
- Mutations in the EFHC1 gene may underlie different types of epilepsy syndromes. PMID: 17159113
- report presents one novel and one previously described mutation in the EFHC1 gene in Italian families, reinforcing the role of this gene in juvenile myoclonic epilepsy PMID: 17634063
- In this case of juvenile myoclonic epilepsy, A molecular genetic analysis led to the identification of a polymorphism (A-->G) in position 10 in the intron 3 (rs949626) of the EFHC1 gene. PMID: 17972043
- Nine percent of consecutive juvenile myoclonic epilepsy cases from Mexico and Honduras clinics and 3% of clinic patients from Japan carry mutations in Myoclonin1/EFCH1 PMID: 18505993
- Under reducing condition Ca(2+) or Mg(2+) ions bind to EFHC1C in a 1/1 molar ratio, while under oxidizing condition this ratio is reduced, showing that EFHC1C dimerization blocks Ca(2+) and Mg(2+) binding PMID: 18593566
- The results of this study show that four coding SNPs, rs3804506, rs3804505, rs1266787, and rs17851770, of EFHC1 may not be susceptibility alleles for juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. PMID: 18823326
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy 1 (EJM1); Juvenile absence epilepsy 1 (JAE1)
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle pole.
-
组织特异性:Widely expressed. Not detected in lymphocytes.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 16406
OMIM: 254770
KEGG: hsa:114327
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000360107
UniGene: Hs.403171
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-