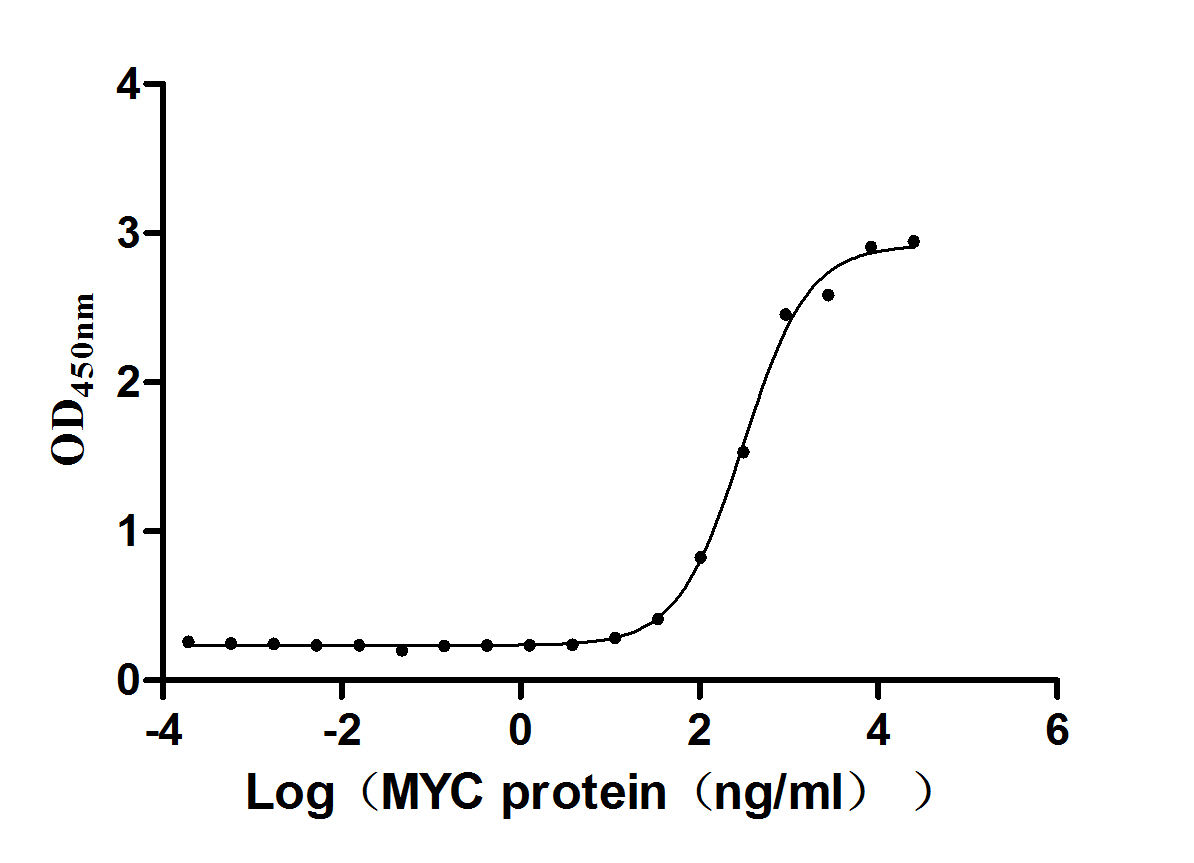
Recombinant Human EF-hand domain-containing protein 1 (EFHC1)
-
中文名称:人EFHC1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP708490HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人EFHC1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP708490HU
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人EFHC1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP708490HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人EFHC1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP708490HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人EFHC1重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP708490HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
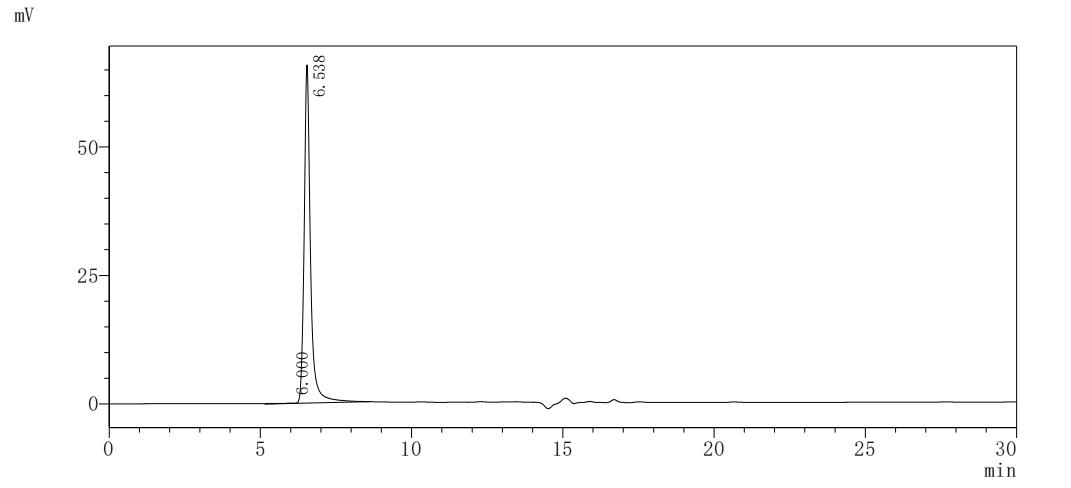
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:EFHC1
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:EF hand domain (C terminal) containing 1 ; EF hand domain containing protein 1; EF-hand domain-containing protein 1; Efhc1; EFHC1_HUMAN; EJA1; EJM1; FLJ10466; FLJ37290; JAE; Myoclonin 1; Myoclonin-1
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:full length protein
-
表达区域:1-640
-
氨基酸序列MVSNPVHGLP FLPGTSFKDS TKTAFHRSQT LSYRNGYAIV RRPTVGIGGD RLQFNQLSQA ELDELASKAP VLTYGQPKQA PPADFIPAHV AFDKKVLKFD AYFQEDVPMS TEEQYRIRQV NIYYYLEDDS MSVIEPVVEN SGILQGKLIK RQRLAKNDRG DHYHWKDLNR GINITIYGKT FRVVDCDQFT QVFLESQGIE LNPPEKMALD PYTELRKQPL RKYVTPSDFD QLKQFLTFDK QVLRFYAIWD DTDSMYGECR TYIIHYYLMD DTVEIREVHE RNDGRDPFPL LMNRQRVPKV LVENAKNFPQ CVLEISDQEV LEWYTAKDFI VGKSLTILGR TFFIYDCDPF TRRYYKEKFG ITDLPRIDVS KREPPPVKQE LPPYNGFGLV EDSAQNCFAL IPKAPKKDVI KMLVNDNKVL RYLAVLESPI PEDKDRRFVF SYFLATDMIS IFEPPVRNSG IIGGKYLGRT KVVKPYSTVD NPVYYGPSDF FIGAVIEVFG HRFIILDTDE YVLKYMESNA AQYSPEALAS IQNHVRKREA PAPEAESKQT EKDPGVQELE ALIDTIQKQL KDHSCKDNIR EAFQIYDKEA SGYVDRDMFF KICESLNVPV DDSLVKELIR MCSHGEGKIN YYNFVRAFSN
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Microtubule-associated protein which regulates cell division and neuronal migration during cortical development. Necessary for mitotic spindle organization. Necessary for radial and tangential cell migration during brain development, possibly acting as a regulator of cell morphology and process formation during migration. May enhance calcium influx through CACNA1E and stimulate programmed cell death.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- EFHC1 mutations cause microtubule-associated defects in juvenile myoclonic epilepsy PMID: 28370826
- NHGRI gene-level evidence and variant-level evidence establish EFHC1 as the first non-ion channel microtubule-associated protein whose mutations disturb R-type VDCC and TRPM2 calcium currents in overgrown synapses and dendrites within abnormally migrated dislocated neurons, thus explaining CTC convulsions and "microdysgenesis" neuropathology of juvenile myoclonic epilepsy PMID: 27467453
- some EFHC1 mutations may be pathogenic only when introduced into specific genetic backgrounds to juvenile myoclonic epilepsy PMID: 25489633
- Myoclonin1/EFHC1 mutation was suggested releated to juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. PMID: 23756480
- These results show how Myoclonin1/EFHC1 mutations disrupt brain development and potentially produce structural brain abnormalities on which epileptogenesis is established. PMID: 22926142
- we conclude that mutations in the Myoclonin1/EFHC1 gene are an important cause of juvenile myoclonic epilepsy in Mexican patients. PMID: 22727576
- homozygous Phe229Leu mutation associated with primary intractable epilepsy in infancy PMID: 22690745
- The juvenile myoclonic epilepsy-related protein EFHC1 interacts with the redox-sensitive TRPM2 channel linked to cell death. PMID: 22226147
- Mutation analyses identified five missense mutations in EFHC1 that cosegregated with epilepsy or EEG polyspike wave in affected members of six unrelated families with JME and did not occur in 382 control individuals PMID: 15258581
- The combination of these polymorphisms could not be found in any control individuals, suggesting that they might be involved in genetic predisposition to migraine in this family. PMID: 16378686
- Deletion analyses revealed that the N-terminal region of EFHC1 is crucial for the association with the mitotic spindle and the midbody. Our results suggest that EFHC1 could play an important role during cell division. PMID: 16824517
- We found no evidence that EFHC1 is a major genetic risk factor for JME susceptibility in Dutch patients. PMID: 17054699
- Mutations in the EFHC1 gene may underlie different types of epilepsy syndromes. PMID: 17159113
- report presents one novel and one previously described mutation in the EFHC1 gene in Italian families, reinforcing the role of this gene in juvenile myoclonic epilepsy PMID: 17634063
- In this case of juvenile myoclonic epilepsy, A molecular genetic analysis led to the identification of a polymorphism (A-->G) in position 10 in the intron 3 (rs949626) of the EFHC1 gene. PMID: 17972043
- Nine percent of consecutive juvenile myoclonic epilepsy cases from Mexico and Honduras clinics and 3% of clinic patients from Japan carry mutations in Myoclonin1/EFCH1 PMID: 18505993
- Under reducing condition Ca(2+) or Mg(2+) ions bind to EFHC1C in a 1/1 molar ratio, while under oxidizing condition this ratio is reduced, showing that EFHC1C dimerization blocks Ca(2+) and Mg(2+) binding PMID: 18593566
- The results of this study show that four coding SNPs, rs3804506, rs3804505, rs1266787, and rs17851770, of EFHC1 may not be susceptibility alleles for juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. PMID: 18823326
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy 1 (EJM1); Juvenile absence epilepsy 1 (JAE1)
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle pole.
-
组织特异性:Widely expressed. Not detected in lymphocytes.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 16406
OMIM: 254770
KEGG: hsa:114327
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000360107
UniGene: Hs.403171
Most popular with customers
-
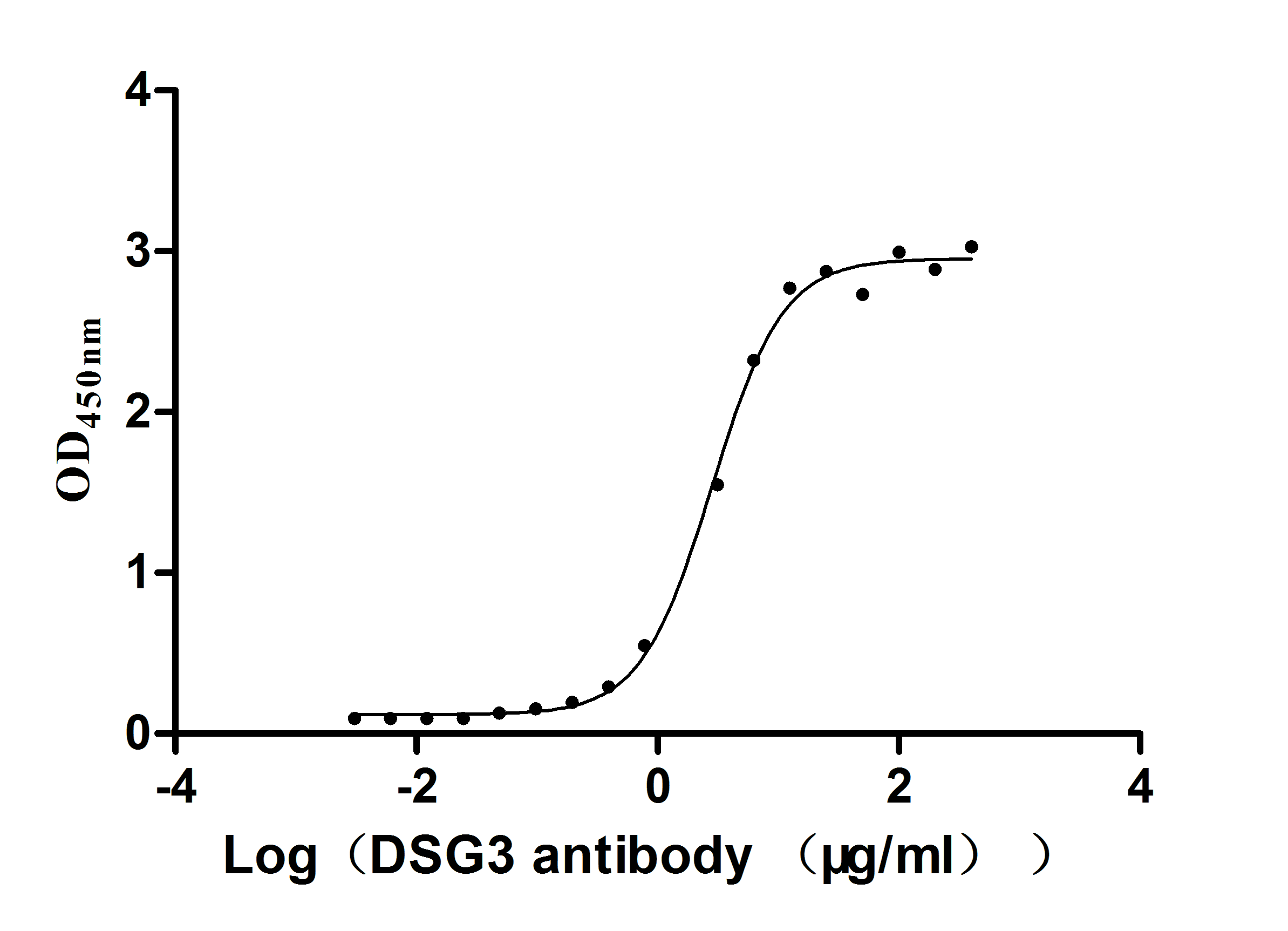
Recombinant Mouse Desmoglein-3 (Dsg3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human papillomavirus type 16 Protein E7 (E7) (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: Human papillomavirus type 16
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
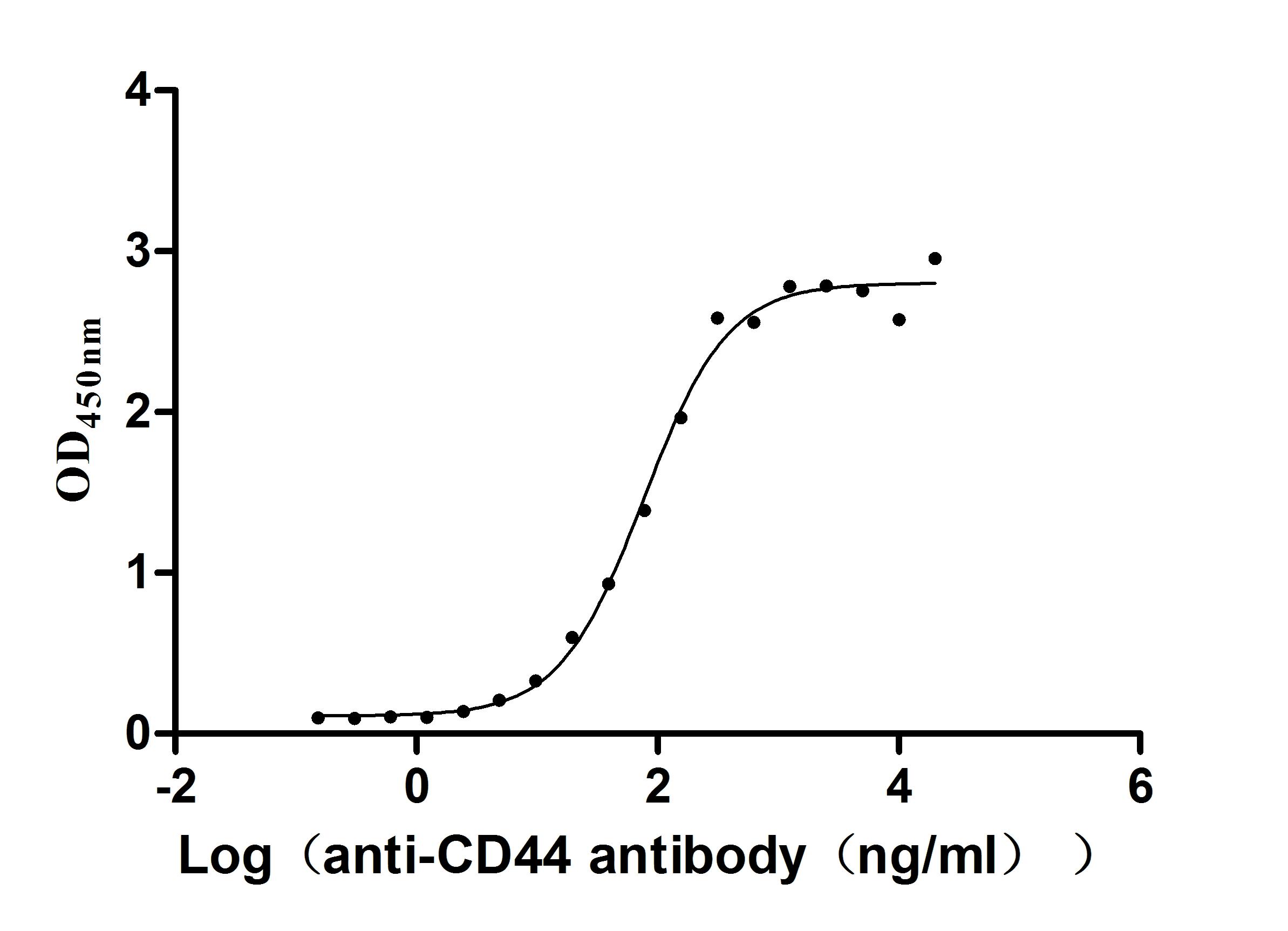
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis CD44 antigen (CD44), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human Claudin-6 (CLDN6)-VLPs, Fluorescent (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
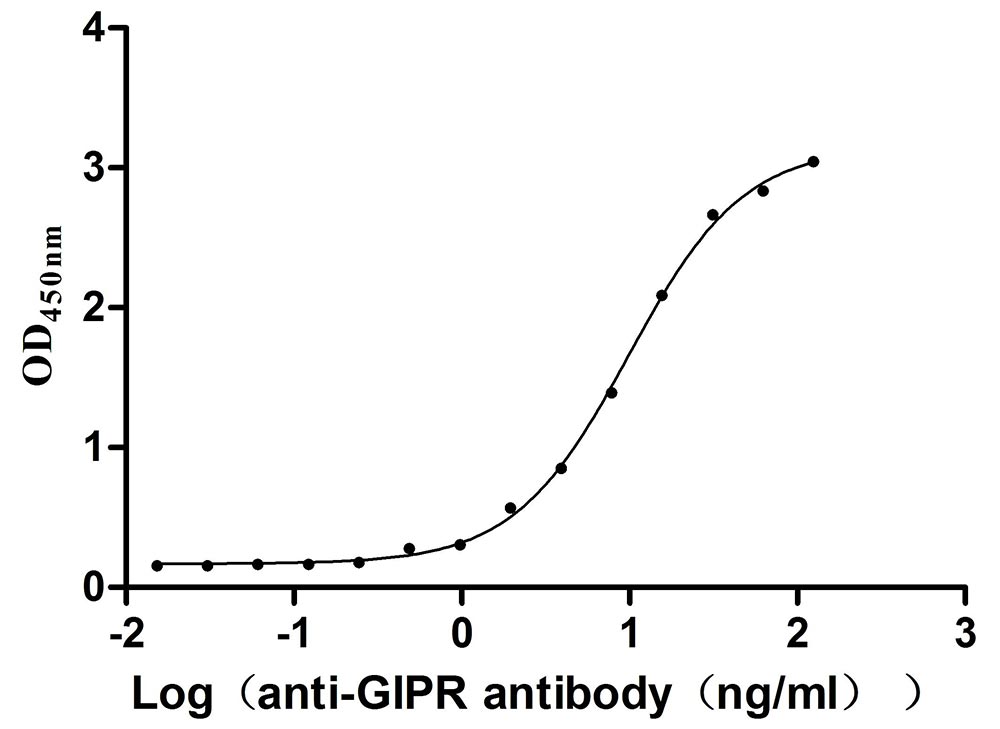
Recombinant Mouse Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor (Gipr), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
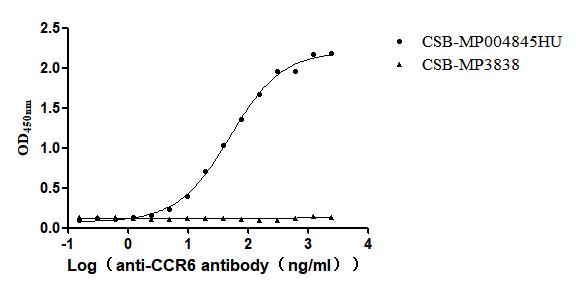
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 6(CCR6)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 9 (CCR9)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)



f4-AC1.jpg)