SMN1 Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
-
货号:CSB-RA567382A0HU
-
规格:¥1320
-
图片:
-
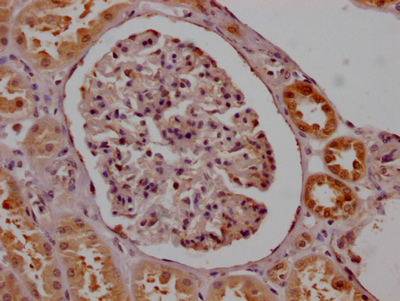
IHC image of CSB-RA567382A0HU diluted at 1:100 and staining in paraffin-embedded human kidney tissue performed on a Leica BondTM system. After dewaxing and hydration, antigen retrieval was mediated by high pressure in a citrate buffer (pH 6.0). Section was blocked with 10% normal goat serum 30min at RT. Then primary antibody (1% BSA) was incubated at 4℃ overnight. The primary is detected by a Goat anti-rabbit IgG polymer labeled by HRP and visualized using 0.05% DAB.
-
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品描述:
The SMN1 encodes the survival motor neuron (SMN) protein, which in conjunction with several Gemin proteins forms an SMN complex whose chaperone function facilitates the assembly of spliceosomal snRNP particles, essential components of the spliceosome complex, and hence plays a critical role in pre-mRNA splicing. Loss or mutation of the SMN1 gene causes spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), an autosomal recessive neuromuscular disease with α-motor neuron dysfunction and muscular atrophy. SMN is also implicated in mRNA transport in the axon of the nerve, the disturbance of which might explain the vulnerability of motor neurons in SMA.
This recombinant SMN1 antibody was developed with the Single B cell platform. The main process included identification and isolation of single B cells; amplification and cloning of SMN1 antibody gene; expression, screening, and identification of antibody specificity. And this SMN1 antibody has been validated in ELISA, IHC. -
Uniprot No.:Q16637
-
基因名:
-
别名:Survival motor neuron protein (Component of gems 1) (Gemin-1), SMN1, SMN2, SMN SMNT, SMNC
-
反应种属:Human
-
免疫原:A synthesized peptide derived from human SMN1
-
免疫原种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
标记方式:Non-conjugated
-
克隆类型:Monoclonal
-
抗体亚型:Rabbit IgG
-
纯化方式:Affinity-chromatography
-
克隆号:8B10
-
浓度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存缓冲液:Rabbit IgG in phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4, 150mM NaCl, 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol.
-
产品提供形式:Liquid
-
应用范围:ELISA, IHC
-
推荐稀释比:
Application Recommended Dilution IHC 1:50-1:200 -
Protocols:
-
储存条件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
货期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:The SMN complex catalyzes the assembly of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs), the building blocks of the spliceosome, and thereby plays an important role in the splicing of cellular pre-mRNAs. Most spliceosomal snRNPs contain a common set of Sm proteins SNRPB, SNRPD1, SNRPD2, SNRPD3, SNRPE, SNRPF and SNRPG that assemble in a heptameric protein ring on the Sm site of the small nuclear RNA to form the core snRNP (Sm core). In the cytosol, the Sm proteins SNRPD1, SNRPD2, SNRPE, SNRPF and SNRPG are trapped in an inactive 6S pICln-Sm complex by the chaperone CLNS1A that controls the assembly of the core snRNP. To assemble core snRNPs, the SMN complex accepts the trapped 5Sm proteins from CLNS1A forming an intermediate. Within the SMN complex, SMN1 acts as a structural backbone and together with GEMIN2 it gathers the Sm complex subunits. Binding of snRNA inside 5Sm ultimately triggers eviction of the SMN complex, thereby allowing binding of SNRPD3 and SNRPB to complete assembly of the core snRNP. Ensures the correct splicing of U12 intron-containing genes that may be important for normal motor and proprioceptive neurons development. Also required for resolving RNA-DNA hybrids created by RNA polymerase II, that form R-loop in transcription terminal regions, an important step in proper transcription termination. May also play a role in the metabolism of small nucleolar ribonucleoprotein (snoRNPs).
-
基因功能参考文献:
- A rare variant c.835-5T>G in intron 6 of SMN1 was identified in a patient affected with type I spinal muscular atrophy. PMID: 29799103
- Intron 2b-retained SMN transcript and intron3-retained SMN transcript were ubiquitously expressed in human cells and tissues. The intron-retained transcripts were mainly localized in the nucleus and decreased through non-nonsense-mediated decay pathway. PMID: 29580671
- overexpressed exogenous SMN1 at the ribosomal DNA (rDNA) locus of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) generated from a SMA patient using an rDNA-targeting vector PMID: 29209912
- Autosomal-recessive proximal spinal muscular atrophy (Werdnig-Hoffmann, Kugelberg-Welander) is caused by mutation of the SMN1 gene. PMID: 29478602
- While the above conclusions are firmly supported by the experimental data presented, we discuss and justify the need of deep proteomic techniques for the study of SMN complex components (orphan and bound) turn-over to understand the physiological relevant mechanisms of degradation of SMN and SMNDelta7 (SMN1 and SMN2)in the cell. PMID: 29292768
- Results report exon 6B, a novel exon, generated by exonization of an intronic Alu-like sequence from both SMN1 and SMN2, and validate the expression of exon 6B-containing transcripts SMN6B and SMN6BDelta7 in human tissues and cell lines. hnRNP C is shown to be a potential regulator of its expression and demonstrate that SMN6B is a substrate of nonsense-mediated decay. Also, an interaction of SMN6B with Gemin2 was found. PMID: 27481219
- Widespread intron retention and markers of the DNA damage response were observed with SMN1 depletion in human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells and human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived motor neurons. PMID: 28270613
- Study examined the effect of 2 mutations on SMN protein expression: a G-to-C transversion, leading to a tryptophan-to-serine substitution (p.Trp92Ser) in the Tudor domain; and a single thymine insertion between nucleotides 819 and 820 in exon 6 that causes a frameshift, changing all the amino acids of the C-terminal domain from the point of the mutation onward (p.Thr274Tyrfs). Mutations may affect stability and levels. PMID: 28366534
- The s show by NMR spectroscopy that both RNA recognition motifs of hnRNP A1 can bind simultaneously to a single bipartite motif of the human intronic splicing silencer ISS-N1, which controls survival of motor neuron exon 7 splicing. PMID: 28650318
- Homozygous deletion of the SMN1 gene have been detected in more than 95% of spinal muscular atrophy patients PMID: 28981927
- The increases of the SMN1 and SC35 1.7-kb mRNA levels reached about 4- and 6.5-fold in fibroblasts. PMID: 29080838
- Loganin is capable of increas-ing the SMN protein level under SMN-deficient conditions both inin vitro and in vivo models of spinal muscular atrophy via Akt/mTOR pathway. PMID: 27241020
- Activation of a cryptic 5' splice site in transcripts derived from SMN1 reversed a pathogenic G-to-C mutation at the first position of intron 7. PMID: 28981879
- Mutation in SMN1 is associated with Spinal Muscular Atrophy. PMID: 28950212
- Research has shown that SMN, both on the mRNA and protein level, is highly affected by cellular stress. In this review we will summarize the research that highlights the roles of SMN in the disease process and the response of SMN to various environmental stresses. PMID: 28852871
- Ongoing research may yield other treatments, especially for children who have not responded to Spinraza. A gene therapy delivered by adeno-associated virus type 9 (AAV9) is designed to replace or correct SMN1 . Cure SMA is supporting research in this area as well as studies of small molecules that correct SMN2 splicing or spur it to produce more protein. PMID: 28328128
- In lesional SSc dermal fibroblasts, GKT-137831 reduced alpha-SMA and CCN2 protein overexpression and collagen gel contraction PMID: 29049376
- Carrier risks for individuals having two copies of SMN1 in SMA families with 2-copy alleles were deduced. A meta-analysis including large sample sizes from the Chinese population was performed in order to generate a solid data basis for this calculation. PMID: 27422779
- From the computational analysis, it is also possible that SMN's Lys45 and Asp36 act as two electrostatic clips at the SMN-Gemin2 complex structure interface PMID: 28570645
- our studies show that this G-motif represents a novel and essential determinant for axonal localization of the Anxa2 mRNA mediated by the SMN complex. PMID: 28258160
- Loss of SMN1 is associated with Spinal muscular atrophy. PMID: 26908606
- A rare variant in exon 7 of SMN1 in three patients affected with type I or type II SMA. Most of the SMN1 transcripts exhibited complete loss of exon 7 in vivo. The variant disrupts Tra2beta1 binding. PMID: 26419278
- These results establish that SMN overexpression in motor neurons slows disease onset and outcome by ameliorating pathological signs in this model of mutant TDP-43-mediated amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). PMID: 27466204
- A long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) that arises from the antisense strand of SMN, SMN-AS1, is enriched in neurons and transcriptionally represses SMN expression by recruiting the epigenetic Polycomb repressive complex-2. PMID: 28017471
- We show that genes of the classical apoptosis pathway are involved in the smn-1-mediated neuronal death, and that this phenotype can be rescued by the expression of human SMN1, indicating a functional conservation between the two orthologs. Finally, we determined that Plastin3/plst-1 genetically interacts with smn-1 to prevent degeneration, and that treatment with valproic acid is able to rescue the degenerative phenotype PMID: 27260405
- SMN functions as a natural inhibitor for IL-1beta-induced NF-kappaB signaling by targeting TRAF6 and the IKK complex. PMID: 28214532
- U12-dependent intron retention is induced upon siRNA knock-down of SMN1 in HeLa cells. PMID: 27557711
- Deletion in SMN1 gene is associated with spinal muscular atrophy. PMID: 27754957
- Itch monoubiquitinates SMN and monoubiquitination of SMN plays an important role in regulating its cellular localization. PMID: 26908624
- Data indicate that survival motor neuron 1 protein (SMN1) gene copy number can be precisely determined for the diagnosis of spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). PMID: 27577201
- SMN may assemble translational platforms associated with and governed by the plasma membrane. PMID: 26743087
- A strong correlation was observed between the SMN2 copy number and spinal muscular atrophy phenotype PMID: 27510309
- The results of this study show that, the plasmid containing UTR elements causes to twice more SMN gene expression in transfected cells. PMID: 26607476
- Data show that the coding sequence of survival of motor neuron 2 (SMN2) differs from that of survival motor neuron 1 (SMN1) by a single nucleotide (c.840C>T) at codon 280 in exon 7. PMID: 26724723
- The Cajal bodies fail to recruit SMN and spliceosomal snRNPs, but contain the proteasome activator PA28, a molecular marker associated with the cellular stress response. PMID: 22302308
- PLS3 is a genuine spinal muscular atrophy protective modifier in SMN1-deleted individuals PMID: 26573968
- Measurements of SMN and PLS3 transcript and protein levels in induced pluripotent stem cell-derived motor neurons show limited value as Spinal muscular atrophy biomarkers. PMID: 26114395
- The diverse a-SMN vs FL-SMN C-terminus may dictate different protein interactions and complex formation explaining the different localization and role in the neuronal compartment, and the lower expression and stability of a-SMN. PMID: 26214005
- SMN and symmetric arginine dimethylation of RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain control transcriptional termination PMID: 26700805
- Among 43 identified patients with spinal muscular atrophy, 37 (86.0%) showed homozygous deletion of SMN1 exon 7. PMID: 26665550
- Study detected 3 small mutations in 4 patients without homozygous deletion of the SMN1 gene, suggested that about 4% of spinal muscular atrophy patients have subtle mutations and might be considered in laboratory examination PMID: 24563475
- SMN1 Gene Point Mutations in Type I-IV Proximal Spinal Muscular Atrophy Patients with a Single Copy of SMN1 PMID: 26606804
- investigate the oligomeric nature of the SMN.Gemin2 complexes from humans and fission yeast (hSMN.Gemin2 and ySMN.Gemin2) PMID: 26092730
- The copy numbers and gene structures of SMN1 genes were different in Chinese spinal muscular atrophy patients and healthy controls. PMID: 25888055
- This work both reveals a new autoregulatory pathway governing SMN expression, and identifies a new mechanism through which SMN can modulate specific mRNA expression via Gemin5. PMID: 25911097
- suggest that imaging flow cytometry technology has the potential for identifying SMN protein expression level and pattern as an evaluation tool of clinical studies PMID: 25264200
- successfully determined various gene dosages of SMN1 and SMN2 genes in homologous or heterologous subjects. By using the UFTPL-CE method, the SMN1 and SMN2 genes were fully resolved with the resolution of 2.16+/-0.37 (n=3 PMID: 24909772
- Findings are consistent with a role for SMN in myotube formation through effects on muscle differentiation and cell motility. PMID: 24760765
- cellular SMN proteins regulated miR-9 expression and that miR-9 expression was related to spinal muscular atrophy severity. PMID: 24751385
- Subtle mutation detection of SMN1 gene in Chinese spinal muscular atrophy patients: implication of molecular diagnostic procedure for SMN1 gene mutations. PMID: 25014214
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Spinal muscular atrophy 1 (SMA1); Spinal muscular atrophy 2 (SMA2); Spinal muscular atrophy 3 (SMA3); Spinal muscular atrophy 4 (SMA4)
-
亚细胞定位:Nucleus, gem. Nucleus, Cajal body. Cytoplasm. Cytoplasmic granule. Perikaryon. Cell projection, neuron projection. Cell projection, axon. Cytoplasm, myofibril, sarcomere, Z line.
-
蛋白家族:SMN family
-
组织特异性:Expressed in a wide variety of tissues. Expressed at high levels in brain, kidney and liver, moderate levels in skeletal and cardiac muscle, and low levels in fibroblasts and lymphocytes. Also seen at high levels in spinal cord. Present in osteoclasts and
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 11117
OMIM: 253300
KEGG: hsa:6606
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000370119
UniGene: Hs.202179
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-