Recombinant Human Methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria type C protein (MMACHC)
-
中文名称:人MMACHC重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP896896HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人MMACHC重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP896896HU
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人MMACHC重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP896896HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人MMACHC重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP896896HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:人MMACHC重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP896896HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:MMACHC
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:1810037K07Rik; BOS_3654; cblC; DKFZp564I122; FLJ25671; Methylmalonic aciduria (cobalamin deficiency) cblC type with homocystinuria; Methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria type C protein; Methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria type C protein homolog; MGC134307; MMAC_HUMAN; MMACHC; OTTHUMP00000009243; RP11 291L19.3; RP23-177C18.3
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:full length protein
-
表达区域:1-282
-
氨基酸序列MEPKVAELKQ KIEDTLCPFG FEVYPFQVAW YNELLPPAFH LPLPGPTLAF LVLSTPAMFD RALKPFLQSC HLRMLTDPVD QCVAYHLGRV RESLPELQIE IIADYEVHPN RRPKILAQTA AHVAGAAYYY QRQDVEADPW GNQRISGVCI HPRFGGWFAI RGVVLLPGIE VPDLPPRKPH DCVPTRADRI ALLEGFNFHW RDWTYRDAVT PQERYSEEQK AYFSTPPAQR LALLGLAQPS EKPSSPSPDL PFTTPAPKKP GNPSRARSWL SPRVSPPASP GP
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Cobalamin (vitamin B12) cytosolic chaperone that catalyzes the reductive decyanation of cyanocob(III)alamin (cyanocobalamin, CNCbl) to yield cob(II)alamin and cyanide, using FAD or FMN as cofactors and NADPH as cosubstrate. Cyanocobalamin constitutes the inactive form of vitamin B12 introduced from the diet, and is converted into the active cofactors methylcobalamin (MeCbl) involved in methionine biosynthesis, and 5'-deoxyadenosylcobalamin (AdoCbl) involved in the TCA cycle. Forms a complex with the lysosomal transporter ABCD4 and its chaperone LMBRD1, to transport cobalamin across the lysosomal membrane into the cytosol. The processing of cobalamin in the cytosol occurs in a multiprotein complex composed of at least MMACHC, MMADHC, MTRR (methionine synthase reductase) and MTR (methionine synthase) which may contribute to shuttle safely and efficiently cobalamin towards MTR in order to produce methionine. Also acts as a glutathione transferase by catalyzing the dealkylation of the alkylcob(III)alamins MeCbl and AdoCbl, using the thiolate of glutathione for nucleophilic displacement to generate cob(I)alamin and the corresponding glutathione thioether. The conversion of incoming MeCbl or AdoCbl into a common intermediate cob(I)alamin is necessary to meet the cellular needs for both cofactors. Cysteine and homocysteine cannot substitute for glutathione in this reaction.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- The epimutation is present in three generations and results from PRDX1 mutations that force antisense transcription of MMACHC. PMID: 29302025
- Partial CblC-type inherited Methylmalonic acidemia (MMACHC heterozygous mutation exonl: c. 80A >G, c. 609G >A) can onset with severe metabolic Atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. PMID: 29068997
- The crystal structure of ceCblC provides insights into how architectural differences at the alpha- and beta-faces of cobalamin promote the thiol oxidase activity of ceCblC but mute it in wild-type human CblC. PMID: 28442570
- Sequencing of the MMACHC gene is used for confirming the diagnosis of cblC disease. MMACHC mutations were found in all the nine patients. 7 different mutations were identified, including c.609G>A, c.455_457delCCC, c.394C>T, c.445_446insA, c.658_660delAAG, c.452A>G and IVS1+1G>A. The most frequent mutation was c.609G>A (6/9). Two patients had homozygous mutations (c.445_446insA/c.445_446insA and c.609G>A/c.609G>A). PMID: 26563984
- Case Report: c.567dupT,p.(Ile190Tyrfs*13) MMACHC heterozygous mutation underlying methylmalonic academia in infant. PMID: 27383490
- Five different known mutations in either MUT or MMACHC genes were identified in seven of the eight Chinese patients with methyl malonic acidemia. PMID: 25982642
- MMACHC mutation was found in children diagnosed with hemolytic uremic syndrome secondary to cobalamin C disorder. PMID: 26253414
- the MMACHC-MMADHC complex is a 1:1 heterodimer, where the interaction region overlaps with the MMACHC-Cbl binding site PMID: 26483544
- These results indicated that hypergonadotropic hypogonadism may be a novel clinical manifestation of cblC disease, but more reports on additional patients are needed to support this hypothesis. PMID: 26283149
- an adult patient with bull's eye macular lesions and no clinically relevant systemic symptoms was diagnosed with cblC by genetic screening and follow-up biochemical laboratory tests. PMID: 25687216
- A novel mutation p.G155R of the MMACHC gene is identified in prenatal diagnosis of combined methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria. PMID: 26149271
- Results propose a model whereby membrane-bound LMBD1 and ABCD4 facilitate the vectorial delivery of lysosomal vitamin B12 to cytoplasmic MMACHC. PMID: 25535791
- mutation analysis of the MMACHC gene in four patients revealed novel heterozygous mutations at nucleotide 276 (c.276G > A [p.Glu926Glu] and c.276G > T [p.Glu92Asp]), which is located at the end of exon 2. PMID: 24853097
- HCFC1 plays a role in craniofacial development, which is in part mediated through the regulation of MMACHC expression PMID: 25281006
- The gene responsible for cblC, named MMACHC, catalyzes the reductive decyanation of cyanocobalamin. PMID: 24577983
- data suggest that the interaction of methionine synthase with MMACHC may play a role in the regulation of the cellular processing of cobalamins that is required for cobalamin cofactor synthesis PMID: 23825108
- Subcellular location of MMACHC and MMADHC, two human proteins central to intracellular vitamin B(12) metabolism. PMID: 23270877
- The function of MMADHC is exerted through its structured C-terminal domain via interactions with MMACHC. PMID: 22832074
- a structural framework provides a framework for understanding catalytic function and disease mechanism for the multifunctional MMACHC complex. PMID: 22642810
- MMADHC was confirmed as a binding partner for MMACHC both in vitro (SPR) and in vivo (bacterial two-hybrid system). PMID: 21071249
- defects occurring in the MMACHC gene are the major cause of this disease in Chinese patients with combined methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria PMID: 20631720
- MMACHC-wt and MMACHC-R161Q are both very thermolabile proteins in their apo forms, with melting temperatures (T(m)) of 39.3+/-1.0 and 37.1+/-0.7 degrees C, respectively PMID: 20219402
- Mutations in MMACHC are associated with altered cellular oxidative stress and apoptosis processes in the presence or absence of vitamin B(12). PMID: 19760748
- MMACHC with the G147D mutation is unable to bind either cyanocobalamin or hydroxocobalamin, providing a straight forward explanation for the absence of response to either vitamin form. PMID: 19700356
- Diverse and clinically significant structural heart defects appear to be highly prevalent in cblC type methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria. PMID: 19767224
- Data show that the catalytic turnover numbers for the dealkylation of methylcobalamin and 5'-deoxyadenosylcobalamin by MMACHC are 11.7 +/- 0.2 and 0.174 +/- 0.006 h(-1) at 20 degrees C, respectively. PMID: 19801555
- One mutation, 271dupA, in MMACHC accounted for 40% of all disease alleles. PMID: 16311595
- Mutation analysis of the MMACHC gene showed that both patients were homozygous for 394C --> T which suggests a founder effect in Late onset cobalamin C disorder. PMID: 17431913
- c.271dupA (accounting for 55% of the MMACH alleles in our cohort) followed by c.394C>T (16%) and c.331C>T (9%) were the most frequent mutations. PMID: 18164228
- Most patients (eight of nine patients investigated) were compound heterozygotes for the 271dupA mutation and a missense mutation. PMID: 18245139
- MMACHC catalyzes a reductive decyanation reaction that removes the cyanide group in vitamin B(12) or cyanocobalamin PMID: 18779575
- A new mutation (146_154 del CCTTCCTGG) in the MMACHC gene was detected in a Chinese family with methylmalonic aciduria. PMID: 19199254
- Epigenetic inactivation of the MMACHC gene is responsible for methionine dependence in human melanoma cell line MeWo-LC1. PMID: 19200761
- MMACHC was sequenced from the DNA of 118 cblC individuals. Eleven novel mutations were identified.Genotype-phenotype correlations of common mutations were apparent. PMID: 19370762
- These studies suggest that the CblC protein is responsible for early processing of both CNCbl (decyanation) and alkylcobalamins (dealkylation) in mammalian cells. PMID: 19447654
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria type cblC (MMAHCC)
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm, cytosol.
-
蛋白家族:MMACHC family
-
组织特异性:Widely expressed. Expressed at higher level in fetal liver. Also expressed in spleen, lymph node, thymus and bone marrow. Weakly or not expressed in peripheral blood leukocytes.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 24525
OMIM: 277400
KEGG: hsa:25974
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000383840
UniGene: Hs.13024
Most popular with customers
-
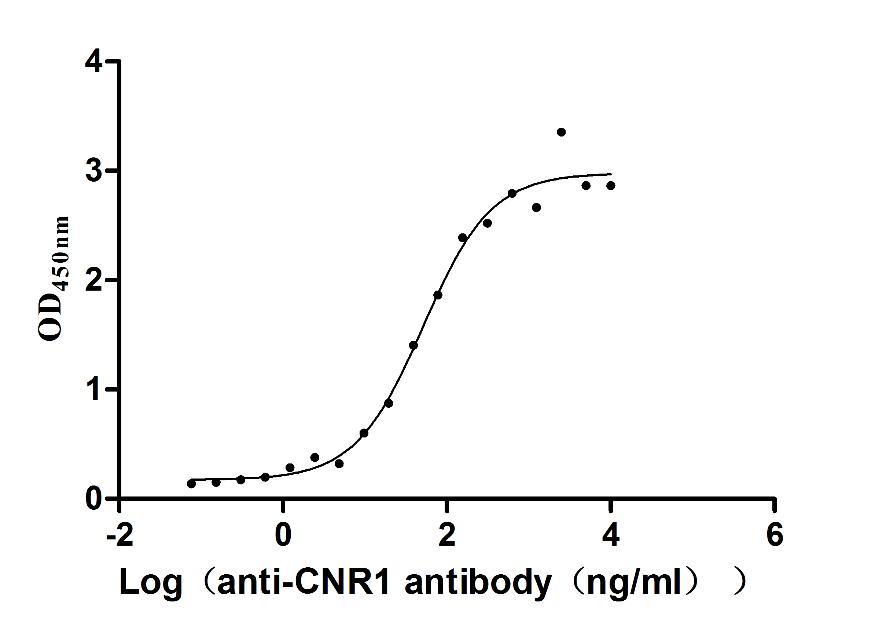
Recombinant Human Cannabinoid receptor 1 (CNR1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
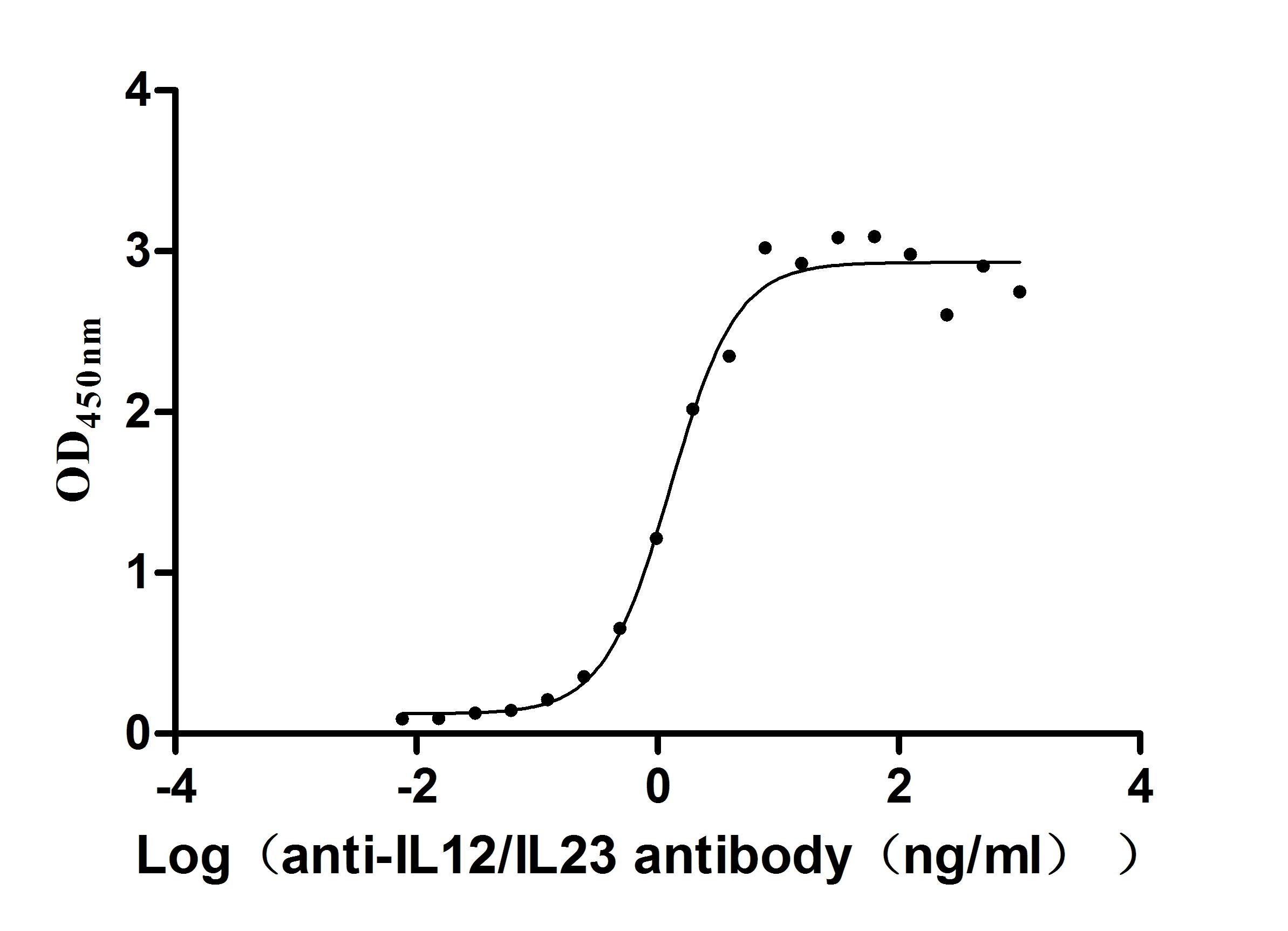
Recombinant Human IL12B&IL12A Heterodimer Protein (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
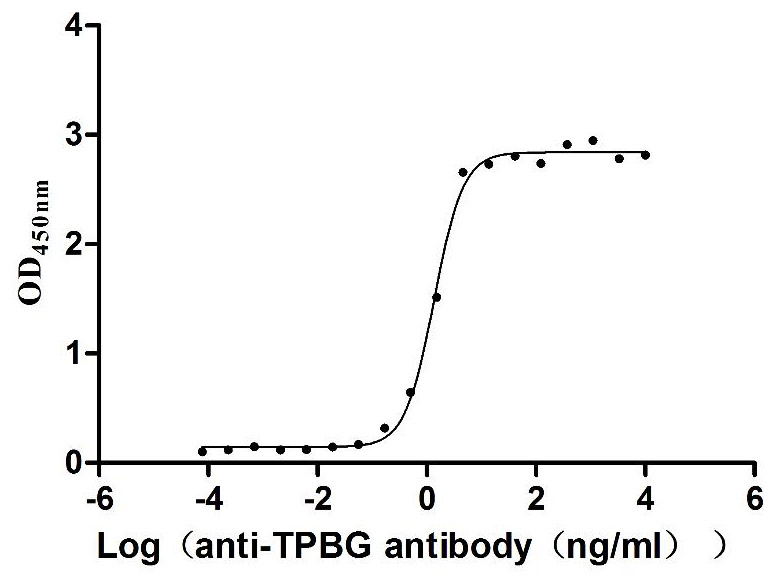
Recombinant Human Trophoblast glycoprotein (TPBG), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP1R), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 3DL2 (KIR3DL2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Dipeptidase 3(DPEP3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Dipeptidase 3(DPEP3) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 15(TNFSF15) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)