Recombinant Human N (G),N (G)-dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase 1 (DDAH1)
-
中文名称:Recombinant Human N(G),N(G)-dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase 1(DDAH1),Yeast
-
货号:CSB-YP006579HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Human N(G),N(G)-dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase 1(DDAH1),Yeast
-
货号:CSB-EP006579HU-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Human N(G),N(G)-dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase 1(DDAH1),Yeast
-
货号:CSB-BP006579HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Human N(G),N(G)-dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase 1(DDAH1),Yeast
-
货号:CSB-MP006579HU
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:DDAH1
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:DDAH; DDAH I; DDAH-1; DDAH1; DDAH1_HUMAN; DDAHI; Dimethylargininase 1; Dimethylargininase-1; Dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase 1; N(G); N(G)-dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase 1; NG NG dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length of Mature Protein
-
表达区域:2-285
-
氨基酸序列AGLGHPAAF GRATHAVVRA LPESLGQHAL RSAKGEEVDV ARAERQHQLY VGVLGSKLGL QVVELPADES LPDCVFVEDV AVVCEETALI TRPGAPSRRK EVDMMKEALE KLQLNIVEMK DENATLDGGD VLFTGREFFV GLSKRTNQRG AEILADTFKD YAVSTVPVAD GLHLKSFCSM AGPNLIAIGS SESAQKALKI MQQMSDHRYD KLTVPDDIAA NCIYLNIPNK GHVLLHRTPE EYPESAKVYE KLKDHMLIPV SMSELEKVDG LLTCCSVLIN KKVDS
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Hydrolyzes N(G),N(G)-dimethyl-L-arginine (ADMA) and N(G)-monomethyl-L-arginine (MMA) which act as inhibitors of NOS. Has therefore a role in the regulation of nitric oxide generation.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- MiR-21-mediated DDAH1/ADMA/NO signal pathway. PMID: 29682517
- DDAH-1 expression is associated with promotion of angiogenesis stimulating factor VEGF. PMID: 28741166
- These findings suggest that DDAH1 functions as a tumor suppressor in gastric cancer (GC) and may be exploited as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for GC. PMID: 28580735
- Data demonstrate that DDAH1 deficiency promotes the epithelial to mesenchymal transition in renal proximal tubular epithelial cells and causes fibrosis, and oxidative stress in aging and diabetic kidneys. The study provides the first direct evidence that the DDAH1 has a marked effect on kidney fibrosis and oxidative stress induced by aging or diabetes. PMID: 28594240
- Results confirmed DDAH1 3'-UTR as a target for miR-21, and endogenous miR-21 showed increased inhibitory effect on DDAH1-V3 transcript. PMID: 27663503
- Inflammatory factors expressed in response to myocardial ischemia contributed to up-regulation of DDAH1. PMID: 28145161
- DDAH1 plays dual roles in a particular matter-induced cell death in alveolar epithelial cells. PMID: 26996393
- rs3087894 in DDAH1 was significantly associated with hypertension and showed conflicting results in different ethnic groups. This is therefore a candidate for further studies with the aim of helping to ascertain the mechanisms of hypertension in different populations. PMID: 26786611
- wild-type rs480414 was 92% sensitive and 53% specific for pulmonary hypertension in bronchopulmonary dysplasia PMID: 26663142
- results suggest that miR-21 may regulate renal fibrosis by the Wnt pathway via directly targeting DDAH1 PMID: 26455824
- The most significant associations were detected for PECAM1*V/V + DDAH1*C (OR = 4.17 CI 1.56-11.15 Pperm = 0.005) PMID: 26662939
- FoxO1 regulates asymmetric dimethylarginine via downregulation of dimethylaminohydrolase 1 in HUVECs and subjects with carotid atherosclerosis. PMID: 26226438
- Genebased analyses revealed associations of the DDAH1 gene with longitudinal Blood Pressure phenotypes, associations with essential hypertension, Blood Pressure salt sensitivity, preeclampsia, or preclinical stages of atherosclerosis. PMID: 25424718
- DDAH1 deficiency attenuates endothelial cell cycle progression and angiogenesis. PMID: 24260221
- the advanced glycation end products-receptor for advanced glycation end products-mediated reactive oxygen species generation could be involved in endothelial dysfunction in diabetic end-stage renal disease patients PMID: 23766377
- DDAH1 genotypes were closely related to asymmetric dimethylarginine levels, but not to measures of endothelium-dependent vasodilation in an elderly population. PMID: 23892448
- Only the DDAH1-V1 transcript is responsible for ADMA metabolism, and transcript specific primers are recommended to determine DDAH1 mRNA expression. PMID: 23864585
- Elevated asymmetric dimethylaginine is not a part of the proatherogenic risk profile in the young adult offspring of patients with premature Coronary artery disease. PMID: 23022711
- A significant decrease in asymmetric dimethylarginine levels was found in ex-extremely low birth weight young adults compared to term birth weight young adults. PMID: 21420186
- Data suggest that estradiol alone has no effect on DDAH/asymmetric dimethylarginine/nitric oxide pathway in arterial endothelium, but rather counters oxidized LDL; estradiol restores DDAH activity and prevents loss of eNOS (nitric oxide synthase 3). PMID: 22982060
- DDAH1 gene DNA methylation is impoetant in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. PMID: 22700861
- Genetic polymorphisms in DDAH genes influence serum ADMA levels in individuals with T1 diabetes mellitus. PMID: 22521321
- High DDAH1 is associated with pediatric diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma. PMID: 22492959
- Non-diabetic hypertensive subjects with a hypertensive response to exercise compared to those with normal response were characterized by augmented asymmetric dimethylarginine and osteoprotegerin levels. PMID: 21975354
- did not find evidence for association with pre-eclampsia PMID: 21174581
- In acute congestive heart failure acute renal impairment function and the modulation of metabolism and extracellular transport by the DDAH-1/CAT-1 system determine high ADMA and SDMA levels after therapy for acute congestive heart failure. PMID: 21722652
- Data show that DDAH inhibition reduces fibroblast-induced collagen deposition in an ADMA-independent manner and reduces abnormal epithelial proliferation in an ADMA-dependent manner. PMID: 21677199
- HDL significantly increased the attenuated endothelial cell NO production induced by ox-LDL, which was attributed to its effect on DDAH/ADMA pathway PMID: 21264497
- Indicate that DDAH1 is required for metabolizing asymmetrical dimethylarginine and N(omega)-monomethyl-L-arginine. PMID: 21493890
- Results provide evidence that SNP rs1241321 in DDAH1 is associated with type 2 diabetes and its long-term outcome. PMID: 21303562
- DDAH1 exerts a unique role in activating Akt that affects endothelial function independently of degrading endogenous nitirc oxide synthase inhibitors. PMID: 21212404
- Recent studies in this review suggest that DDAH may regulate endothelial nitric oxide activity and endothelial function through both asymmetric dimethylarginine-dependent and -independent mechanisms. PMID: 19682581
- Expression of hDDAH1 messenger RNA is found in all organs of DDAH1 transgenic mice investigated, whereas human DDAH1 is absent in wild-type littermates. PMID: 19666120
- Circulating methylarginine levels and the decline in renal function in patients with chronic kidney disease are modulated by DDAH1 polymorphisms. PMID: 20010544
- Results suggest that the DDAH1 loss-of-function polymorphism is associated with both increased risk of thrombosis stroke and coronary artery disease in the Chinese Han population. PMID: 20167924
- Recombinant human DDAH1 overexpression protects transgenic mice from adverse structural and functional changes in cerebral arterioles in hyperhomocysteinemia but not from accelerated carotid artery thrombosis induced by the HM/LF diet. PMID: 20019334
- hydrolyzes methylated inhibitors of nitric oxide synthase is present in circulating human red blood cells PMID: 11811522
- The first evidence of the importance of DDAH1 polymorphisms in pre-eclampsia susceptibility was provided. PMID: 15501905
- By increasing the synthesis of the proangiogenic factor nitric oxide, DDAH promotes postnatal angiogenesis and arteriogenesis. PMID: 15781754
- DDAH-1 and DDAH-2 messenger RNA and protein were demonstrated in first trimester placental tissue, primary extravillous trophoblasts and extravillous trophoblast-derived cell lines. PMID: 16920729
- it is concluded that L-arginine regulates asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) metabolism dose-dependently by competing for DDAH thus maintaining the metabolic balance of L-arginine and ADMA, and endothelial NO homeostasis PMID: 17075694
- DDAH-1 activity leads to accumulation of asymmetric dimethylarginine and reduction in nitric oxide signaling. PMID: 17273169
- Demonstrate a critical role for DDAH-1 and endogenous methylarginines in the pathogenesis of endothelial dysfunction. PMID: 17881609
- human dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase-1 is inhibited by S-nitroso-L-homocysteine and hydrogen peroxide PMID: 17895252
- maintenance of normoglycemia and not glycemia-independent actions of insulin maintained dimethylarginine tissue levels by preserving physiological DDAH activity. PMID: 18292189
显示更多
收起更多
-
蛋白家族:DDAH family
-
组织特异性:Detected in brain, liver, kidney and pancreas, and at low levels in skeletal muscle.
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 2715
OMIM: 604743
KEGG: hsa:23576
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000284031
UniGene: Hs.713411
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 18 (TNFSF18), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
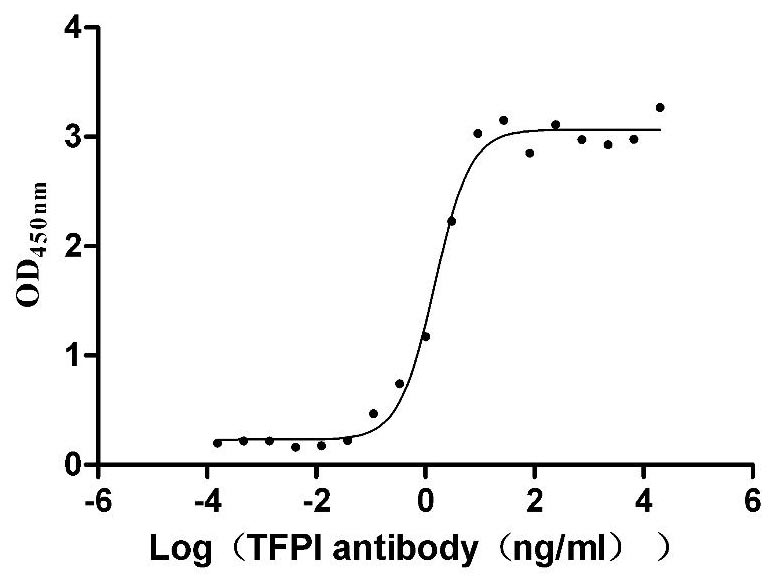
Recombinant Human Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca mulatta Semaphorin-4D isoform 1 (SEMA4D), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque)
-
Recombinant Human Claudin-6 (CLDN6)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
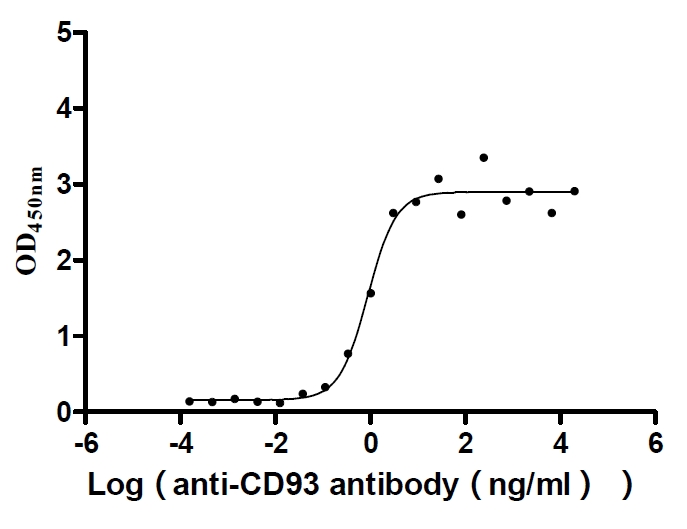
Recombinant Human Complement component C1q receptor (CD93), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
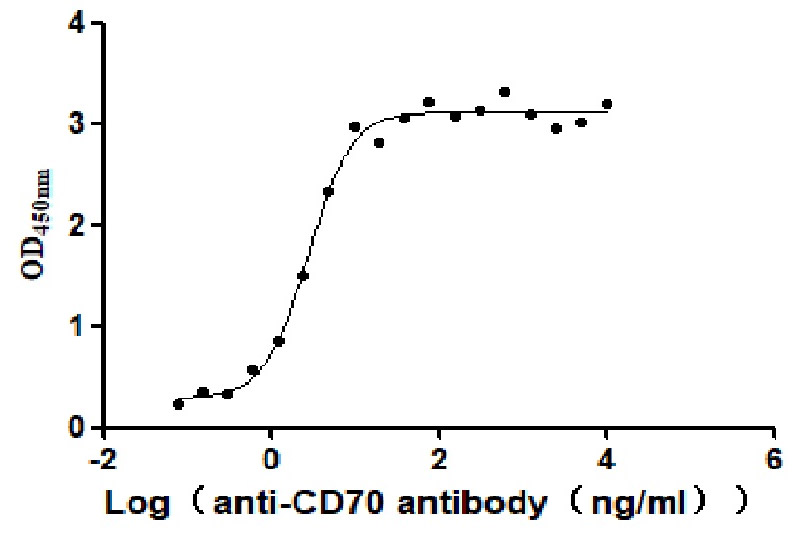
Recombinant Human CD70 antigen (CD70), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)



-AC1.jpg)
-AC1.jpg)