Recombinant Human Retinoschisin (RS1)
In Stock-
货号:CSB-EP020534HUe0
-
规格:¥1344
-
图片:
-
其他:
产品详情
-
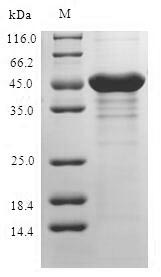
纯度:Greater than 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
基因名:RS1
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Retinoschisin; RS1; X-linked juvenile retinoschisis protein; XLRS1_HUMAN
-
种属:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白长度:Full Length of Mature Protein
-
来源:E.coli
-
分子量:50.0kDa
-
表达区域:24-224aa
-
氨基酸序列STEDEGEDPWYQKACKCDCQGGPNALWSAGATSLDCIPECPYHKPLGFESGEVTPDQITCSNPEQYVGWYSSWTANKARLNSQGFGCAWLSKFQDSSQWLQIDLKEIKVISGILTQGRCDIDEWMTKYSVQYRTDERLNWIYYKDQTGNNRVFYGNSDRTSTVQNLLRPPIISRFIRLIPLGWHVRIAIRMELLECVSKCA
Note: The complete sequence including tag sequence, target protein sequence and linker sequence could be provided upon request. -
蛋白标签:N-terminal GST-tagged
-
产品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
缓冲液:Tris-based buffer,50% glycerol
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:3-7 business days
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:Binds negatively charged membrane lipids, such as phosphatidylserine and phosphoinositides. May play a role in cell-cell adhesion processes in the retina, via homomeric interaction between octamers present on the surface of two neighboring cells. Required for normal structure and function of the retina.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- molecular detail such as the precise localization of mutant protein in the cell as well as its ability to assemble into a functionally active oligomer might largely influence disease severity among XLRS patients PMID: 29851975
- These results establish that extracellular delivery of RS1 rescues the structural and functional deficits in the Rs1h knockout mouse model and that this ex vivo gene therapy approach can inhibit progression of disease. PMID: 27390514
- Taken together, RS1 mutation was found to segregate with retinoschisis phenotype while none of the other identified variations were co-segregating with the systemic defects. Hereby, we infer that the multisystemic defects harbored by the patient are a rare coexistence of XLRS, developmental delay, sensorineural hearing loss, and reduced axial tone reported for the first time in the literature. PMID: 28574807
- Results suggest a regulatory effect of retinoschisin on Na/K-ATPase signaling and localization, whereas Na/K-ATPase-dysregulation caused by retinoschisin deficiency could represent an initial step in XLRS pathogenesis. PMID: 28615319
- these findings support distinct mechanisms of pathology for two classes of X-linked retinoschisis -associated mutations in the retinoschisin assembly. PMID: 27798099
- A novel RS1 (97delT) mutation was identified in a Taiwanese family with X-linked retinoschisis (XLRS). This finding expands the RS1 mutation spectrum and may help to further understand the molecular pathogenesis of XLRS. PMID: 24529551
- Clinical and genetic characterization of affected homozygous females in XLRS affords the rare opportunity to explore the molecular mechanisms of XLRS and the manifestation of these mutations as disease in humans. PMID: 25894957
- A novel RS1 (304C > T) mutation in a Taiwanese family with X-linked retinoschisis. PMID: 26043410
- We identified a novel causative mutation of RS1 in a Chinese family with X-linked juvenile retinoschisis. PMID: 25168411
- the disease and p.Arg197Cys mutation of RS1 gene was identified PMID: 25799783
- X-linked retinoschisis despite striking differences in phenotypic presentation in affected subjects, homozygosity of one affected female, and seemingly dominant inheritance in three subsequent generations because of multiple consanguinity. PMID: 25054456
- Sequencing of the RS1 gene identified 16 mutations, nine of which were novel. PMID: 24505212
- Severe RS1 missense changes were associated with a lower ERG b/a ratio than were mild changes in X-linked retinoschisis suggesting the effect of the mutations on protein structure influenced the retinal dysfunction. PMID: 23847049
- Two novel exonic deletions within the RS1 gene locus, are reported. PMID: 24227916
- There is profound phenotypic variability in patients with XLRS. Nonsense, splice-site, or frame-shifting mutations in RS1 consistently caused electronegative bright-flash ERG, delayed flicker response, and abnormal PERG PMID: 23453514
- Four novel RS1 gene mutations have been described in male Polish patients with X-linked juvenile retinoschisis. PMID: 23288992
- aggregation propensity in the RS1 C110Y mutant is dependent upon the formation of suitable aggregating substrates for propagation of aggregation and not directly related to or determined by overall structural instability PMID: 22292953
- Clinical follow-up of an X-linked juvenile retinoschisis (XLRS) patient with a typical juvenile retinoschisis phenotype revealed no significant decline in visual acuity during this time period. PMID: 22171610
- Ten hemizygous mutations in RS1 were detected in patients from 14 of the 20 families with retinoschisis. PMID: 22245991
- Loss of RS1 due to mutations in the X-linked retinoschsis gene leads to splitting within the retinal layers. PMID: 22183371
- adaptive optics scanning laser ophthalmoscopy images of two patients with molecularly characterized XLRS revealed increased cone spacing and abnormal packing in the macula of each patient, but cone coverage and function were near normal. PMID: 22110067
- RS1 mutation putative severity and age both had significant effects on retinal function in X-linked retinoschisis only in the severe mutation group, as judged by electroretinography analysis of the b-wave amplitude and the b/a-ratio PMID: 22039241
- Data suggest that retinoschisin secretion is regulated by the F-actin cytoskeleton, that cGMP or inhibition of ROCK alters F-actin structure enhancing the secretion, and that the microtubule cytoskeleton is also involved in this process. PMID: 21738583
- Two novel mutations (W112X and S134P) and three previously identified missense mutations (R102Q, R200H, and R213W) were found. PMID: 21701876
- Retinoschisin, the protein involved in the pathogenesis of X-linked juvenile retinoschisis, membrane association is severely impaired in the absence of ATP1A3 and ATP1B2. PMID: 21196491
- analyzed the biochemical consequences of several RS1 signal-sequence mutants (c.1A>T, c.35T>A, c.38T>C, and c.52G>A) in X-linked retinoschisis disease PMID: 20809529
- The R213W mutation in RS1 causes various severities of retinoschisis in a large Chinese family. PMID: 20806044
- Clinical follow-up of ten young XLRS (X-linked retinoschisis) patients with a typical congenital retinoschisis phenotype revealed no significant decline in retinal function during this time period. PMID: 20569020
- A novel p.D126G mutation appeared to be associated with a severe phenotype with vitreous hemorrhage developing in infancy. PMID: 20151283
- Results show that missense mutations of retinoschisin which cause intracellular retention also lead to an unfolded protein response. PMID: 19849666
- Novel and known missense mutations of XLRS1 gene in the diagnosis retinoschisis. PMID: 12055472
- Two novel point mutations of the XLRS1 gene in two Japanese patients with X-linked juvenile retinoschisis. One novel splice donor site mutation (IVS2 + 1g to a) and one missense mutation of exon 6 (Ala211Thr) were found. PMID: 12383832
- Basis of RS1 is intracellular retention of mutant proteins, which may explain why disease severity is not mutation-specific. PMID: 12417531
- Electroretinographic findings in three family members with X-linked juvenile retinoschisis associated with a novel Pro192Thr missense mutation of the XLRS1 gene. PMID: 12457918
- X-linked retinoschisis is caused by defective discoidin domain structure, subunit assembly, and endoplasmic reticulum processing of retinoschisin PMID: 12746437
- analysis of folding of mutant RS1 protein PMID: 12782284
- Each family had a different mutation, Trp96stop, 522+1g-->a, and Lys167Asn in the XLRS1 gene. PMID: 12920343
- four base pair deletion (375- 378 del AGAT) in exon 5 of the XLRS1 gene was found in all affected males. PMID: 12967815
- Molecular testing revealed a novel 473-bp deletion including exon 4 in the XLRS1 gene in both siblings. This resulted in a frameshift mutation and a premature termination at codon 78. PMID: 14986011
- One patient with more severe clinical presentation had a RS1 exon 1 deletion and a P193S mutation was found in the other patient with mild macular involvement PMID: 15281981
- In three patients, we identified three different missense mutations (p.S73P, p.Y89C, p.R209C) in the functionally important discoidin domain of the RS1 gene. PMID: 15531314
- assembly of RS1 into a disulfide-linked homo-octamer appears to be critical for its function as a retinal cell adhesion protein PMID: 15644328
- A novel Leu103Phe mutation is an additional missense mutation which is responsible for the pathogenesis of X-linked retinoschisis. PMID: 16768192
- We identified a novel point mutation (1A>T transversion) in the initiation codon of the XLRS1 gene in affected males PMID: 17031297
- Retinoschisin protein(RS) is expressed in the pinealocytes but not in interstitial glial cells. The lack of structural abnormalities in the RS1(-/Y) mice suggests that RS serves a different function in the pineal gland than in the retina. PMID: 17093404
- Review. Many mutations have been found in RS1, which encodes a 224-AA secreting retinal protein, retinoschisin. Retinoschisin octamerisation is implicated in cell-cell interactions & cell adhesion perhaps by interacting with beta2 laminin. PMID: 17172462
- We describe a novel nonsense mutation in the conserved region of Rs1 in a Japanese XLRS family. PMID: 17295148
- Multiple fine white dots at the macula may be the initial fundus feature in RS1 mutation. PMID: 17296904
- Mutations in RS1 to be associated with XLRS in the Indian population. PMID: 17515881
- Severe X linked juvenile retinoschisis phenotypes are associated with the frameshift mutation 26 del T, splice donor site mutation (IVS1+2T to C), and Arg102Gln, Asp145His, Arg209His, and Arg213Gln mutations. PMID: 17615541
显示更多
收起更多
-
相关疾病:Retinoschisis juvenile X-linked 1 (XLRS1)
-
亚细胞定位:Secreted. Cell membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Extracellular side.
-
组织特异性:Restricted to the retina (at protein level). Detected in the inner segment of the photoreceptors, the inner nuclear layer, the inner plexiform layer and the ganglion cell layer (at protein level). At the macula, expressed in both the outer and inner nucle
-
数据库链接:
HGNC: 10457
OMIM: 300839
KEGG: hsa:6247
STRING: 9606.ENSP00000369320
UniGene: Hs.715725
Most popular with customers
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Melanoma-associated antigen 4 (MAGEA4) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
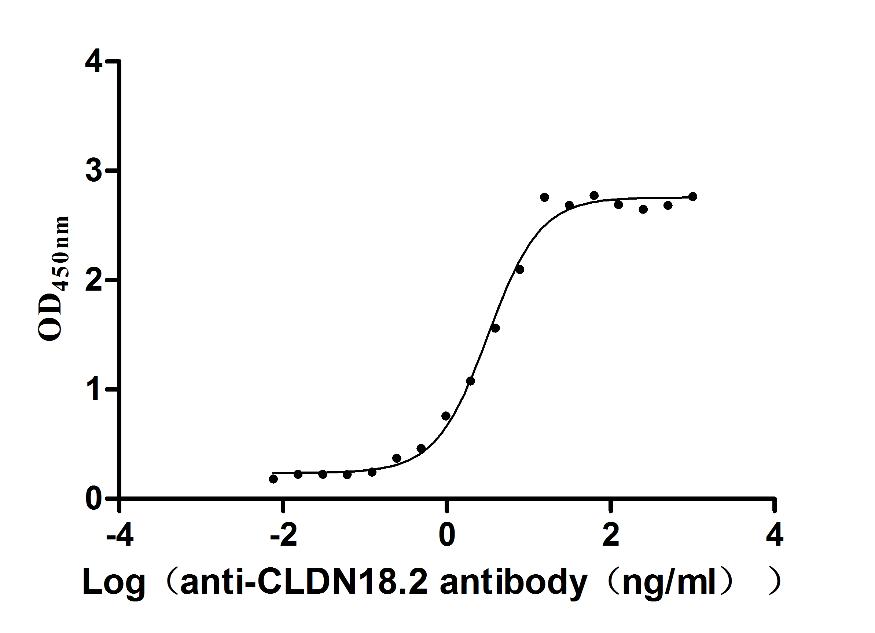
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Claudin (CLDN18)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
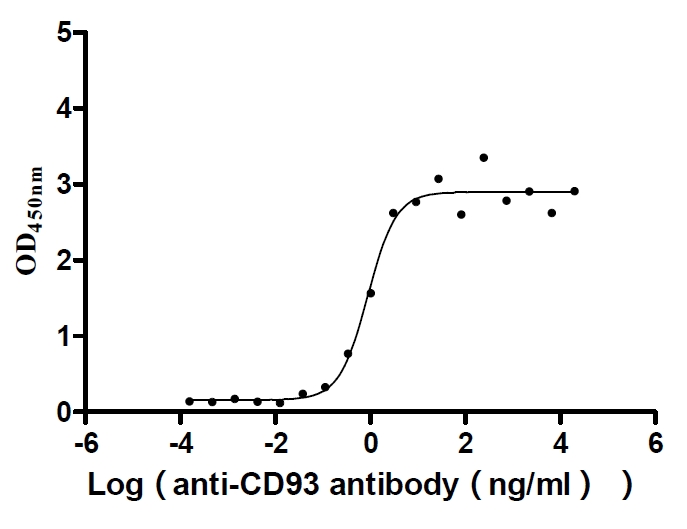
Recombinant Human Complement component C1q receptor (CD93), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Myosin regulatory light chain 12A (MYL12A) (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Cadherin-1(CDH1),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
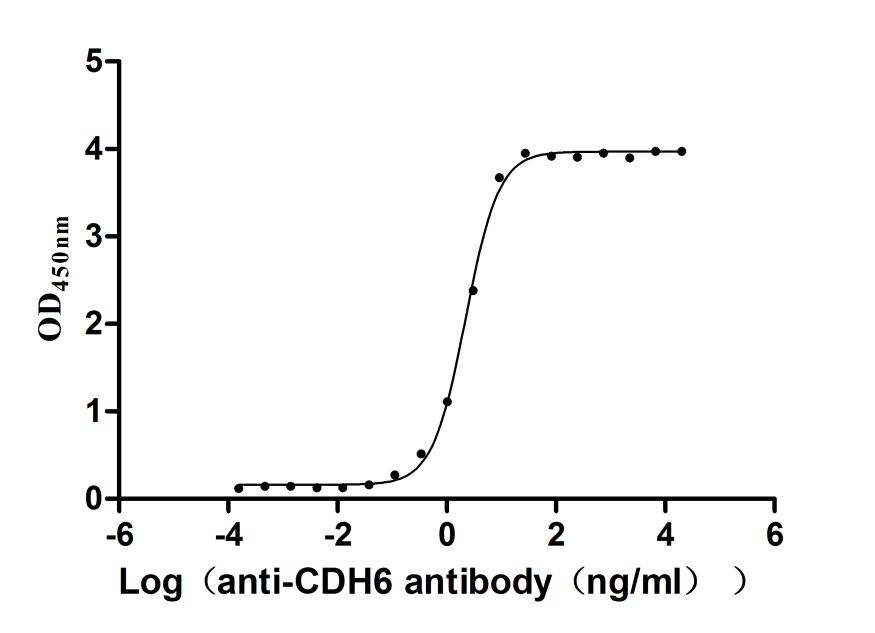
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Cadherin 6(CDH6),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)