Recombinant Mouse Acid-sensing ion channel 1 (Asic1), partial
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse Acid-sensing ion channel 1(Asic1),partial,Yeast
-
货号:CSB-YP740680MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse Acid-sensing ion channel 1(Asic1),partial,Yeast
-
货号:CSB-EP740680MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse Acid-sensing ion channel 1(Asic1),partial,Yeast
-
货号:CSB-EP740680MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse Acid-sensing ion channel 1(Asic1),partial,Yeast
-
货号:CSB-BP740680MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:Recombinant Mouse Acid-sensing ion channel 1(Asic1),partial,Yeast
-
货号:CSB-MP740680MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Asic1
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Asic1; Accn2; Asic; Bnac2; Acid-sensing ion channel 1; ASIC1; Acid-sensing ion channel; Amiloride-sensitive cation channel 2; neuronal; Brain sodium channel 2; BNaC2
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Proton-gated sodium channel; it is activated by a drop of the extracellular pH and then becomes rapidly desensitized. Generates a biphasic current with a fast inactivating and a slow sustained phase. Has high selectivity for sodium ions and can also transport lithium ions with high efficiency. Can also transport potassium ions, but with lower efficiency. It is nearly impermeable to the larger rubidium and cesium ions. Mediates glutamate-independent Ca(2+) entry into neurons upon acidosis. This Ca(2+) overloading is toxic for cortical neurons and may be in part responsible for ischemic brain injury. Heteromeric channel assembly seems to modulate channel properties. Functions as a postsynaptic proton receptor that influences intracellular Ca(2+) concentration and calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II phosphorylation and thereby the density of dendritic spines. Modulates activity in the circuits underlying innate fear.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- ASICs promote the inflammatory response and apoptosis of RAW 264.7 cells. PMID: 30074209
- These data demonstrate the involvement of an ASIC1a-mediated insular synaptic depression mechanism in extinction learning. PMID: 27924869
- ASIC1a expression in astrocytes. Injection of rAAV-ASIC1a-shRNA into the dentate gyrus of the wide type TLE mouse model resulted in the inhibition of astrocytic ASIC1a expression and a reduction in spontaneous seizures PMID: 27526777
- The findings of this study suggested a key role for ASIC1a in normal olfactory function. PMID: 28912013
- Study suggests Acid-sensing ion channel 1a plays an inhibitory role in vasodilation in response to external protons, functional hyperemia, and exercise capacity. PMID: 28784852
- Asic1 showed heightened mRNA expression, coherent with the repeated cross-fostering paradigm (RCF)-mice's respiratory hypersensitivity to CO2 and altered nociception. PMID: 27121911
- Notch1 signaling may be required for ASIC1a-mediated neurite growth and neuronal differentiation in neuroblastoma cells. PMID: 28030818
- The s observed no preference for sodium at the "GAS belt" in the central constriction. Instead, they identified a band of glutamate and aspartate side chains at the lower end of the pore that enables preferential sodium conduction. PMID: 28498103
- Asic1a KO mice exhibited prominent deficits in multiple fear-related behaviors. PMID: 28657172
- ASIC1a Deficient Mice Show Unaltered Neurodegeneration in the Subacute MPTP Model of Parkinson Disease PMID: 27820820
- The manuscript demonstrates that postsynaptic neurons of the medial nucleus of the trapezoid body at the mouse calyx of Held synapse express functional homomeric Acid-sensing ion channel-1a (ASIC-1as) that can be activated by protons (coreleased with neurotransmitter from acidified synaptic vesicles). These ASIC-1as contribute to the generation of postsynaptic currents and, more relevant, to calcium influx, which could be PMID: 28159907
- nonselective cation channels ( channels consist of at least one alpha-ENaC and one or more acid-sensing ion channel 1a (ASIC1a) proteins. PMID: 28283476
- ASIC1a is an important mediator of AHR. PMID: 27820848
- Ca(2+) influx through ASIC1 mediates chronic hypoxia and ET-1-induced NFATc3 nuclear import and 2) the scaffolding protein PICK1 is necessary for NFATc3 nuclear import. PMID: 27190058
- This study provides evidence that ASIC1a is involved in group I metabotropic glutamate (mGlu) receptor-induced increase in action potential firing. PMID: 28137639
- the potentiation of ASICs by quinine depends on the presence of the ASIC1a, ASIC2a subunits, but not ASIC1b, ASIC3 subunits. Furthermore, we have determined the amino acids in ASIC1a that are involved in the modulation of ASICs by pHi. PMID: 27402850
- These results reveal new insights into the role of acid-sensing ion channels 1a in hippocampal synaptic plasticity and the underlying mechanisms PMID: 26996240
- Studies with ASIC1a-ASIC2a chimeras showed that swapping the thumb domain between subunits results in faster channel desensitization. Likewise, the covalent modification of Cys residues at selected positions in the beta-ball-thumb interface accelerates the desensitization of the mutant channels. PMID: 27015804
- differential surface trafficking of ASIC1a, ASIC2a, and ASIC2b, was investigated. PMID: 26746198
- This study demonstrated that asic1 proteins consist of distinct responsible for ion conduction, mechanical force sensing, and transduction to coordinately fulfill their function as sophisticated MS channels. PMID: 26924440
- Acid-sensing ion channel 1a drives AMPA receptor plasticity following ischaemia and acidosis in hippocampal CA1 neurons PMID: 26174503
- Deletion of the Asic1a gene significantly prevents RIP1 phosphorylation and brain damage, suggesting ASIC1a-mediated RIP1 activation has an important role in ischemic neuronal injury. PMID: 26523449
- Study suggests that ASIC1a activity facilitates NMDAR function and exacerbates NMDAR-mediated neuronal death in pathological conditions PMID: 25947342
- The data of this study suggest that ASIC1a may be a mediator of SCA1 pathogenesis and targeting ASIC1a could be a novel approach to treat SCA1. PMID: 24788087
- ASIC1A inhibits neuronal plasticity underlying addiction-related behavior; disrupting ASIC1A in the mouse nucleus accumbens increases cocaine-conditioned place preference. PMID: 24952644
- We conclude that this optogenetic method offers a minimally invasive approach that enables examining the biological consequences of ASIC1a currents in any structure of the CNS and in the modulation of animal behaviors. PMID: 24727474
- Data suggest that mitochondrial ASIC1a may serve as an important regulator of MPT pores, which contributes to oxidative neuronal cell death. PMID: 23852371
- Suggest that ASIC1a channels might be involved in controlling neuromuscular transmission, muscle contraction and fatigue in female mice. PMID: 24336653
- Mutations in binding motifs of ASIC1a reduce surface expression and pH sensitivity; C-terminal motifs are important for ASIC1a trafficking and channel function. PMID: 23727453
- ASIC1-/- mice exhibit blunted chronic hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension and diminished calcium entry. PMID: 24186095
- ASIC1a plays an important role in the modulation of behavioral sensitivity to cocaine. PMID: 23644053
- In summary, this study provides direct evidence for the presence of two distinct proton coordination sites in the extracellular region of ASIC1a, which jointly facilitate pore opening in response to extracellular acidification. PMID: 24142696
- Our results indicated that in AsTg mice, the Ca(2)(+) response to the acid was facilitated in macrophages by a low threshold of ASIC1 and NCX1 molecules and the activity of these channel was possibly regulated by adiponectin. PMID: 24084100
- Regulation of ASIC channels by a stomatin/STOML3 complex located in a mobile vesicle pool in sensory neurons. PMID: 22773952
- The results of this study revealed the molecular mechanism of ASIC1a internalization and suggest the importance of endocytic pathway in functional regulation of ASIC1a channels as well as neuronal damages mediated by these channels. PMID: 23595764
- the lower palm domain mediates conformational movements that drive pore opening and closing events in ASIC1a PMID: 23300086
- Currents from ASIC1a(-/-) muscle afferents were less pH-sensitive and displayed faster recovery, currents from ASIC2(-/-) showed diminished potentiation by zinc, and currents from ASIC3(-/-) displayed slower desensitization than those from wild-type. PMID: 23109675
- Anions modulate a variety of acid-sensing ion channel properties and are dependent on subunit composition. The mechanism of modulation for ASIC2a and -3 is distinct from that of ASIC1a. PMID: 23135698
- ASIC1a has two desensitized states with markedly different stabilities. PMID: 23048040
- Thus, our results reveal a novel mechanism underlying central sensitization and pain hypersensitivity, and reinforce the critical role of ASIC1a channels in these processes. PMID: 22553040
- Our results indicate that ion selectivity is accomplished by the contribution of multiple sites in the pore of ASIC1a. PMID: 22371494
- ASIC1a N366Q, which showed increased glycosylation and dendritic targeting, potentiated acidosis-induced spine loss. PMID: 22442073
- correct folding of extracellular ectodomain plays a critical role in ASIC1a biogenesis and function PMID: 22046405
- findings reveal a mechanism whereby snake venoms produce pain, and highlight an unexpected contribution of ASIC1 channels to nociception PMID: 22094702
- GABA(A) receptors and glycine receptors modify ASICs in neurons through mechanisms that require the opening of chloride channels. PMID: 21789198
- These data suggest that phenylketonuria-related brain injury is independent of ASIC1a expression PMID: 21663378
- Insights into the mechanism of pore opening of acid-sensing ion channel 1a. PMID: 21388961
- ASIC1, ASIC2, and ASIC3 are expressed in bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (DCs) at the mRNA and protein levels; extracellular acid can evoke ASIC-like currents in DCs. PMID: 21321108
- this study suggested new neuroprotective strategies for stroke patients via inhibition of polyamine synthesis and subsequent spermine-ASIC interaction. PMID: 21307247
- Results indicate that PICK1 regulates trafficking and function of ASIC1a in a lipid binding-dependent manner. PMID: 21176140
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:Amiloride-sensitive sodium channel (TC 1.A.6) family, ASIC1 subfamily
-
组织特异性:Expressed in brain areas receiving strong excitatory corticofugal input. In hippocampus, expressed in the hilus of the dentate gyrus. In the cerebral cortex expressed in anterior and posterior cingulate cortex, sensory and motor cortices. In the sensory c
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:11419
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000023758
UniGene: Mm.440107
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Glucagon receptor (GCGR), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
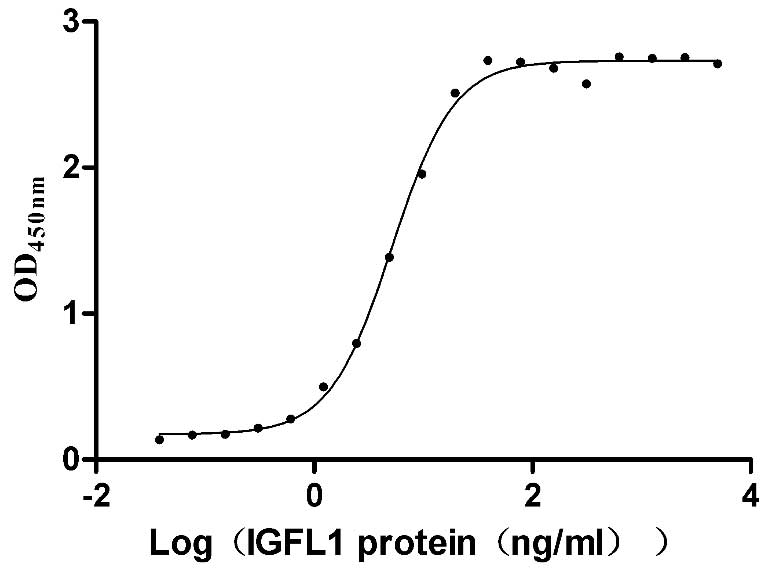
Recombinant Human IGF-like family receptor 1 (IGFLR1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
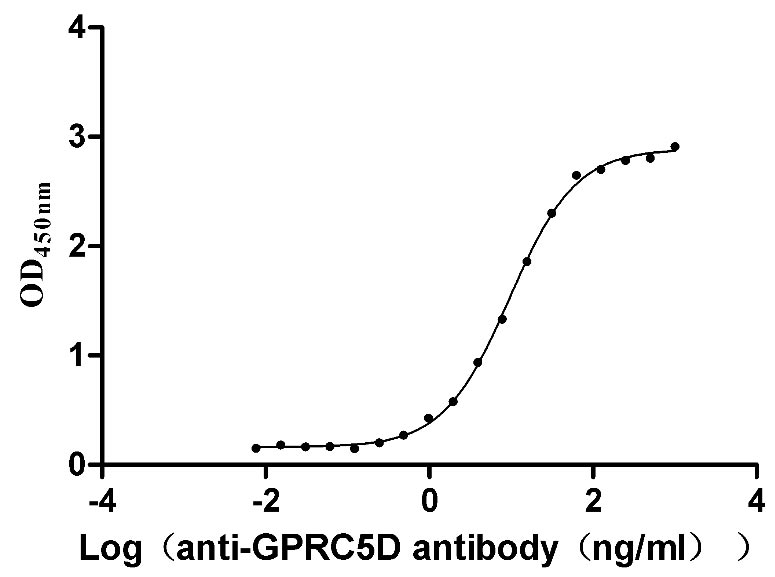
Recombinant Human G-protein coupled receptor family C group 5 member D (GPRC5D)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
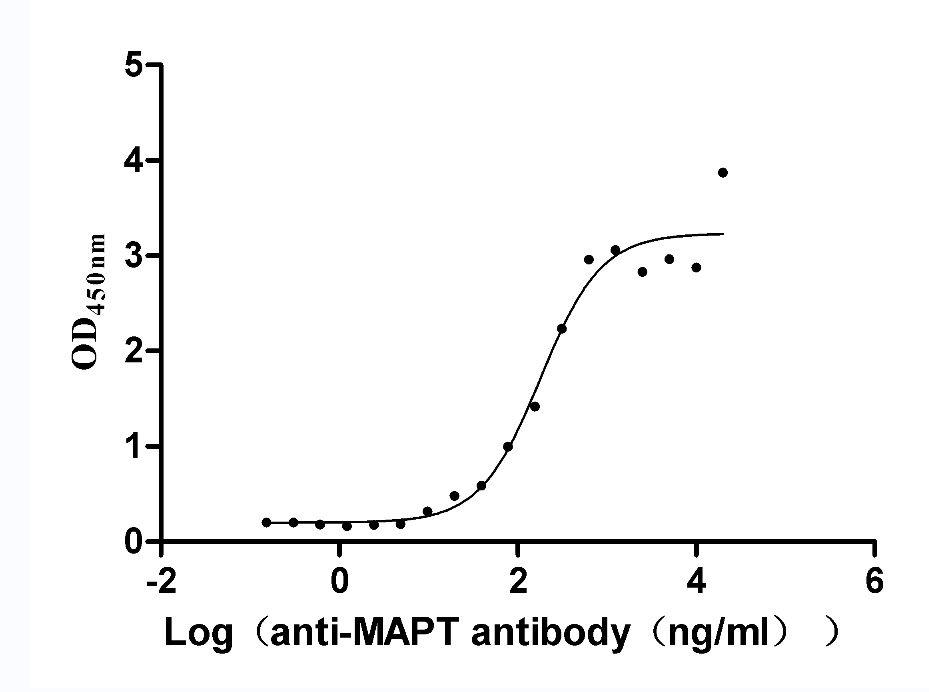
Recombinant Rat Microtubule-associated protein tau (Mapt) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
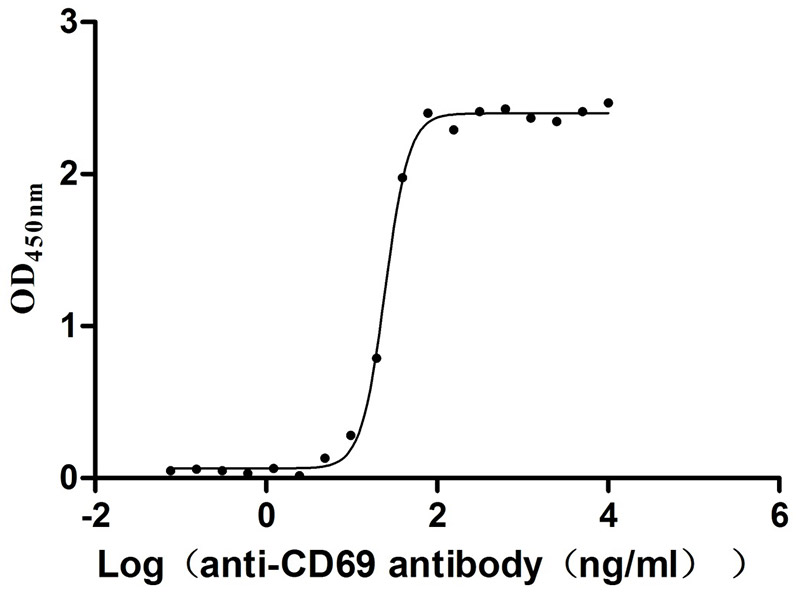
Recombinant Human Early activation antigen CD69 (CD69), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator(BTLA), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Dipeptidase 3(DPEP3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)