Recombinant Rat Corticotropin-releasing factor receptor 1 (Crhr1), partial
-
货号:CSB-YP005965RA1
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP005965RA1
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-EP005965RA1-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-BP005965RA1
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
货号:CSB-MP005965RA1
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:Crhr1; Crhr; Corticotropin-releasing factor receptor 1; CRF-R-1; CRF-R1; CRFR-1; Corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor 1; CRH-R-1; CRH-R1
-
种属:Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相关产品
靶点详情
-
功能:G-protein coupled receptor for CRH (corticotropin-releasing factor) and UCN (urocortin). Has high affinity for CRH and UCN. Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and down-stream effectors, such as adenylate cyclase. Promotes the activation of adenylate cyclase, leading to increased intracellular cAMP levels. Inhibits the activity of the calcium channel CACNA1H. Required for normal embryonic development of the adrenal gland and for normal hormonal responses to stress. Plays a role in the response to anxiogenic stimuli.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- Irritability-like behavior following abstinence from ethanol exposure is partially mediated by activation of the CRF1 receptor. PMID: 28833238
- CRHR1 blockade using Antalarmin (ANT) improved behavioral impairments, while conferring neuroprotection and blunting neuroinflammation in all hippocampal sub-regions post ischemia. Also observed reduced BDNF and TrkB mRNA and protein levels at the hippocampus, and increased expression at the hypothalamus and amygdala post ischemia, site-specific alterations which were regularized by pre-ischemic CRHR1 blockade. PMID: 28647536
- These results indicate that the central CRF signal, rather than the peripheral CRF signal would be related to anxiety and other behavioral changes, and CRF1 receptor antagonism in the central nervous system may be critical for identifying drug candidates for anxiety and mood disorders PMID: 28689880
- Study found that bilateral microinjection of selective CRF1 receptor antagonist CP376395 into the bed nucleus of stria terminalis (BNST) decreased the bradycardiac response to arterial pressure increase without affecting the baroreflex tachycardiac response; CRF2 receptor antagonist antisauvagine-30 microinjection reduced the tachycardiac response to arterial pressure decrease without affecting the reflex bradycardia. PMID: 28612996
- the involvement of the HPA axis in traumainduced anxiety was demonstrated, and trauma-induced anxiety was attenuated by decreasing the hyperactivity of the HPA axis via miR34b by targeting CRHR1. PMID: 28498394
- Results suggest that corticotrophin-releasing factor type 1 receptor (CRF1) is involved in the modulation of the functions of the pituitary; moreover, protein expression and the distribution patterns of CRF1 are regulated by glucocorticoids in the rat anterior pituitary. PMID: 27801962
- These results revealed a prominent role for CRF1 signaling in mast cells as a positive modulator of stimuli-induced degranulation. PMID: 28684600
- age-related alterations in acute central anorexigenic and hypermetabolic effects of CRF show different non-parallel patterns in males and females. Our findings underline the importance of gender differences. They also call the attention to the differential age-related changes in the CRF1 and CRF2 receptor systems PMID: 27637621
- switch in G protein coupling for type 1 corticotropin-releasing factor receptors promotes excitability in epileptic brains PMID: 27303056
- Study identified the activation of CRFR1 in the basolateral amygdala as a key mechanism interfering with the effectiveness of immediate fear extinction training. PMID: 27844053
- The findings demonstrate that the long-term effect of acute stress on the expression of cocaine locomotor sensitization is partially mediated by CRFR1 in the ventromedial caudate putamen. PMID: 28431969
- Chronic noise significantly accelerated the progressive overproduction of corticosterone and upregulated CRF and CRFR1 mRNA and protein, both of which persisted 7-14days after noise exposure. PMID: 27538655
- maternal care is impaired by Bed Nucleus Stria Terminalis CRF-R1 activation, and this appears to be the result of a central action, rather than an effect of elevated circulating levels of CORT. PMID: 26630389
- Exposure to acute traumatic stress in early adolescent can cause permanent changes in neural network, resulting in dysregulation of corticotrophin releasing factor expression, miR-34c expression in hypothalamus, anxiety-like behavior, and memory impairment, suggesting that the miR-34c expression in hypothalamus may be an important factor involved in post traumatic stress syndrome. PMID: 26925271
- Study demonstrates sex differences in CRF receptor 1 and 2 mRNA changes within unique subnuclei of the dorsal raphe nucleus and the posterior ventral tegmental area PMID: 26696011
- Competing roles of CRHR1 and CRHR2 on stress-induced in vivo serotonin synthesis. PMID: 26454419
- CRF1 receptor levels did not differ significantly between genotypes but receptor blockade normalized both cue- and contextual fear in SERT(-/-) during acquisition, but not expression of fear-potentiated startle PMID: 26302762
- Both acute and chronic noise increased CRH-R1 mRNA in the hypothalamus but decreased it in the hippocampus. PMID: 26333123
- Study revealed that the alteration of central CRFR1 expression might play an important role in etiology of post-traumatic stress disorder in adulthood PMID: 25882722
- Findings suggest that an early potentiation of CRF signaling at CRFR1 occurs following opioid exposure that begins to drive both opioid-induced hyperalgesia and eventually intake escalation. PMID: 24330252
- The point mutations occurring in the CRF1-R gene of msP rats do not seem to influence basal anxiety while they appear to affect active responses to stress. PMID: 25260340
- Activation of CRF1 receptors is required for the emergence of nicotine abstinence-induced anxiety-like behavior, hyperalgesia and excessive nicotine intake. PMID: 23869743
- the increase in CRHR1 expression in the hypothalamus of stressed rats correlates with a decrease in the repressive chromatin state caused by reduced H3K9 trimethylation levels. PMID: 24867333
- Neuromodulatory effects of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and corticotropin-releasing factor receptor (CRFR) 1 in visceral pain and stress-induced defecation in the WKY rat model of irritable bowel syndrome were investigated. PMID: 25260633
- results indicate that CRF1 receptors in the dPAG play a pervasive role in the regulation of defensive responses associated with both generalized anxiety and panic. Recruitment of CRF2 receptors only impacts upon the former type of behaviors. PMID: 25146701
- impaired miR449a expression causes dysregulation of Crhr1 expression in the anterior pituitary, resulting in prolonged HPA axis activation in restrained Low birth weight offspring. PMID: 25480379
- Our results implicate CRHR1 and CRHR2 in coordinating the regulation of CRH neuronal activity in stress and behavioral responses. PMID: 25275258
- We present evidence demonstrating prenatal hypoxia exposure induced anxiety-like behavior in adult male rat offspring and CRHR1 in paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus is involved. PMID: 25433848
- The analgesic effect can be mediated by both CRF1 and CRF2 receptors. CRF-1 receptor, in contrast to the CRF2 receptors, may be involved in the regulation of the basal level of pain sensitivity. PMID: 25665407
- Water-avoidance stress may activate peripheral CRF1 but not CRF2 signaling and stimulates gastric contractions without altering gastric emptying PMID: 23645119
- results suggest that post-stress alcohol drinking may be driven by a high-nociception high-arousal state, and that brain CRF1R signaling mediates these stress effects. PMID: 24269607
- This study demonistrated that crhr1 links peripuberty stress with deficits in social and stress-coping behaviors in rats model. PMID: 24630468
- findings demonstrate that stress affects CRF1 expression in brain but also in ova, pointing to a possible mechanism of transgenerational transmission. PMID: 23726318
- Data show that corticotropin releasing factor receptor 1 (CRF1) antagonists, NGD 98-2 and NGD 9002 prevented icv CRF-induced colonic secretomotor stimulation and blocked the induction of visceral sensitization. PMID: 24040053
- Gestational intermittent hypoxia elicited a sex-dependent anxiety-like behavior in male offspring and activation of corticotropin-releasing hormone and CRH type-1 receptor mRNA in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus and in male hypothalamus. PMID: 23529784
- MiR-449a plays an important role in stress-induced, glucocorticoid-mediated downregulation of CRF-R1 expression. PMID: 23893957
- The CRHR1-triggered ERK 1/2 pathway is involved in the activation of p53 in rat hepatic cells. PMID: 23538210
- The results of this study suggested that differences in monoaminergic neurotransmission and CRFR1 expression are associated with the coping strategy adopted by the animal and with the tendency to develop depression-related behaviors. PMID: 23732652
- Peripheral CRF stimulates gastric contractions through CRF(1). PMID: 23205497
- CRFR1 signaling plays a role in the anxiogenic effects of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) within the bed nucleus of stria terminalis. PMID: 23376701
- Non-pain-related activation of CRF1 receptors in the amygdala can trigger pain-responses in normal animals. PMID: 23410057
- These findings clearly demonstrate a gender-selective effect of gestational intermittent hypoxia to increase anxiety-like behavior and this anxiogenic effect might be linked to embryogenically-driven upregulation of PVN CRHR1. PMID: 23164543
- CRHR1 agonism stimulates rat and mouse fetal testis steroidogenesis PMID: 23133512
- Corticotropin-releasing factor receptor binding in the amygdala changes across puberty in a sex-specific manner PMID: 23117932
- CRHR1 does not have a role in basal alcohol intake or relapse-like drinking situations with a low stress load. PMID: 22113086
- During adolescence, nicotine reward is enhanced by recent stressor exposure in a manner that involves signaling at CRF-R1. PMID: 21720754
- Data suggest that corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH) regulates dendritic outgrowth in cultured hippocampal neurons/pyramidal cells; signaling via CRH-R1 stimulates dendritic growth; CRH-R2 activation results in inhibition of dendritic growth. PMID: 22249942
- The corticotropin-releasing factor CRF(1) receptor antagonist R278995/CRA0450 is centrally active under standard conditions as it inhibits REM sleep and promotes wakefulness. PMID: 22314225
- Intracerebroventricular corticotropin-releasing factor and restraint increased both Fos-positive CRF and non-CRF neurons in the parvocellular paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus through activation of CRF1 and/or CRF2. PMID: 21964377
- The non-competitive antagonist behaviour appeared to be correlated to the CRF(1) receptor off-rate kinetics. PMID: 21449919
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Endosome.
-
蛋白家族:G-protein coupled receptor 2 family
-
组织特异性:Detected in brain, especially in cerebellum. Detected in pituitary gland, and at lower levels in the olfactory bulb.
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: rno:58959
STRING: 10116.ENSRNOP00000006764
UniGene: Rn.10499
Most popular with customers
-
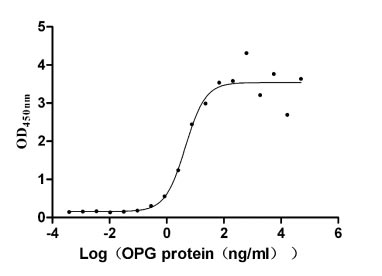
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 11B (TNFRSF11B) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
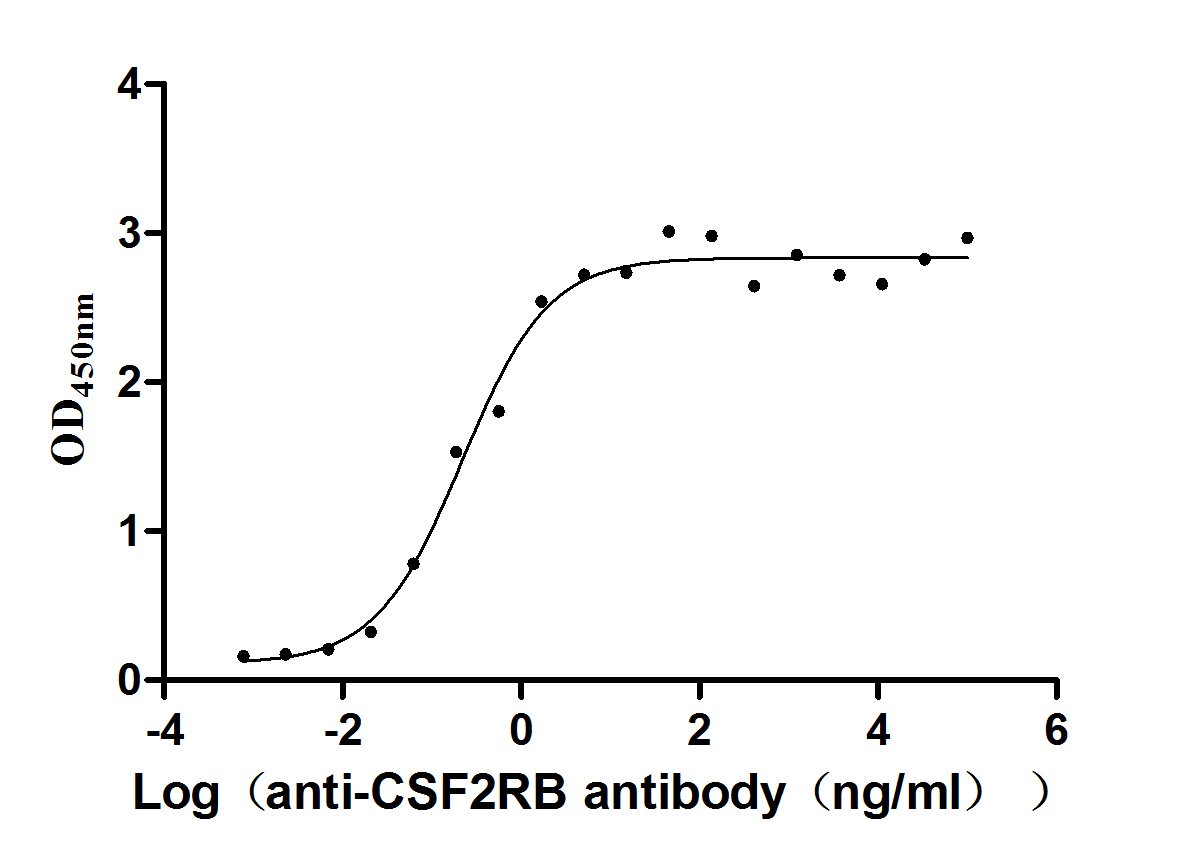
Recombinant Human Cytokine receptor common subunit beta (CSF2RB), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
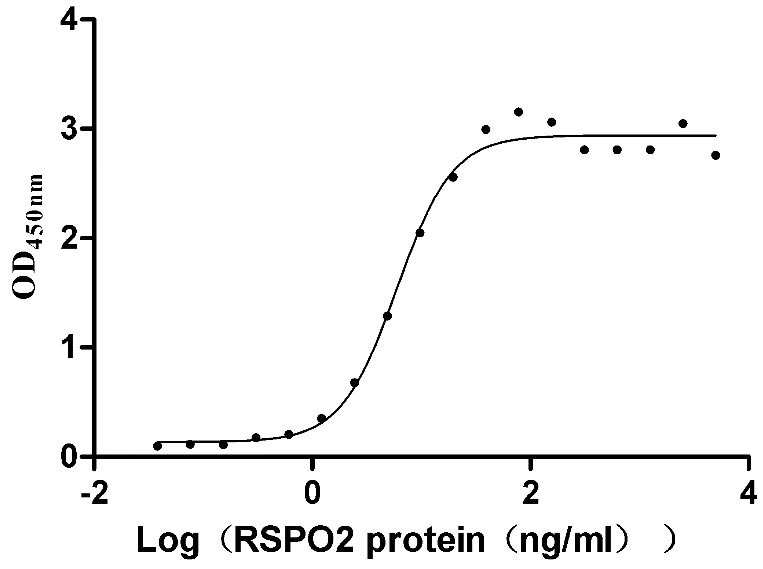
Recombinant Human E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase ZNRF3 (ZNRF3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Zymogen granule protein 16 homolog B (ZG16B) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
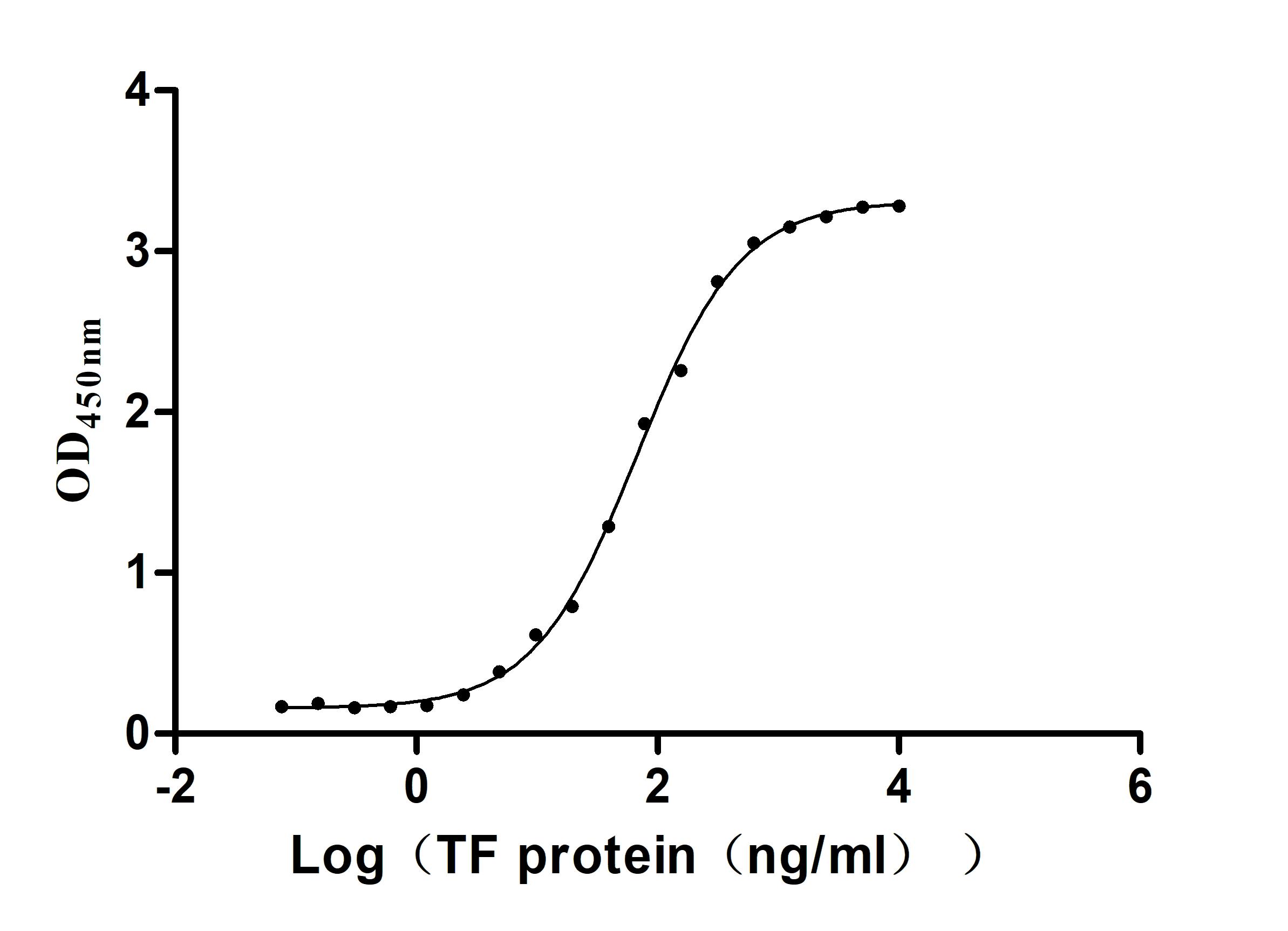
Recombinant Human Serotransferrin(TF) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
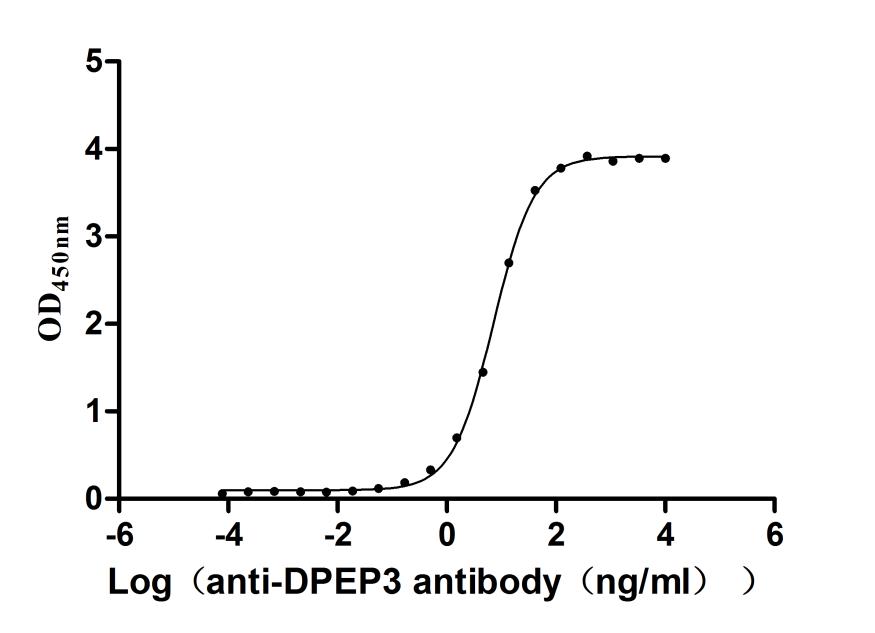
Recombinant Human Dipeptidase 3(DPEP3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
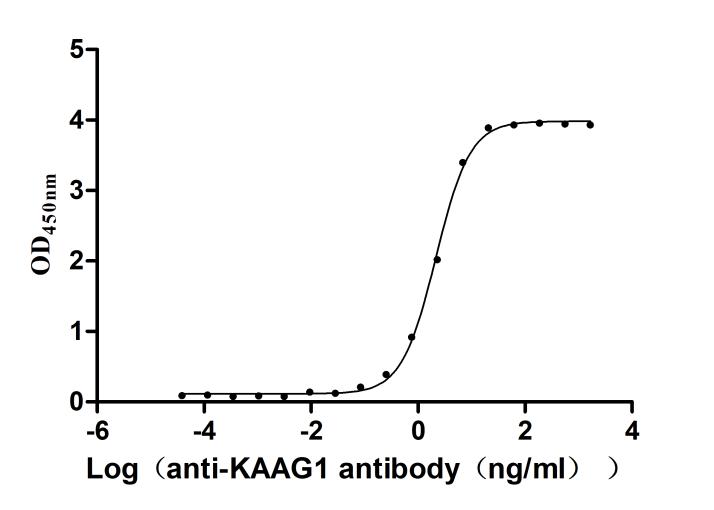
Recombinant Human Kidney-associated antigen 1(KAAG1) (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 15(TNFSF15) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)



-AC1.jpg)










