CLDN3:极为关键的紧密连接蛋白,Claudins家族再添药物靶点!
日期:2023-03-01 10:57:18
Claudins家族是近年发现的紧密连接蛋白的一种,其表达数量和分布结构的变化直接影响紧密连接的结构和功能。紧密连接是相邻细胞间重要的膜连接复合体,Claudin蛋白是其主要骨架蛋白。目前已发现有近30个家族成员,根据功能的差异可将其分为两类,如Claudin-1、Claudin-3、Claudin-4和Claudin-5;另一类则与构成特定的通道有关,如Claudin-2、Claudin-7、Claudin-10和Claudin-16等。
Claudins蛋白已成为当前肿瘤发病机制、诊断和治疗研究中的热点(Claudin家族热门靶点文章报道CLDN4;CLDN6;CLDN9)。近年来也有不少关于Claudin-3与肿瘤相关的研究报道,这些研究均提示Claudin-3的异常表达与肿瘤的发生、发展密切有关。因此,Claudin-3有望成为Claudins家族的下一个新药靶点!
1. 什么是紧密连接蛋白?
紧密连接蛋白由细胞质附着蛋白、跨膜蛋白和细胞骨架蛋白共同组成。紧密连接主要存在于上皮细胞、内皮细胞间的连接复合体中,使相邻细胞膜紧靠在一起,形成环绕细胞的物理屏障结构。其中,跨膜蛋白包括以下3种完整膜蛋白:连接黏附分子(JAM)、咬合蛋白(Occludin)、闭合蛋白(Claudin)。目前认为,跨膜蛋白中起主要作用的是Occludin和Claudin,尤其以Claudin的作用最为重要,这是形成紧密连接功能的主要蛋白 [1]。
Claudin主要作用是维持细胞间的物理屏障功能及细胞极性。肿瘤的发生、发展及转移是一个多因素造成的分阶段过程,但是目前普遍认为细胞间的黏附力丧失可导致细胞紧密连接破坏,与肿瘤细胞的浸润和转移相关,这使得Claudin家族成为备受关注的治疗靶点 [2]。
2. 什么是CLDN3?
紧密连接蛋白3(Claudin3/CLDN3)属于跨膜紧密连接蛋白Claudins家族的一员。CLDN3相对分子质量20 kDa-34 kDa,是紧密连接中最重要的骨架蛋白。在结构上,Claudins由面向细胞质的N末端、C末端,2个细胞外环、4个跨膜结构域组成(图1) [3]。其中,面向胞浆的C末端还含有由80-90个氨基酸残基组成的PDZ结构域,它与ZO1、ZO2、ZO3和多PDZ结构域蛋白1(MUPP1)相互作用,这是紧密连接蛋白复合体与其他多种蛋白的结合位点。
CLDN3在维持细胞间物理屏障功能和参与分子细胞间传递方面发挥着重要作用,是参与血脑屏障、肠道屏障、血睾屏障构成的重要组成部分。CLDN3不仅在人体前列腺、胰腺细胞、肝细胞等多种腺细胞,同时还在乳腺导管上皮、子宫内膜、食管黏膜、肺泡上皮、和胆管上皮细胞等多种上皮细胞内均有表达 [4-6]。
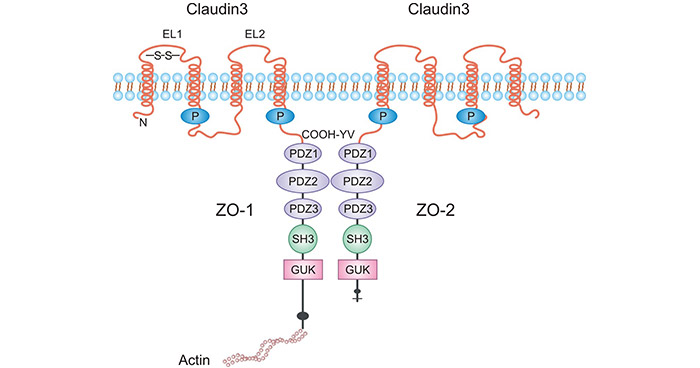
图1. CLDN3的结构 [3]
3. CLDN3的配体
产气荚膜梭菌肠毒素(CPE)是CLDN3第二胞外环的高亲和力天然配体。这种毒素结合其受体CLDN3,形成膜孔复合物,通过细胞膜穿透作用使得细胞溶解坏死(图2) [7-8]。CLDN3在人类CRC、食管癌、上皮性卵巢癌等癌症组织中均呈高表达,而产气荚膜梭状芽孢杆菌内毒素能够有效地抑制CLDN3表达的恶性肿瘤,这为CLDN3成为靶向治疗恶性肿瘤提供了可能性 [7-8]。
除了CLDN3,产气荚膜梭菌肠毒素也是CLDN4蛋白的一种天然的配体。因此,CPE毒素与CLDN3和CLDN4蛋白结合可导致细胞迅速溶解 [9]。最近有研究发现,CPE以表达CLDN-3、-4蛋白的肿瘤细胞作为靶点,抑制肿瘤细胞。例如在胰腺癌细胞,CLDN-3、-4高表达,利用细胞病变效应(CPE)瘤内注射异种嫁接的胰腺癌细胞,结果引起肿瘤细胞大面积坏死,明显延缓肿瘤生长 [10]。
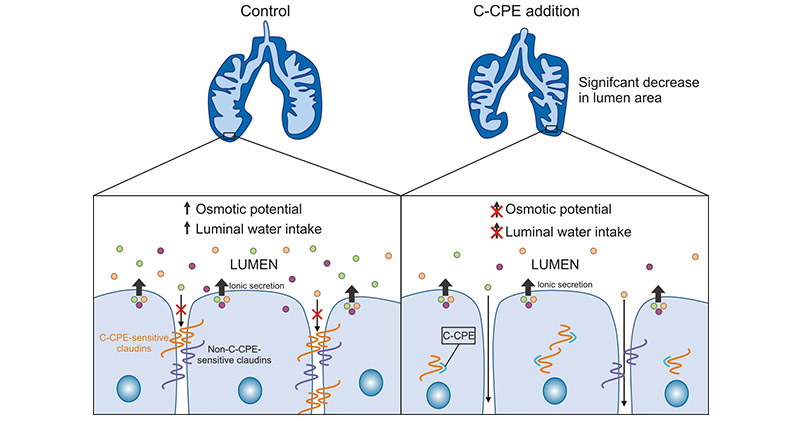
图2. CLDN3结合CPE促进细胞溶解坏死 [8]
4. CLDN3在肿瘤中的作用机制
CLDN3在维持上皮细胞极性、基因转录、抑制肿瘤、细胞增殖分化、新陈代谢相关的基因和炎症免疫反应等方面有着重大的作用。CLDN3具体作用可能取决于组织的高度特异性及细胞内精确的分子信号通路。目前,CLDN3的异常表达与肿瘤之间关系的确切机制尚不完全清楚。
在肝癌中,CLDN3能够通过下调糖原合成酶激酶GSK3B、钙黏蛋白相关蛋白CTNNB1、锌指家族转录抑制因子SNAI2和血管钙黏蛋白CDH2的表达,使Wnt/β-catenin-EMT转移轴失活,从而显著抑制肝癌的转移 [11-12]。此外,CLDN3的敲除也会降低肝脏内相关胆汁酸代谢基因(Cyp27a1、Ces1b和Akr1c6)的表达 [13]。丢失CLDN3或4可通过激活Akt磷酸化而活化PI3K通路,导致PI3K活性剂Twist转录因子表达水平增加,表明它们的缺失可以促进上皮间质转化 [14]。
在肺腺癌组织中,CLDN3的表达量显著升高,并且CLDN3的过表达与肺腺癌细胞的恶性潜能及ERK1/2和PI3K-Akt信号通路相关 [14]。在结直肠癌组织中,CLDN3在CRC组织中的水平可通过SCF/c-kit/JNK/AP-1信号转导通路的激活可以使之升高 [15]。在卵巢癌中,CLDN3表达受到棕榈酰转移酶ZDHHC12调控,提示靶向ZDHHC12介导的CLDN3 S-棕榈酰化可能是卵巢癌治疗的潜在策略 (图3) [16]。另有研究表明,CLDN3可能通过维持E-cadherin的表达和限制β-连环蛋白(β-catenin)信号转导,介导了与体内其他细胞的相互作用,从而抑制了生长和转移潜能 [17]。
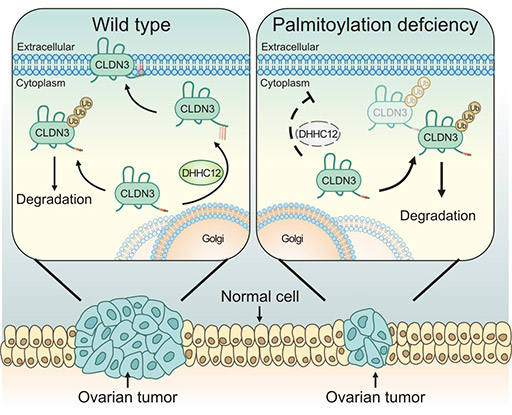
图3. CLDN3表达受到棕榈酰转移酶ZDHHC12调控 [16]
5. CLDN3在肿瘤等疾病中的作用
CLDN3作为构成内皮细胞紧密连接的主要蛋白,当其表达发生异常时可导致内皮细胞间结构遭到损坏。紧密连接的破坏可能导致细胞黏附减弱,引起肿瘤细胞的极性丢失、生长失控乃至肿瘤侵袭和转移。研究发现,CLDN3与多种肿瘤相关,同时在肝功能等疾病中也扮演重要角色。
5.1 CLDN3与肿瘤
在结直肠癌中,发现表皮生长因子(EGF)能增加结直肠癌细胞系HT-29细胞CLDN3表达,促进细胞迁移,同时增加了新的癌巢的形成,说明过表达的CLDN3提高结直肠癌细胞的侵袭潜能 [14],而EGF是多种恶性肿瘤发生时增高的标志物,EGF受体拮抗剂吉非替尼等已经应用于临床抗肿瘤治疗。
在前列腺癌中,相对于前列腺增生组织,CLDN3表达上调。利用Northen印迹发现,与周围正常组织比较,人类前列腺癌组织上皮细胞中的CLDN3基因转录信使RNA水平显著增高 [18];在鼻咽癌中,CLDN3也是如此,CLDN3在鼻咽癌组织中的表达率要高于鼻咽癌旁组织。然而,在病理分期更高的鼻咽癌组织,CLDN3的表达率更高 [19]。
在宫颈癌Hela细胞株中,生长抑素SST可以促进CLDN3和CLDN4的基因表达,从而对宫颈癌的发展和扩散有抑制作用 [20-22]。在乳腺癌中,CLDN3与BRCA1突变有关 [23]。在鳞状上皮细胞癌中,CLDN3蛋白水平的降低与肿瘤TNM分期、淋巴结转移及肿瘤复发显著相关 [24-25];在肝癌中,CLDN3与肝癌患者的生存期显著相关,提示可作为肝癌的一个潜在预后标志物。这些研究表明,CLDN3可能是一种重要的疾病标志物和治疗靶点 [5-6]。
5.2 CLDN3与其它疾病
血脑屏障结构的破坏是导致早期脑缺血的主要病理学基础。CLDN3与血脑屏障的结构、功能密切相关,可通过人为改变紧密连接蛋白CLDN3的表达来改变血脑屏障的通透性 [26];胆固醇结石GSD是一种主要常见于成人的肝脏疾病,发病率随着年龄的增长而增高,敲除CLDN3基因的小鼠肝脏中,旁细胞的屏障功能受到损坏,可加速以磷酸钙为核心的胆固醇结石形成 [27]。事实上,CLDN3作为肝脏中表达最多的TJ蛋白,一旦CLDN3表达失调,可导致多种肝脏疾病的发生发展,如慢性肝病肠道菌群失调、慢性肝病、肝胆系统恶性肿瘤 [28]。
6. CLDN3的临床研究前景
CLDN3是紧密连接中的一个关键蛋白,参与了紧密连接的选择性渗透和细胞极化,并在细胞间传输物质和能量时发挥连接作用。由于具有较高的组织特异性,CLDN3已被广泛研究,尤其在多种肿瘤的发生和发展中发挥重要作用。对CLDN3表达情况和相关调节因子进行深入研究,以寻找或设计与其特异性结合的靶向因子,干扰细胞表型,可能为CLDN3相关的疾病提供有效策略。来自Pharmsnap的数据显示,已有一些临床前和药物发现阶段的CLDN3相关药物在研(表1)。目前,基于CLDN3的靶向治疗正成为CLDN家族的一个重要研究方向,具有重要的药物研发潜力!
| 药物 | 靶点 | 作用机制 | 药物类型 | 在研适应症 | 在研机构 | 最高研发状态 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABN 501;ABN-501;Anti-CLDN3 monoclonal antibody - Abion | CLDN3 | CLDN3抑制剂 | 单克隆抗体 | 卵巢癌 | ABION, Inc. | 临床前 |
| KM-3907;dual claudin-3/claudin-4 mAb(Kyowa Hakko Kirin) | CLDN3; CLDN1 |
CLDN3抑制剂; CLDN1抑制剂 |
双特异性抗体 | / | / | 药物发现 |
| MORAb-075;anti-claudin-3/4 humanized mAb(Morphotek) | CLDN3; CLDN1 |
CLDN3抑制剂; CLDN1抑制剂 |
单克隆抗体 | / | / | 药 |
表1:CLDN3的临床在研药
为鼎力协助科研和药企人员针对CLDN3在肿瘤等疾病中的临床应用研究,CUSABIO推出CLDN3活性蛋白(Code: CSB-MP005505HU)产品,助力您在CLDN3机制方面的研究或其潜在临床价值的探索。
Recombinant Human Claudin-3(CLDN3)-VLPs (Active)
The high specifity was validated by western blot. (Tris-Glycine gel) Discontinuous SDS-PAGE (reduced) with 5% enrichment gel and 15% separation gel.
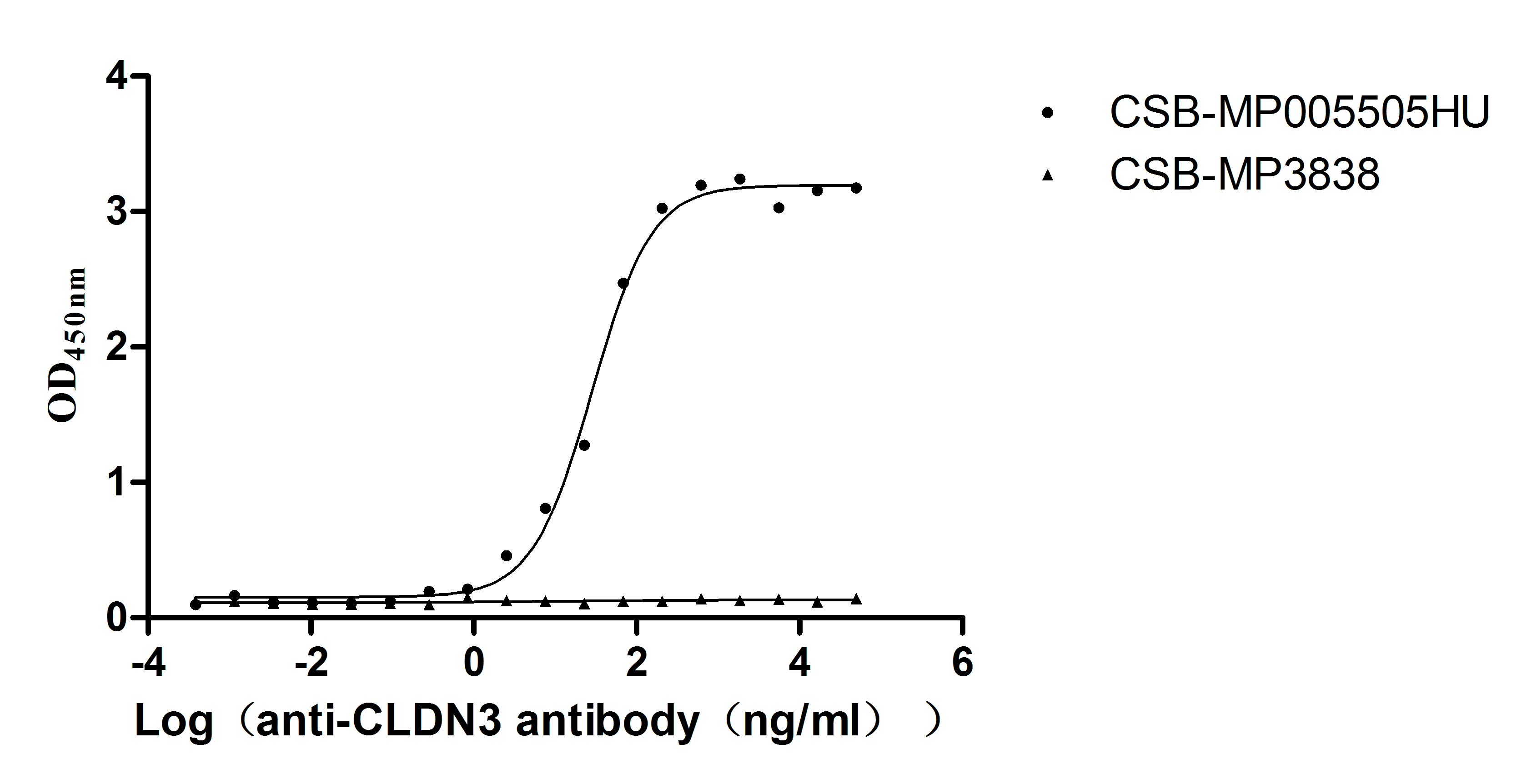
Immobilized Human CLDN3 at 10μg/mL can bind Anti-CLDN3 recombinant antibody (CSB-RA005505MA1HU), the EC50 is 23.62-34.37 ng/mL.VLPs (CSB-MP3838) is negative control.
参考文献:
[1] Fujiwara, Sachiko, et al. "Tight junction formation by a claudin mutant lacking the COOH-terminal PDZ domain-binding motif ." Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1516.1 (2022): 85-94.
[2] Castro Dias, Mariana, et al. "Claudin-3-deficient C57BL/6J mice display intact brain barriers." scientific reports 9.1 (2019): 203.
[3] Che, J., Yue, D., et al. "Claudin-3 Inhibits Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition and Invasion via Suppression of the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway." International Journal of Medical Sciences, 15(4) (2018): 339-351.
[4] Lei, Ningjing, et al. "Claudin-3 inhibits tumor-induced lymphangiogenesis via regulating the PI3K signaling pathway in lymphatic endothelial cells. " Scientific Reports 12.1 (2022): 17440.
[5] Wang, ZhaoHan, et al. "Plasma claudin-3 is associated with tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced intestinal endotoxemia in liver disease." Clinics and Research in Hepatology and Gastroenterology 43.4 (2019): 410-416.
[6] Yang, Y., et al. "Mo1775 Epigenetic Inactivation of Claudin 3 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Its Functional Consequences." Gastroenterology 5.144 ( 2013): S-1023.
[7] Torres, Julia Baguña, et al. "Radiolabeled cCPE peptides for SPECT imaging of claudin-4 overexpression in pancreatic cancer." journal of Nuclear Medicine 61.12 (2020): 1756-1763.
[8] La Charité-Harbec, Simon, et al. "Claudin-3 regulates luminal fluid accumulation in the developing chick lung." Differentiation 124 (2022): 52-59.
[9] Li, Xiangru, et al. "Development of an Anti-Claudin-3 and -4 Bispecific Monoclonal Antibody for Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy." journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 351.1 (2014): 206-213.
[10] Pahle, Jessica, et al. "Effective oncoleaking treatment of pancreatic cancer by claudin-targeted suicide gene therapy with Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin (CPE)." Cancers 13.17 (2021): 4393.
[11] Gasperoni, Jemma G., et al. "Grainyhead-like (Grhl) target genes in development and cancer." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23.5 (2022): 2735.
[12] Ahmad, Rizwan, et al. "Loss of claudin-3 expression induces IL6/gp130/Stat3 signaling to promote colon cancer malignancy by hyperactivating Wnt/β- catenin signaling." Oncogene 36.47 (2017): 6592-6604.
[13] Reiling, Janske, et al. "Low-Dose Lipopolysaccharide Causes Biliary Injury by Blood Biliary Barrier Impairment in a Rat Hepatic Ischemia /Reperfusion Model." Liver Transplantation 23.2 (2017): 194-206.
[14] de Souza, Waldemir F., et al. "Claudin-3 overexpression increases the malignant potential of colorectal cancer cells: roles of ERK1/2 and PI3K-Akt as modulators of EGFR signaling." ploS one 8.9 (2013): e74994.
[15] Wang, Yaxi, et al. "SCF/C-Kit/JNK/AP-1 signaling pathway promotes claudin-3 expression in colonic epithelium and colorectal carcinoma." International journal of molecular sciences 18.4 (2017): 765.
[16] Yuan, Meng, et al. "ZDHHC12-mediated claudin-3 S-palmitoylation determines ovarian cancer progression." Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B 10.8 (2020): 1426-1439.
[17] Che, Juanjuan, et al. "Decreased expression of claudin-3 is associated with a poor prognosis and EMT in completely resected squamous cell lung carcinoma ." Tumor Biology 36 (2015): 6559-6568.
[18] Orea, María J., et al. "Claudin-3 Loss of Expression Is a Prognostic Marker in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24.1 (2023): 803.
[19] Tessier-Cloutier, Basile, et al. "Proteomic analysis of transitional cell carcinoma-like variant of tubo-ovarian high-grade serous carcinoma." Human pathology 101 (2020): 40-52.
[20] Chen, Peng, et al. "Structural basis for CSPG4 as a receptor for TcdB and a therapeutic target in Clostridioides difficile infection." Nature communications 12.1 (2021): 3748.
[21] Xie, Xiaoxi, et al. "Roles of gastrointestinal polypeptides in intestinal barrier regulation." Peptides (2022): 170753.
[22] Liu, Jinhui, et al. "Development of an immune gene prognostic classifier for survival prediction and response to immunocheckpoint inhibitor therapy/ chemotherapy in endometrial cancer." International immunopharmacology 86 (2020): 106735.
[23] Szade, Jolanta, et al. "Comparison of claudin-3 and claudin-4 expression in bilateral and unilateral breast cancer." Neoplasma 68.2 (2020): 283-289.
[24] Feng, Ji, et al. "Capsaicin inhibits migration and invasion via inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by up-regulation of claudin-3 expression." Journal of Functional Foods 89 (2022): 104934.
[25] Che, Juanjuan, et al. "Claudin-3 inhibits lung squamous cell carcinoma cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasion via suppression of the Wnt /β-catenin signaling pathway." international journal of medical sciences 15.4 (2018): 339.
[26] Haseloff, Reiner F., et al. "Transmembrane proteins of the tight junctions at the blood-brain barrier: structural and functional aspects ." Seminars in cell & developmental biology. vol. 38. Academic Press, 2015.
[27] Tanaka, Hiroo, et al. "Claudin-3 regulates bile canalicular paracellular barrier and cholesterol gallstone core formation in mice." journal of hepatology 69.6 (2018): 1308-1316.
[28] Baier, Felix Alexander, et al. "Loss of Claudin-3 Impairs Hepatic Metabolism, Biliary Barrier Function, and Cell Proliferation in the Murine Liver." Cellular and molecular gastroenterology and hepatology 12.2 (2021): 745-767.











