Recombinant Mouse Macrophage receptor MARCO (Marco), partial
-
中文名称:小鼠Marco重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-YP726671MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Marco重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP726671MO
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Marco重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-EP726671MO-B
-
规格:
-
来源:E.coli
-
共轭:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Marco重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-BP726671MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名称:小鼠Marco重组蛋白
-
货号:CSB-MP726671MO
-
规格:
-
来源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
产品详情
-
纯度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Marco
-
Uniprot No.:
-
别名:MarcoMacrophage receptor MARCO; Macrophage receptor with collagenous structure
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白长度:Partial
-
蛋白标签:Tag type will be determined during the manufacturing process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
产品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
复溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
储存条件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保质期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
货期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事项:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶点详情
-
功能:Pattern recognition receptor (PRR) which binds Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Also plays a role in binding of unopsonized particles by alveolar macrophages. Binds to the secretoglobin SCGB3A2.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- the absence of MARCO does not interfere with the efficiency of HSV-1 entry and that the inhibitory effect on viral adsorption by poly(I), a ligand of MARCO, is independent of MARCO. PMID: 29769337
- presence of MARCO allows rapid Adenovirus (AD) gene expression and strong virus-stimulated innate responses; blockage or lack of MARCO results in strong impairment of these processes;. MARCO is involved in innate Ad recognition and the elevated Ad sensitivity of MARCO-expressing macrophages is due to the expression of this receptor on the cell surface PMID: 28765216
- Common damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) were internalized through the class A scavenger receptors MSR1 and MARCO in vitro. In ischemic murine brain, DAMP internalization was largely mediated by MSR1. Combined deficiency for Msr1 and Marco in infiltrating myeloid cells caused impaired clearance of DAMPs, more severe inflammation, and exacerbated neuronal injury in a murine model of ischemic stroke. PMID: 28394332
- Increasing MARCO expression by targeting Nrf2 signaling or the Akt-TFEB-MARCO pathway are promising strategies to improve bacterial clearance and survival in postinfluenza bacterial pneumonia. PMID: 28408365
- free actin likely contributes to impaired host defense by blocking scavenger receptor binding of bacteria. PMID: 28385809
- this study shows that Marco functions as co-receptor along with TLRs for HMGB1 in M1-type inflammatory macrophages PMID: 28338748
- MARCO Is Processed by either Macropinocytosis or Endocytosis-Autophagy Pathway PMID: 26545255
- our data demonstrate that MARCO differentially affects TLR-induced DC activation and suggest targeting of MARCO could lead to different outcomes that depend on the inflammatory context encountered by dendritic cells. PMID: 25089703
- Vaccinia virus bound directly to MARCO, and overexpression of MARCO increased susceptibility to vaccinia infection. PMID: 25089661
- MARCO-/- dendritic cells demonstrated enhanced migratory capacity in response to CCL-21 in vitro. PMID: 23840879
- herpes simplex virus type 1 binds to MARCO to enhance its capacity for disease. PMID: 23739639
- results indicate that accumulation of SQSTM1 leads to increased activation of NFE2L2 and the subsequent increase in MARCO and MSR1 PMID: 24035364
- this study, we confirm that tolerized mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages selectively increase expression of MARCO and increase phagocytosis PMID: 23667110
- MARCO is an important component of anti-Streptococcus pneumoniae responses in murine nasopharyngeal macrophages during bacterial colonization. PMID: 23197261
- Fetuin-A-containing calciprotein particles facilitate the clearance of mineral debris by macrophages via SR-A. PMID: 22753077
- These results indicate that MARCO suppresses a protective early inflammatory response to influenza, which modulates viral clearance and delays recovery. PMID: 21562316
- SR-A/MARCO-mediated rapid ligand internalization prevented sensing by surface TLRs while increasing ligand availability in intracellular compartments, thus allowing sensing and robust responses by intracellular sensors. PMID: 21098741
- MARCO is an important phagocytic receptor used by human and mouse macrophages to clear C. sordellii from the infected uterus PMID: 20810988
- The MARCO receptor may account for the variable species susceptibility towards dalcetrapib-mediated chylomicron uptake by macrophages PMID: 20074633
- TLR4 engagement by LPS leads to increased expression of NARCO, which feedback-regulates LPS responses, changling cytokine & anti-LPS Ab production. MARCO contributes to the efficient capturing & clearance of invading microbial pathogens. PMID: 20162551
- An arginine-rich segment in domain V of MARCO and particularly its RXR motifs play a critical role in high affinity bacterial binding. PMID: 11820786
- MARCO receptor is important for actin cytoskeleton rearrangements and the down-regulation of antigen uptake function during DC and microglial cell maturation PMID: 12842997
- MARCO has an important role in mounting an efficient and appropriately regulated innate immune response against inhaled particles and airborne pathogens PMID: 15263032
- Th1 adjuvants increased, whereas Th2-polarizing factors decreased expression of MARCO on J774 macrophage-like cells; MARCO-deficient mice exhibited 2.7 times lower IL-12 production in responses to stimulation PMID: 16339540
- both MARCO and SR-A could be involved in the positioning and differentiation of macrophages, possibly through interaction with endogenous ligands PMID: 16339556
- MARCO is the primary alveolar macrophages receptor responsible for silica uptake and cell death signaling PMID: 16984918
- Marco decreases inflammation in the lungs exposed to ozone. PMID: 17332894
- Together, these data indicate that SRA controls inflammatory cytokines produced by alveolar macrophages in the context of P. carinii infection. PMID: 17548480
- We have confirmed a role for Marco in the clearance of apoptotic cells and a generalized defect in both endocytosis and phagocytosis PMID: 19201851
- MARCO expression by CBA/J macrophages is increased in response to both in vitro and in vivo L. major infections, but not to L. amazonensis infection. MARCO has a role in macrophage infection by L. major in vitro as well as in vivo. PMID: 19292770
- results show MARCO-expressing macrophages secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines in response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis trehalose 6,6'-dimycolate(TDM) by cooperation between MARCO & TLR2/CD14; MARCO identified as novel component required for TLR signaling PMID: 19521507
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cell membrane; Single-pass type II membrane protein.
-
组织特异性:Expressed in subpopulations of macrophages in the spleen and the medullary cord of lymph nodes (at protein level).
-
数据库链接:
KEGG: mmu:17167
STRING: 10090.ENSMUSP00000027639
UniGene: Mm.1856
Most popular with customers
-
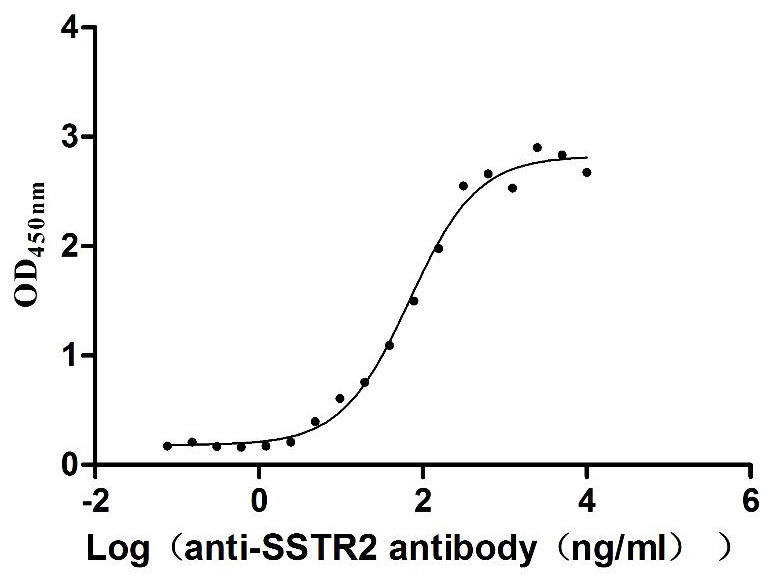
Recombinant Human Somatostatin receptor type 2 (SSTR2)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Interleukin-17A (IL17A) (T26A) (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
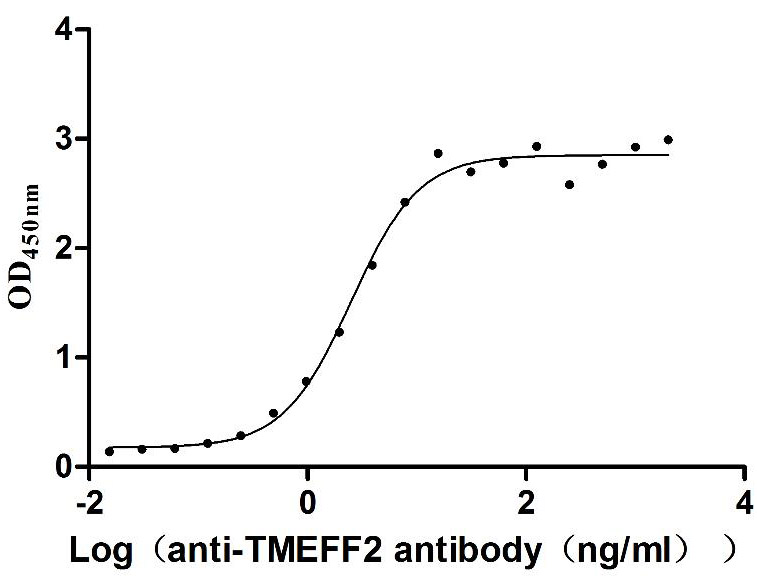
Recombinant Human Tomoregulin-2 (TMEFF2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
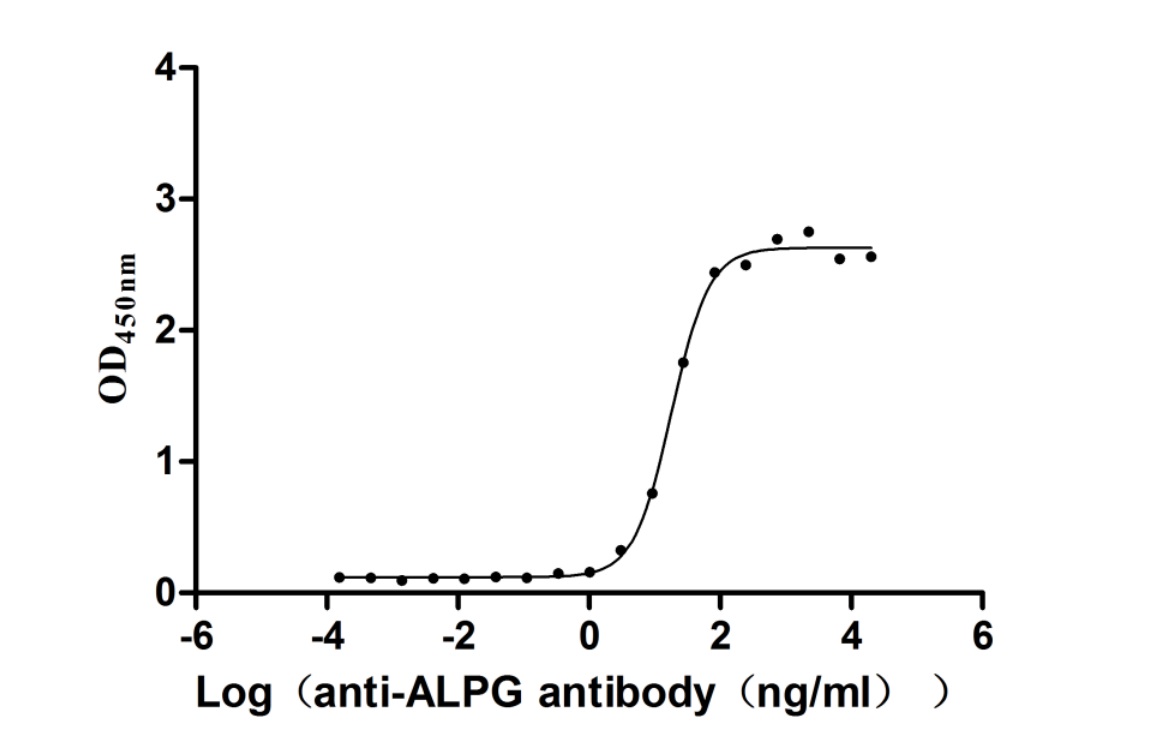
Recombinant Human Alkaline phosphatase, germ cell type (ALPG) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
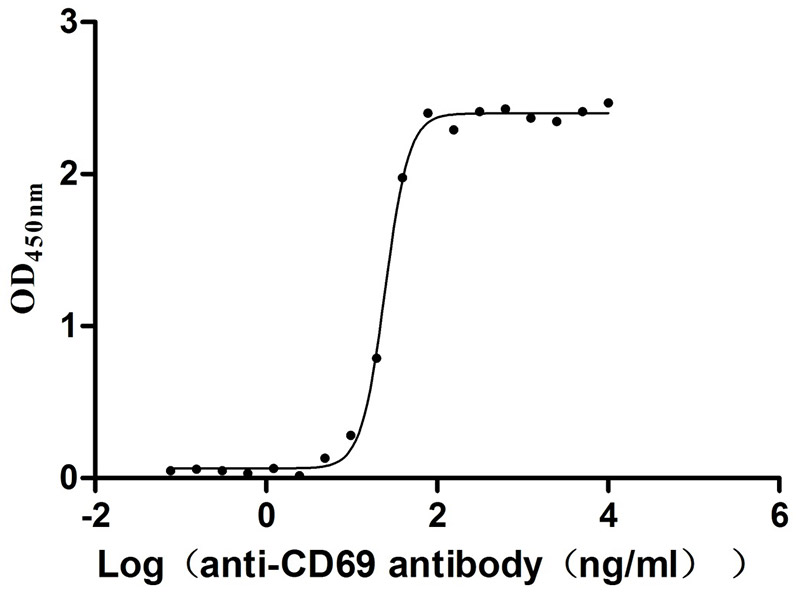
Recombinant Human Early activation antigen CD69 (CD69), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
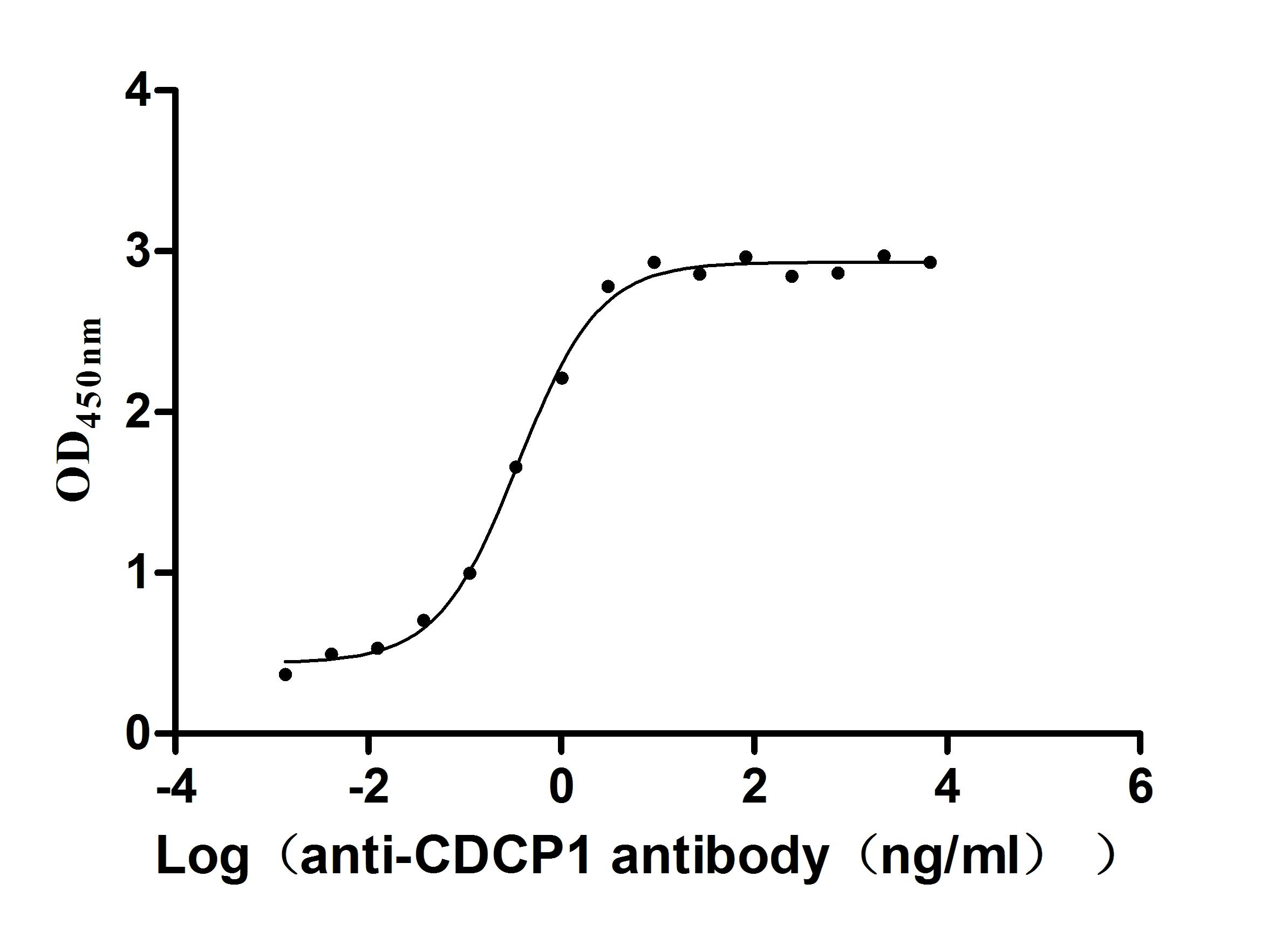
Recombinant Human CUB domain-containing protein 1 (CDCP1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
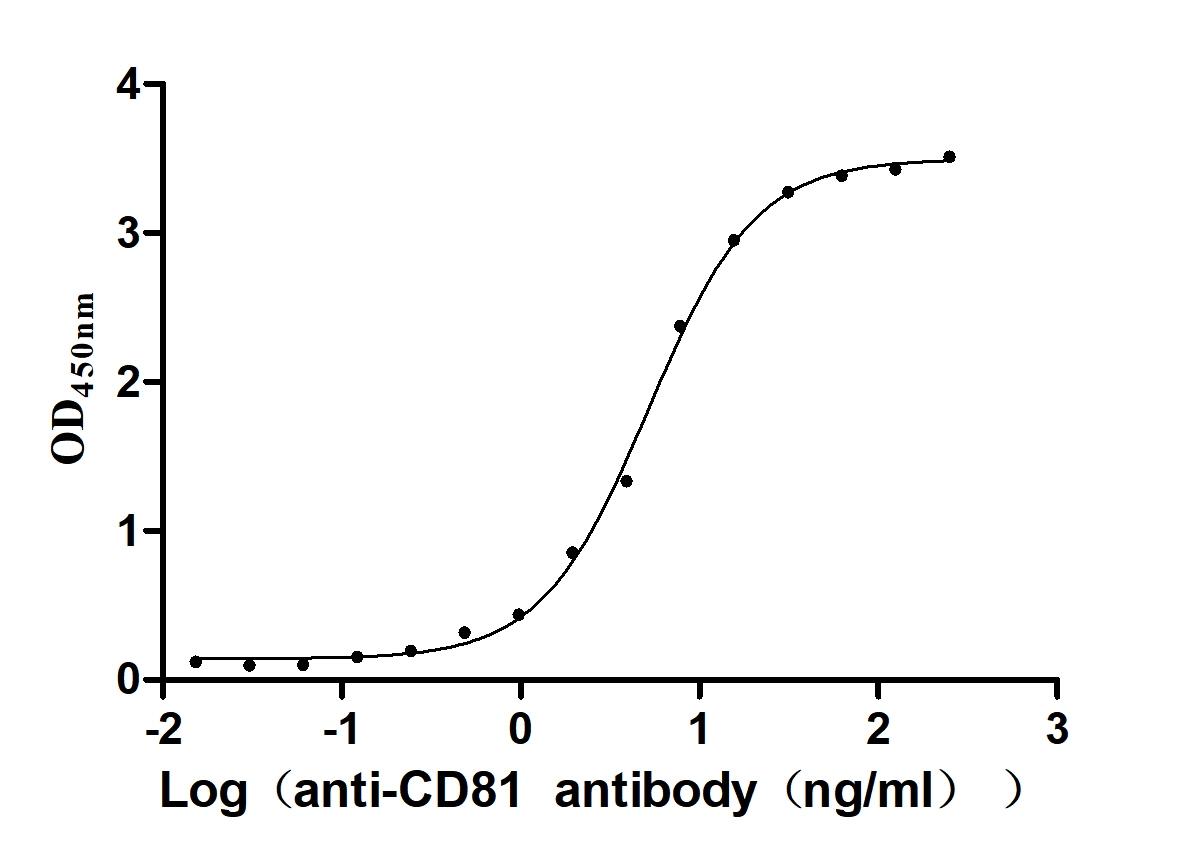
Recombinant Human CD81 antigen (CD81), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
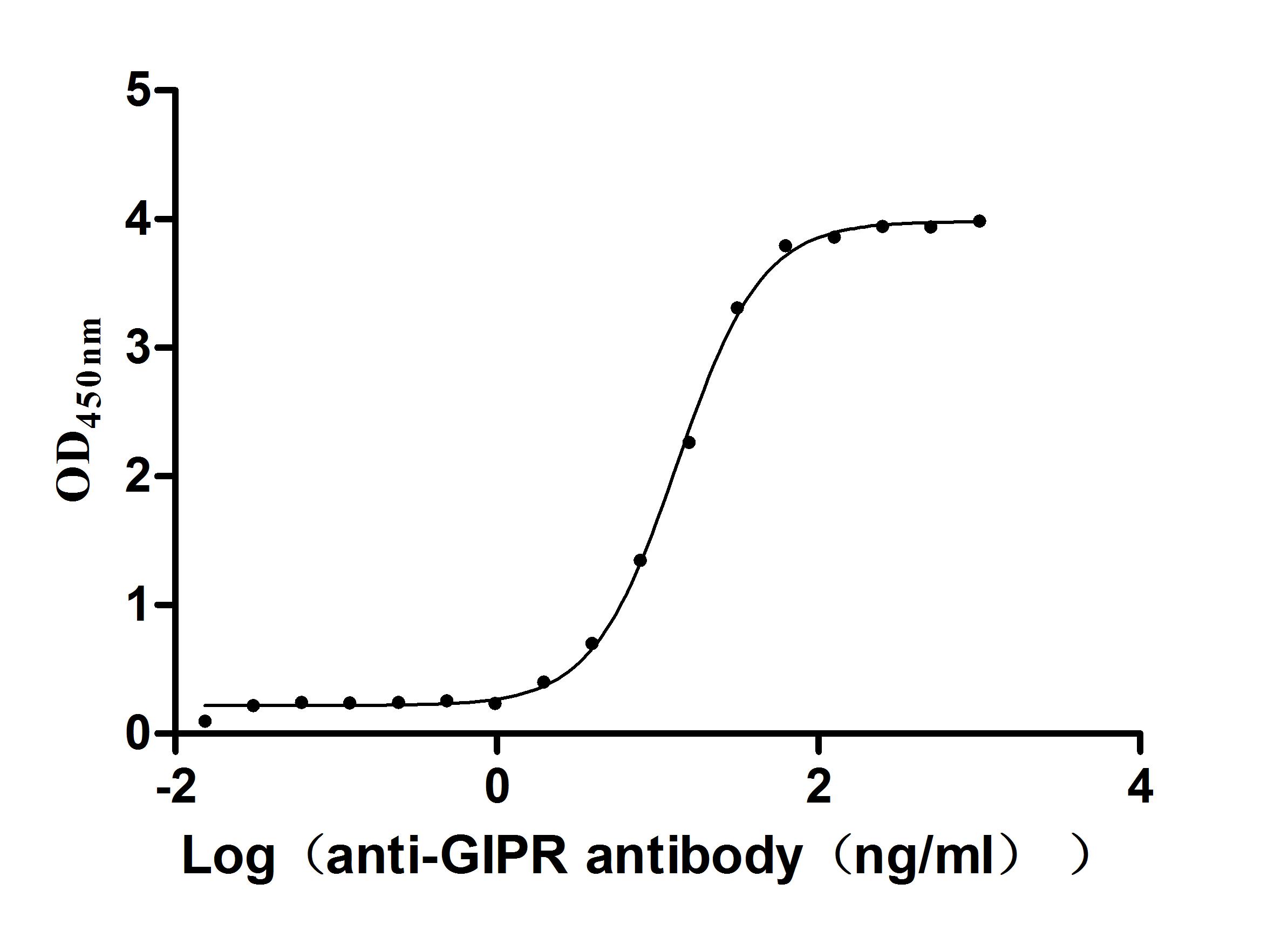
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor (GIPR), partial (Active)
Express system: yeast
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)


-AC1.jpg)