-
中文名称:小鼠β连环蛋白/联蛋白(β-Cat)酶联免疫试剂盒
-
货号:CSB-E11307m
-
规格:96T/48T
-
价格:¥3200/¥2500
-
其他:
产品详情
-
产品描述:
This Mouse CTNNB1 ELISA Kit was designed for the quantitative measurement of Mouse CTNNB1 protein in serum, plasma, tissue homogenates, cell lysates. It is a Sandwich ELISA kit, its detection range is 0.156 ng/mL-10 ng/mL and the sensitivity is 0.039 ng/mL.
-
别名:Ctnnb1 ELISA Kit; CatnbCatenin beta-1 ELISA Kit; Beta-catenin ELISA Kit
-
缩写:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
种属:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
样本类型:serum, plasma, tissue homogenates, cell lysates
-
检测范围:0.156 ng/mL-10 ng/mL
-
灵敏度:0.039 ng/mL
-
反应时间:1-5h
-
样本体积:50-100ul
-
检测波长:450 nm
-
研究领域:Cardiovascular
-
测定原理:quantitative
-
测定方法:Sandwich
-
精密度:
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): CV%<8% Three samples of known concentration were tested twenty times on one plate to assess. Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): CV%<10% Three samples of known concentration were tested in twenty assays to assess. -
线性度:
To assess the linearity of the assay, samples were spiked with high concentrations of mouse β-cat in various matrices and diluted with the Sample Diluent to produce samples with values within the dynamic range of the assay. Sample Serum(n=4) 1:1 Average % 92 Range % 87-96 1:2 Average % 99 Range % 95-103 1:4 Average % 101 Range % 94-106 1:8 Average % 95 Range % 89-98 -
回收率:
The recovery of mouse β-cat spiked to levels throughout the range of the assay in various matrices was evaluated. Samples were diluted prior to assay as directed in the Sample Preparation section. Sample Type Average % Recovery Range Serum (n=5) 91 86-98 EDTA plasma (n=4) 99 92-106 -
标准曲线:
These standard curves are provided for demonstration only. A standard curve should be generated for each set of samples assayed. 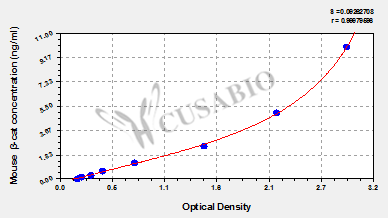
ng/ml OD1 OD2 Average Corrected 10 2.854 2.961 2.908 2.715 5 2.156 2.244 2.200 2.007 2.5 1.433 1.498 1.466 1.273 1.25 0.774 0.768 0.771 0.578 0.625 0.457 0.443 0.450 0.257 0.312 0.324 0.339 0.332 0.139 0.156 0.245 0.228 0.237 0.044 0 0.189 0.197 0.193 -
数据处理:
-
货期:3-5 working days
引用文献
- Perindopril sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma to chemotherapy: A possible role of leptin / Wnt/ β-catenin axis with subsequent inhibition of liver cancer stem cells S Zakaria,Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal,2022
- Evaluation of chemopreventive potential of xanthone from Swertia chirata against DMBA/croton oil-induced chemical carcinogenesis in Swiss mice A Barua,/,2022
- Hair Growth Promotion Activity and Its Mechanism of Polygonum multiflorum Yunfei Li. et al,Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine,2015
靶点详情
-
功能:Key downstream component of the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. In the absence of Wnt, forms a complex with AXIN1, AXIN2, APC, CSNK1A1 and GSK3B that promotes phosphorylation on N-terminal Ser and Thr residues and ubiquitination of CTNNB1 via BTRC and its subsequent degradation by the proteasome. In the presence of Wnt ligand, CTNNB1 is not ubiquitinated and accumulates in the nucleus, where it acts as a coactivator for transcription factors of the TCF/LEF family, leading to activate Wnt responsive genes. Involved in the regulation of cell adhesion, as component of an E-cadherin:catenin adhesion complex. Acts as a negative regulator of centrosome cohesion. Involved in the CDK2/PTPN6/CTNNB1/CEACAM1 pathway of insulin internalization. Blocks anoikis of malignant kidney and intestinal epithelial cells and promotes their anchorage-independent growth by down-regulating DAPK2. Disrupts PML function and PML-NB formation by inhibiting RANBP2-mediated sumoylation of PML. Promotes neurogenesis by maintaining sympathetic neuroblasts within the cell cycle. Involved in chondrocyte differentiation via interaction with SOX9: SOX9-binding competes with the binding sites of TCF/LEF within CTNNB1, thereby inhibiting the Wnt signaling.
-
基因功能参考文献:
- O-GlcNAcylation of CTNNB1 is associated with tumorigenicity of colorectal cancer. PMID: 29391154
- this study identified activation of beta-catenin-mediated signaling in cardiac macrophages post-myocardial infarction PMID: 29356094
- This study reports that the gain-of-function mutation of full-length basally-expressing Htt in Huntington's disease cell Q111 (STHdhQ111/HdhQ111) upregulated microRNA-214 and decreased beta catenin & its transcriptional activity in an aggregate-independent manner. PMID: 29894684
- beta-catenin plays an essential role in differentiation and function of ameloblasts during amelogenesis PMID: 30066216
- Janus kinase 2 protein (JAK2) and beta-catenin were found to interact with cadherin-22 (Cdh22) and involved in CDH22 signaling in female germ line stem cells (FGSCs). PMID: 29063123
- In fibrocystin/polyductin complex-defective cholangiocytes, beta-catenin and IL-1beta are responsible for signal transducer and activator of transcription 3-dependent secretion of CXCL10 PMID: 29140564
- Data illustrates a cooperative effect of the direct oncogenic signaling of mutant beta-catenin and MET in hepatocytes with hepatic tumor-promoting stroma induced by beta-catenin deficiency PMID: 29152756
- Data show that beta-catenin can physically interact with Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2) components in the cranial mesenchyme (CM). PMID: 29223978
- Study identified FXR/beta-catenin interaction whose modulation through beta-catenin suppression promotes FXR activation and decreases hepatic bile acids, which may provide unique therapeutic opportunities in cholestatic liver diseases PMID: 28714273
- In this study, we found that the wnt co-receptor Lrp6 was a potent positive regulator of beta-catenin signaling in TDI-induced asthma models, both in vivo and in vitro. Additionally, for the first time, we demonstrated that RAGE could mediate phosphorylation of Lrp6, suggesting a functional cross talk between RAGE and the canonical wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway involved in mediating beta-catenin activation. PMID: 29656209
- These data indicate that SMAD3- and beta-catenin-dependent induction occurs in the taurine transporter knockout mouse PMID: 28849477
- beta-catenin in osterix-expressing cells is required for postnatal osteoblast differentiation, osteoblast proliferation, and bone resorption, and is essential for the anabolic actions of parathyroid hormone in bone. PMID: 29124436
- Adherens as well as tight junction marker proteins were rapidly and consistently upregulated in both the germinal as well as the functional layer of the oral mucosa. This represents a previously unknown parameter of the epithelial radiation response to clinically relevant fractionation protocols. CONCLUSION: Fractionated irradiation significantly enhanced the expression of all proteins investigated. This study revealed a PMID: 29675597
- the beta-catenin C-terminus indirectly represses p53, and this function is essential for embryogenesis. PMID: 27499244
- aberrant expression of AF1q may activate Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and result in podocyte injury. PMID: 29069662
- this study suggested that stabilized beta-catenin ameliorated some Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome-like symptoms of lpr/lpr mice by potentiating Fas-independent signal-mediated T cell apoptosis PMID: 29250557
- findings indicate that beta-catenin signaling plays a critical role in postnatal bone remodeling. Our study provides new insights into the regulation of epiphyseal bone homeostasis at postnatal stage PMID: 29230102
- Study validates the DNAJB1-PRKACA fusion kinase as an oncogenic driver and candidate drug target for fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma in mouse model in which tumorigenesis was significantly enhanced by genetic activation of beta-catenin. PMID: 29162699
- BCAS2 is an upstream regulator of beta-catenin gene expression and plays a role in dendrite growth at least partly through beta-catenin in the forebrain. PMID: 27713508
- LncRNA MALAT1 is dysregulated in diabetic nephropathy and involved in high glucose-induced podocyte injury via its interplay with beta-catenin and SRSF1. PMID: 28444861
- These findings suggest a suppressive function for Ctbp2 in reducing the protein level of beta-catenin, along with priming its position on core pluripotency genes to hinder beta-catenin deposition, which is central to commitment to the appropriate lineage. PMID: 29026198
- Beta-catenin deletion in cathepsin K (CtsK)-expressing cells causes a severe loss of bone mass. PMID: 27804995
- the GSK-3beta/beta-catenin signal pathway mediates the adverse effects of Ti particles on osteoblast differentiation and bone destruction PMID: 28617442
- HIV and drug abuse mediate astrocyte senescence in a beta-catenin-dependent manner leading to neuronal toxicity. PMID: 28612507
- The absence of hepatic beta-catenin predisposes mice to hepatic injury and fibrosis following iron overload, which was reminiscent of hemochromatosis and associated with enhanced steatohepatitis and fibrosis. PMID: 28341391
- beta-catenin and p65 are activated in separate cellular compartments during liver regeneration, with p65 activity in nonparenchymal compartment contributing to the activation of hepatocyte beta-catenin, cyclin D1 expression, and subsequent proliferation PMID: 28474571
- beta-catenin mutations were not involved in early-stage hepatocarcinogenesis induced by protoporphyrinogen oxidase inhibitors PMID: 28580885
- the inhibition of beta-catenin's TCF-dependent transcriptional activity, independent of its protein expression level, retains the naive ground state pluripotency in mouse embryonic stem cells. PMID: 28577307
- Beta-catenin signaling plays an important part in protecting renal fibrogenesis. PMID: 27460630
- Rspo3-LGR4 axis protects hepatocytes from hypoxia/reoxygenation injury via activating beta-catenin. PMID: 29555474
- Modulation of beta-catenin levels or disruption of its cell adhesion role is correlated with aggressive tumorigenesis in basal ErbB2-driven mammary tumors with preexisting beta-catenin activation. Our data also emphasize the tumor suppressor role of beta-catenin, similar to other adherens junction proteins, in maintaining junctional integrity during tumor progression. PMID: 28096336
- study uncovers a role for Pdpn in mammary SC function and, importantly, identifies Pdpn as a new regulator of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling, a key pathway in mammary development and tumorigenesis PMID: 29361573
- CEACAM1 controls epithelial-mesenchymal transition in vitro and in vivo by site-specific regulation of beta-catenin phosphorylation PMID: 27572314
- beta-catenin (CTNNB1) maintains lung progenitors by promoting a hierarchical lung progenitor gene signature, suppressing gastrointestinal (GI) genes, and regulating NK2 homeobox 1 (NKX2.1) and SRY box 2 (SOX2) in a developmental stage-dependent manner. PMID: 29440304
- findings provide the first line of evidence that links beta-catenin function to the cell proliferation and progenitor establishment during larynx and vocal fold development. PMID: 29386246
- In mice that were separated from their mothers, cdh-1 is upregulated in the prefrontal cortex in both males and females. In addition, hippocampal CDH-1 mRNA levels were positively correlated with recognition memory performance in females. Maternal-separated reared male mice exhibited higher beta -Cat mRNA levels in the hippocampus. PMID: 28435022
- PTEN-beta-catenin signaling is a novel regulator involved in modulating Treg development and may lead to a potential therapeutic target in liver ischemia/reperfusion injury PMID: 28152578
- These results indicate that Wnt/beta-catenin signaling may play a key role in fibrotic scar formation after traumatic spinal cord injury. PMID: 29410176
- Data show that phospholipase C (PLC)-beta1 (PLC-beta1) overexpression determines an increase in beta-catenin translocation and that PLC-beta1, inositol polyphosphate multikinase (IPMK) and beta-catenin are mediators of the same signaling pathway. PMID: 27563828
- FGF23 promotes myocardial fibrosis and exacerbates diastolic dysfunction induced by myocardial infarction or ischemia/reperfusion , which is associated with the upregulation of active beta-catenin and TGF-beta PMID: 27579618
- Suggest that Pygo2 has a tumor promoting function related to Wnt/ss-catenin signaling activity during intestinal tumor initiation and progression. PMID: 27811361
- Data suggest that Wnt signaling directs fatty acid metabolism via canonical mechanism involving activation of beta-catenin in osteoblasts; beta-catenin accumulation and activation are required for normal lipid catabolism in osteoblasts and white adipose tissue. PMID: 29077850
- Stretch induced p120 degradation and the endocytosis of E-cadherin, which induced beta-catenin translocation into the nucleus, a key event in lung injury progress and repair. PMID: 27911872
- Expression of a dominant stable form of beta-catenin in hepatocytes results in severe cholestasis and biliary type fibrosis. PMID: 27895309
- These data suggested that Wnt/beta-catenin pathway might be a potential target to treat the LPS-induced inflammation in ALI. PMID: 29246763
- Data show that Wnt beta-Catenin signaling pathway activation followed by Notch inhibition strongly promotes the mitotic regeneration of new hair cell (HC) in both normal and neomycin-damaged cochleae. PMID: 27564256
- KY1022, a small molecule that destabilizes both beta-catenin and Ras by targeting the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway, inhibitits cellular events, including epithelial mesenchymal transformation, an initial process of metastasis, and apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells. PMID: 27835580
- Cardiomyocyte hypertrophy is blunted with cardiac fibroblast-specific loss of beta-catenin after trans-aortic constriction in vivo. PMID: 28959037
- These results collectively suggest that sustained activation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in endothelial cells might be a cause of heart failure through suppressing neuregulin-ErbB signaling. PMID: 27146149
- Our findings indicate that H2O2 inhibits NaV1.5 expression by activating the Wnt/b-catenin signaling and beta-catenin interacts with TCF4 to transcriptionally suppress cardiac NaV1.5 expression. PMID: 27068063
显示更多
收起更多
-
亚细胞定位:Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Cell junction, adherens junction. Cell junction. Cell membrane. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle pole. Cell junction, synapse. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, cilium basal body.
-
蛋白家族:Beta-catenin family
-
组织特异性:Expressed in cerebellar granule neurons (at protein level).
-
数据库链接:
Most popular with customers
-
Human Transforming Growth factor β1,TGF-β1 ELISA kit
Detect Range: 23.5 pg/ml-1500 pg/ml
Sensitivity: 5.8 pg/ml
-
-
-
Mouse Tumor necrosis factor α,TNF-α ELISA Kit
Detect Range: 7.8 pg/ml-500 pg/ml
Sensitivity: 1.95 pg/ml
-
-
-
-