肿瘤微环境
肿瘤微环境(TME)是指恶性和非转化细胞之间的环境,包括周围的血管、免疫细胞、成纤维细胞、信号分子和细胞外基质(ECM)[1-4]。癌症不仅仅是恶性细胞的聚集,而是复杂的“变态”器官,许多其他细胞被招募并可能被转化的细胞所腐化 [5]。肿瘤微环境中的非恶性细胞在癌症发生的各个阶段都具有动态且常常促进肿瘤的功能 [6]。
除了恶性细胞外,肿瘤微环境中还存在脂肪细胞、成纤维细胞、肿瘤血管、淋巴细胞、树突状细胞和癌相关成纤维细胞。每种细胞类型都具有独特的免疫能力,决定了肿瘤是否能够存活并影响周围的细胞 [7]。
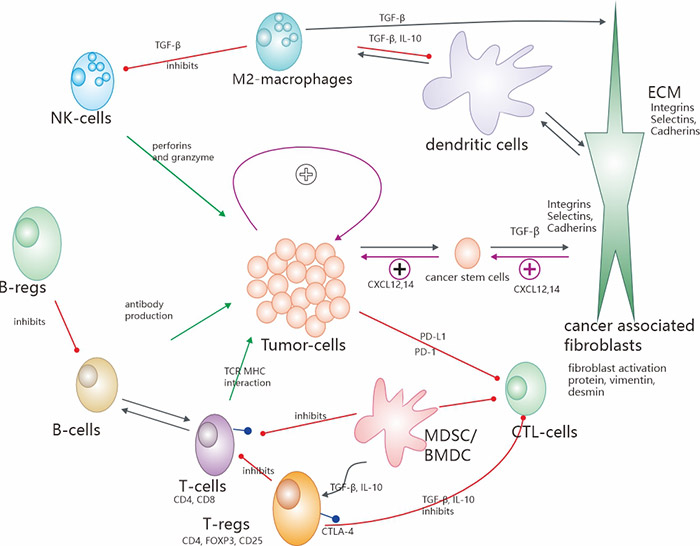
图1. 肿瘤微环境(TME)最重要的机制和相互作用示意图概述
图1展示了肿瘤微环境的最重要机制和相互作用。绿色箭头表示免疫系统的抗肿瘤活动,红色箭头表示抑制免疫系统的抗肿瘤活动。当然,肿瘤本身具有强烈的促进肿瘤生长的效应(中间的循环)。
● Angiogenesis Inhibitor in Cancer
● Angiogenic Activator in Cancer
● ECM and ECM Regulators
● MDSC Cytokines and Growth Factors
● MDS Intracellular Signaling Factors
● MDSC Phenotyping-Negative/Positive Markers
参考文献:
[1] Alfarouk KO, Muddathir AK, Shayoub ME. Tumor acidity as evolutionary spite [J]. Cancers. 2011, 3 (1): 408–14.
[2] NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms. National Cancer Institute. 2011-02-02.
[3] Joyce JA, Fearon DT. T cell exclusion, immune privilege, and the tumor microenvironment [J]. Science. 2015, 348 (6230): 74–80.
[4] Spill F, Reynolds DS, Kamm RD, Zaman MH. Impact of the physical microenvironment on tumor progression and metastasis [J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology. 2016, 40: 41–48.
[5] Frances R. Balkwill, Melania Capasso and Thorsten Hagemann. The tumor microenvironment at a glance [J]. Journal of Cell Science. 2012, 125, 5591–5596.
[6] Hanahan, D. and Coussens, L. M. Accessories to the crime: functions of cells recruited to the tumor microenvironment [J]. Cancer Cell. 2012, 21, 309-322.
[7] Arneth B. Tumor Microenvironment [J]. Medicina (Kaunas). 2019, 56 (1): 15.






